From phys.org:
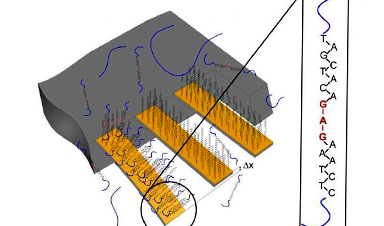
Changes in the genetic make-up of tissue samples can be detected quickly and easily using a new method based on nanotechnology. This report researchers from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute, the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel in first clinical tests with genetic mutations in patients with malignant melanoma. The journal Nano Letters has published the study.
According to estimates by the American Skin Cancer Foundation, today more people develop skin cancer than breast, prostate, lung and colon cancer together. Although malignant melanoma accounts for only about 5 percent of skin cancers, these are the most serious cases and can result in death. Around half of all patients who develop malignant melanoma exhibit a particular genetic change (mutation). This involves a change in the BRAF gene (B gene for Rapid Acceleration of Fibrosarcoma) that leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation.
There are now drugs that exploit these specific mutations and fight the cancer, significantly extending patients’ life expectancy. However, they work only if the corresponding genetic mutation is actually present.
Recent News
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious [...]
Scientists Crack the 500-Million-Year-Old Code That Controls Your Immune System
A collaborative team from Penn Medicine and Penn Engineering has uncovered the mathematical principles behind a 500-million-year-old protein network that determines whether foreign materials are recognized as friend or [...]
Team discovers how tiny parts of cells stay organized, new insights for blocking cancer growth
A team of international researchers led by scientists at City of Hope provides the most thorough account yet of an elusive target for cancer treatment. Published in Science Advances, the [...]
Nanomaterials in Ophthalmology: A Review
Eye diseases are becoming more common. In 2020, over 250 million people had mild vision problems, and 295 million experienced moderate to severe ocular conditions. In response, researchers are [...]
Natural Plant Extract Removes up to 90% of Microplastics From Water
Researchers found that natural polymers derived from okra and fenugreek are highly effective at removing microplastics from water. The same sticky substances that make okra slimy and give fenugreek [...]
Instant coffee may damage your eyes, genetic study finds
A new genetic study shows that just one extra cup of instant coffee a day could significantly increase your risk of developing dry AMD, shedding fresh light on how [...]
Nanoneedle patch offers painless alternative to traditional cancer biopsies
A patch containing tens of millions of microscopic nanoneedles could soon replace traditional biopsies, scientists have found. The patch offers a painless and less invasive alternative for millions of [...]
Small antibodies provide broad protection against SARS coronaviruses
Scientists have discovered a unique class of small antibodies that are strongly protective against a wide range of SARS coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-1 and numerous early and recent SARS-CoV-2 variants. [...]
Controlling This One Molecule Could Halt Alzheimer’s in Its Tracks
New research identifies the immune molecule STING as a driver of brain damage in Alzheimer’s. A new approach to Alzheimer’s disease has led to an exciting discovery that could help [...]
Cyborg tadpoles are helping us learn how brain development starts
How does our brain, which is capable of generating complex thoughts, actions and even self-reflection, grow out of essentially nothing? An experiment in tadpoles, in which an electronic implant [...]
Prime Editing: The Next Frontier in Genetic Medicine
By Dr. Chinta SidharthanReviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. Discover how prime editing is redefining the future of medicine by offering highly precise, safe, and versatile DNA corrections, bringing hope for more [...]
Can scientists predict life longevity from a drop of blood?
Discover how a new epigenetic clock measures how fast you are really aging from just a drop of blood or saliva. A recent study published in the journal Nature Aging constructed [...]
What is different about the NB.1.8.1 Covid variant?
For many of us, Covid-19 feels like a chapter we’ve closed – along with the days of PCR tests, mask mandates and daily case updates. But while life may [...]
Scientists discover single cell creatures can learn new behaviours
It was previously thought that learning behaviours only applied to animals with complex brain and nervous systems, but a new study has proven that this may also occur in individual cells. As a result, this [...]
Virus which ’causes multiple organ failure’ found at popular Spanish holiday destination
British tourists planning trips to Spain have been warned after a deadly virus that can cause multiple organ failure has been detected in the country. The Foreign Office issued the alert [...]
Urgent health warning as dangerous new Covid virus from China triggers US outbreak
A dangerous new Covid variant from China is surging in California, health officials warn. The California Department of Public Health warned this week the highly contagious NB.1.8.1 strain has been detected in [...]
How the evolution of a single gene allowed the plague to adapt, prolonging the pandemics
Scientists have documented the way a single gene in the bacterium that causes bubonic plague, Yersinia pestis, allowed it to survive hundreds of years by adjusting its virulence and [...]
Inhalable Nanovaccines: The Future of Needle-Free Immunization
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for adaptable and scalable vaccine technologies. While mRNA vaccines have improved disease prevention, most are delivered by intramuscular injection, which may not effectively [...]
‘Stealthy’ lipid nanoparticles give mRNA vaccines a makeover
A new material developed at Cornell University could significantly improve the delivery and effectiveness of mRNA vaccines by replacing a commonly used ingredient that may trigger unwanted immune responses [...]
You could be inhaling nearly 70,000 plastic particles annually, what it means for your health
Invisible plastics in the air are infiltrating our bodies and cities. Scientists reveal the urgent health dangers and outline bold solutions for a cleaner, safer future. In a recent [...]
Experts explain how H5 avian influenza adapts to infect more animals
A new global review reveals how rapidly evolving H5 bird flu viruses are reaching new species, including dairy cattle, and stresses the urgent need for coordinated action to prevent [...]
3D-printed device enables precise modeling of complex human tissues in the lab
A new, easily adopted, 3D-printed device will enable scientists to create models of human tissue with even greater control and complexity. An interdisciplinary group of researchers at the University [...]
Ancient DNA sheds light on evolution of relapsing fever bacteria
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and UCL have analyzed ancient DNA from Borrelia recurrentis, a type of bacteria that causes relapsing fever, pinpointing when it evolved to spread through [...]
Cold Sore Virus Linked to Alzheimer’s, Antivirals May Lower Risk
Summary: A large study suggests that symptomatic infection with herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1)—best known for causing cold sores—may significantly raise the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers found that [...]
Nanoparticle-Based Combination Therapy for Resistant Melanoma
A recent study published in Small addresses the persistent difficulty of treating refractory melanoma, an aggressive form of skin cancer that often does not respond to existing therapies. Although diagnostic tools [...]
Our DNA May Evolve Much Faster Than Previously Thought
Rapidly mutating DNA regions were mapped using a multi-generational family and advanced sequencing tools. Understanding how human DNA changes over generations is crucial for estimating genetic disease risks and tracing our [...]
AI therapy may help with mental health, but innovation should never outpace ethics
Mental health services around the world are stretched thinner than ever. Long wait times, barriers to accessing care and rising rates of depression and anxiety have made it harder for people to get timely help. As a result, governments [...]
Global life expectancy plunges as WHO warns of deepening health crisis Post-COVID
The World Health Organization (WHO) has sounded the alarm on the long-term health repercussions of the COVID-19 pandemic in its newly released World Health Statistics Report 2025. The report reveals [...]
Researchers map brain networks involved in word retrieval
How are we able to recall a word we want to say? This basic ability, called word retrieval, is often compromised in patients with brain damage. Interestingly, many patients [...]
Melting Ice Is Changing the Color of the Ocean – Scientists Are Alarmed
Melting sea ice changes not only how much light enters the ocean, but also its color, disrupting marine photosynthesis and altering Arctic ecosystems in subtle but profound ways. As global warming [...]
Your Washing Machine Might Be Helping Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Spread
A new study reveals that biofilms in washing machines may contain potential pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes, posing possible risks for laundering healthcare workers’ uniforms at home. Washing healthcare [...]
Scientists Discover Hidden Cause of Alzheimer’s Hiding in Plain Sight
Researchers found the PHGDH gene directly causes Alzheimer’s and discovered a drug-like molecule, NCT-503, that may help treat the disease early by targeting the gene’s hidden function. A recent study has [...]
How Brain Cells Talk: Inside the Complex Language of the Human Mind
Introduction The human brain contains nearly 86 billion neurons, constantly exchanging messages like an immense social media network, but neurons do not work alone – glial cells, neurotransmitters, receptors, and [...]
Oxford study reveals how COVID-19 vaccines prevent severe illness
A landmark study by scientists at the University of Oxford, has unveiled crucial insights into the way that COVID-19 vaccines mitigate severe illness in those who have been vaccinated. [...]
Annual blood test could detect cancer earlier and save lives
A single blood test, designed to pick up chemical signals indicative of the presence of many different types of cancer, could potentially thwart progression to advanced disease while the malignancy [...]
How the FDA opens the door to risky chemicals in America’s food supply
Lining the shelves of American supermarkets are food products with chemicals linked to health concerns. To a great extent, the FDA allows food companies to determine for themselves whether [...]
Superbug crisis could get worse, killing nearly 40 million people by 2050
The number of lives lost around the world due to infections that are resistant to the medications intended to treat them could increase nearly 70% by 2050, a new [...]
How Can Nanomaterials Be Programmed for Different Applications?
Nanomaterials are no longer just small—they are becoming smart. Across fields like medicine, electronics, energy, and materials science, researchers are now programming nanomaterials to behave in intentional, responsive ways. [...]
Microplastics Are Invading Our Arteries, and It Could Be Increasing Your Risk of Stroke
Higher levels of micronanoplastics were found in carotid artery plaque, especially in people with stroke symptoms, suggesting a potential new risk factor. People with plaque buildup in the arteries [...]
Gene-editing therapy shows early success in fighting advanced gastrointestinal cancers
Researchers at the University of Minnesota have completed a first-in-human clinical trial testing a CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technique to help the immune system fight advanced gastrointestinal (GI) cancers. The results, [...]
Engineered extracellular vesicles facilitate delivery of advanced medicines
Graphic abstract of the development of VEDIC and VFIC systems for high efficiency intracellular protein delivery in vitro and in vivo. Credit: Nature Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59377-y. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-59377-y Researchers at Karolinska [...]
Brain-computer interface allows paralyzed users to customize their sense of touch
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists are one step closer to developing a brain-computer interface, or BCI, that allows people with tetraplegia to restore their lost sense of [...]
Scientists Flip a Gut Virus “Kill Switch” – Expose a Hidden Threat in Antibiotic Treatment
Scientists have long known that bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, live in our gut, but exactly what they do has remained elusive. Researchers developed a clever mouse model that [...]
Enhanced Antibacterial Polylactic Acid-Curcumin Nanofibers for Wound Dressing
Background Wound healing is a complex physiological process that can be compromised by infection and impaired tissue regeneration. Conventional dressings, typically made from natural fibers such as cotton or [...]
Global Nanomaterial Regulation: A Country-by-Country Comparison
Nanomaterials are materials with at least one dimension smaller than 100 nanometres (about 100,000 times thinner than a human hair). Because of their tiny size, they have unique properties [...]
Pandemic Potential: Scientists Discover 3 Hotspots of Deadly Emerging Disease in the US
Virginia Tech researchers discovered six new rodent carriers of hantavirus and identified U.S. hotspots, highlighting the virus’s adaptability and the impact of climate and ecology on its spread. Hantavirus recently [...]
Studies detail high rates of long COVID among healthcare, dental workers
Researchers have estimated approximately 8% of Americas have ever experienced long COVID, or lasting symptoms, following an acute COVID-19 infection. Now two recent international studies suggest that the percentage is [...]
Melting Arctic Ice May Unleash Ancient Deadly Diseases, Scientists Warn
Melting Arctic ice increases human and animal interactions, raising the risk of infectious disease spread. Researchers urge early intervention and surveillance. Climate change is opening new pathways for the [...]
Scientists May Have Found a Secret Weapon To Stop Pancreatic Cancer Before It Starts
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have found that blocking the FGFR2 and EGFR genes can stop early-stage pancreatic cancer from progressing, offering a promising path toward prevention. Pancreatic [...]
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the [...]
AI Predicts Sudden Cardiac Arrest Days Before It Strikes
AI can now predict deadly heart arrhythmias up to two weeks in advance, potentially transforming cardiac care. Artificial intelligence could play a key role in preventing many cases of [...]
NanoApps Medical is a Top 20 Feedspot Nanotech Blog
There is an ocean of Nanotechnology news published every day. Feedspot saves us a lot of time and we recommend it. We have been using it since 2018. [...]
This Startup Says It Can Clean Your Blood of Microplastics
This is a non-exhaustive list of places microplastics have been found: Mount Everest, the Mariana Trench, Antarctic snow, clouds, plankton, turtles, whales, cattle, birds, tap water, beer, salt, human placentas, [...]
New Blood Test Detects Alzheimer’s and Tracks Its Progression With 92% Accuracy
The new test could help identify which patients are most likely to benefit from new Alzheimer’s drugs. A newly developed blood test for Alzheimer’s disease not only helps confirm the presence [...]
The CDC buried a measles forecast that stressed the need for vaccinations
This story was originally published on ProPublica, a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive our biggest stories as soon as they’re published. ProPublica — Leaders at the Centers [...]
Light-Driven Plasmonic Microrobots for Nanoparticle Manipulation
A recent study published in Nature Communications presents a new microrobotic platform designed to improve the precision and versatility of nanoparticle manipulation using light. Led by Jin Qin and colleagues, the [...]
Cancer’s “Master Switch” Blocked for Good in Landmark Study
Researchers discovered peptides that permanently block a key cancer protein once thought untreatable, using a new screening method to test their effectiveness inside cells. For the first time, scientists [...]
AI self-cloning claims: A new frontier or a looming threat?
Chinese scientists claim that some AI models can replicate themselves and protect against shutdown. Has artificial intelligence crossed the so-called red line? Chinese researchers have published two reports on [...]
New Drug Turns Human Blood Into Mosquito-Killing Weapon
Nitisinone, a drug for rare diseases, kills mosquitoes when present in human blood and may become a new tool to fight malaria, offering longer-lasting, environmentally safer effects than ivermectin. [...]















































































Leave A Comment