Longer-Term Projects
Vascular Cartographic Scanning Nanodevice (VCSN)
Frank Boehm’s book Nanomedical Device and Systems Design, Challenges, Possibilities, Visions endeavors to explore and present concepts for advanced nanomedical components, devices, and systems that may emerge over the next ~10-30 years. One of these nanodevices is called the Vascular Cartographic Scanning Nanodevice (VCSN) (Figure 1), which would be manifest as an autonomous, ~1 micron in diameter nanomedical device.
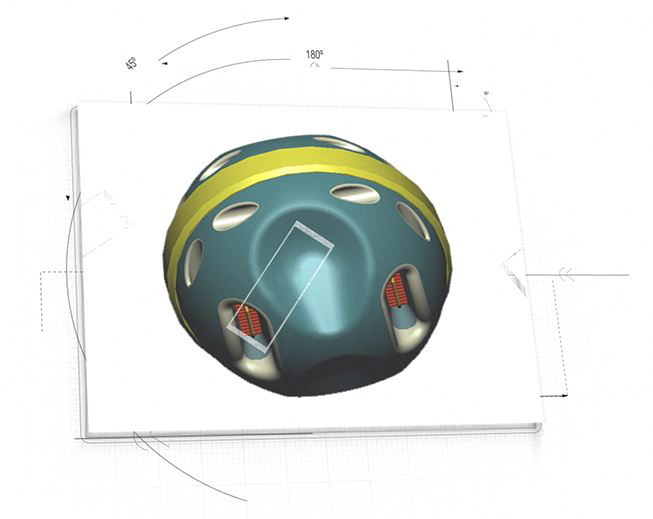
Figure 1: Artistic representation of conceptual Vascular Cartographic Scanning Nanodevice (VCSN)
Up to perhaps many thousands, or tens of thousands of VCSN nanodevices might be introduced into the patient intravenously, via ingestion as a pill, through inhalation, transdermally using a patch, or migrate in vivo utilizing a topical gel. Once within the patient their purpose would be to rapidly scan the entire human vasculature down to the smallest capillary lumen (~3 microns in diameter) in ultrahigh-resolution (sub-micron) three-dimensional (3D) digitized format. At all times they would be under the complete control of the surgeon or physician via “outbody” computer commands. Some of the capabilities of the VCSN are listed below:
- Capable of generating a very high-resolution (under 1 micron) 3D rendering of the complete human vasculature down to the smallest capillaries. It may also be applied to the imaging of the lymphatic system, and in a simplified form, the gastrointestinal tract, using a Gastrointestinal Micro Scanning Device (GMSD), (see description below).
- Ability to distinguish vascular and neurological plaque deposits and lesions with high accuracy.
- Capacity to determine vascular wall thicknesses, along with the identification and highlighting of any “hot spot” sites within the vasculature, such as imminent blockages or aneurysms that are at risk of rupturing.
- Surgeon and physicians would be able to “fly-through” all scanned areas via a joystick and computer display for the highly detailed inspection of any desired site within the system. The acquired spatial data from the VCSN may also enable holographic rendering and virtual travel through all imaged systems.
- Ability to facilitate the targeting of tumors by revealing sites of angiogenesis in close proximity to tumor growth sites.
A number of advantages of the VCSN include:
- High compactness and portability as its operation will require a relatively small footprint. This would enable a simple and quick setup and power-up procedures, which will be a boon for applications in developing countries and remote terrestrial environments.In aerospace, it might be utilized as an element of an on board medical diagnostics suite on military and medical aircraft.
- For space travel, it may be reconfigured for integration into spacesuits and spacecraft, and provide a compact yet very powerful medical imaging capability for future Moon and Mars habitats.
- Frugal energy consumption.
- Inexpensive administration and operation
- Rapid scanning time (~5 minutes).
- Ultrahigh resolution digital imagery and inherent flexibility for display across several formats and ease of file transmission to medical personnel globally via secure telecommunications connectivity
- Potential for enabling the significant reduction or elimination of long waiting queues for critical imaging technologies.
Gastrointestinal Micro Scanning Device (GMSD)
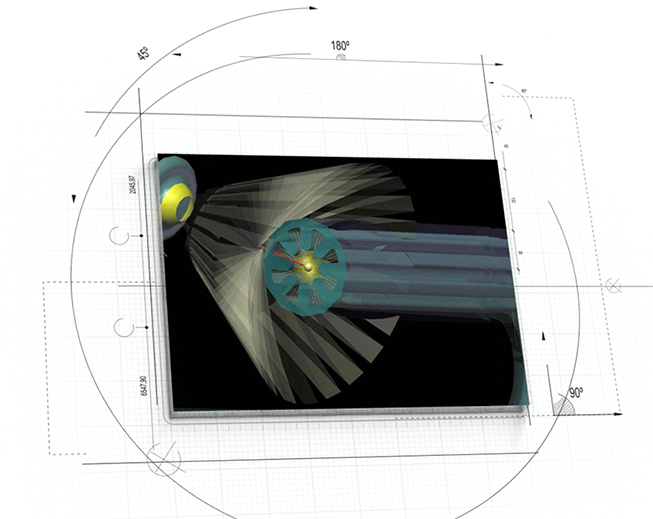
The Gastrointestinal Micro Scanning Device (GMSD) (Figure 2) will serve as far less complex precursor to the VCSN as it will not have the capacity for propulsion or navigation. It might, however, employ nascent forms of quantum computing, nanoelectronics, spatial data acquisition, and Pixel Matrix (see below) technologies that are envisaged for the VCSN. Hence, in addition to serving as formative in vivo spatial data acquisition device, the GMSD may also have utility as a test bed of sorts that is employed to identify and resolve technical, integrative, and functional issues toward the development of the VCSN.
![]()
Figure 2: Artistic representation of conceptual Gastrointestinal Micro Scanning Device (GMSD)
The GMSD system will consist of three distinct components that work in unison to generate very high-resolution 3D topography of the entire internal surface of the GIT. The GMSD would accomplish this task by utilizing:
- Bright Ball (BB) scanning device, which would have a smooth spherical morphology of ~3 mm in diameter
- Pulse Generator/Data Transfer (PGDT) unit would trigger the activity of the internalized BB device via a specifically encrypted signal. The BB would be activated to scan subsequently to receiving this specific signal only. Once activated, the BB would commence to transmit a constant spatial data stream to the PGDT, which would serve as a data transfer device when linked to a computer and the Pixel Matrix (see below) software. The PGDT would be securely affixed to the patient’s abdominal surface and would stay in place for the duration of the scan.
- The Pixel Matrix display would process the PGDT supplied spatial data toward the reconstruction a high resolution “pixel per hit” 3D rendering of the total scanned area of the GIT that has been traversed by the BB. This software would enable “fly-through” and cross-sectional capabilities, allowing medical personnel to traverse the entire GIT (using a joystick, computer mouse, or touch screen display) to investigate any potential problem areas in great detail. The spatial data might also be converted to holographic and virtual reality formats. Using this procedure, the physician and/or surgeon would thus recognize any anomalous topography that is associated with tumor growth, lesions, and other abnormal features that may exist within the GIT.
The operational procedure for the GMSD would be relatively simple to implement, as the BB would be introduced orally to the patient in the same manner as a pill. Subsequently, an adhesive waterproof thin film PGDT patch would be affixed to the skin of patient’s abdomen. At this juncture, a system calibration would be performed to ensure that the communication link between the BB and the PGDT is functioning properly. An initial test scan would also be conducted in order to configure the image resolution. The PGDT would emit a unique pulsed signal (e.g., ultrasonic, near-infrared), which when received by sensors embedded within the surface of the BB would trigger all of the embedded emitters/receivers to fire and emit their scanning beams simultaneously in every direction. Once these procedures are completed the patient would be allowed to leave the physician’s office, clinic, or hospital to go about his/her normal routine. The internalized BB would now move along with the natural peristaltic rhythms of the GIT and be naturally eliminated at the conclusion of the transit duration. The patient would then return to the facility in two or three days (contingent on the assessed GIT transit time) to have the PGDT patch removed.
During the designated scanning period, the PGDT will have been continuously uploading spatial data provided by the BB, which would then be interfaced with a computer via a USB port to stream all of this data to the PM software housed within the computer. The data would now be translated to high-resolution 3D imagery on a display. The PM software would calculate BB orientation and would correlate the interrogating hits obtained within predetermined parameters to construct a cross section of the GIT to depict its internal topography. These digitized fragments would then be sequentially pieced together to form a seamless spatially accurate rendering of the system.
News
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]
Scientists Crack the 500-Million-Year-Old Code That Controls Your Immune System
A collaborative team from Penn Medicine and Penn Engineering has uncovered the mathematical principles behind a 500-million-year-old protein network that determines whether foreign materials are recognized as friend or foe. How does your body [...]
Team discovers how tiny parts of cells stay organized, new insights for blocking cancer growth
A team of international researchers led by scientists at City of Hope provides the most thorough account yet of an elusive target for cancer treatment. Published in Science Advances, the study suggests a complex signaling [...]
Nanomaterials in Ophthalmology: A Review
Eye diseases are becoming more common. In 2020, over 250 million people had mild vision problems, and 295 million experienced moderate to severe ocular conditions. In response, researchers are turning to nanotechnology and nanomaterials—tools that are transforming [...]
Natural Plant Extract Removes up to 90% of Microplastics From Water
Researchers found that natural polymers derived from okra and fenugreek are highly effective at removing microplastics from water. The same sticky substances that make okra slimy and give fenugreek its gel-like texture could help [...]
Instant coffee may damage your eyes, genetic study finds
A new genetic study shows that just one extra cup of instant coffee a day could significantly increase your risk of developing dry AMD, shedding fresh light on how our daily beverage choices may [...]
Nanoneedle patch offers painless alternative to traditional cancer biopsies
A patch containing tens of millions of microscopic nanoneedles could soon replace traditional biopsies, scientists have found. The patch offers a painless and less invasive alternative for millions of patients worldwide who undergo biopsies [...]
Small antibodies provide broad protection against SARS coronaviruses
Scientists have discovered a unique class of small antibodies that are strongly protective against a wide range of SARS coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-1 and numerous early and recent SARS-CoV-2 variants. The unique antibodies target an [...]
Controlling This One Molecule Could Halt Alzheimer’s in Its Tracks
New research identifies the immune molecule STING as a driver of brain damage in Alzheimer’s. A new approach to Alzheimer’s disease has led to an exciting discovery that could help stop the devastating cognitive decline [...]
Cyborg tadpoles are helping us learn how brain development starts
How does our brain, which is capable of generating complex thoughts, actions and even self-reflection, grow out of essentially nothing? An experiment in tadpoles, in which an electronic implant was incorporated into a precursor [...]
Prime Editing: The Next Frontier in Genetic Medicine
By Dr. Chinta SidharthanReviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. Discover how prime editing is redefining the future of medicine by offering highly precise, safe, and versatile DNA corrections, bringing hope for more effective treatments for genetic diseases [...]
Can scientists predict life longevity from a drop of blood?
Discover how a new epigenetic clock measures how fast you are really aging from just a drop of blood or saliva. A recent study published in the journal Nature Aging constructed an intrinsic capacity (IC) clock [...]
What is different about the NB.1.8.1 Covid variant?
For many of us, Covid-19 feels like a chapter we’ve closed – along with the days of PCR tests, mask mandates and daily case updates. But while life may feel back to normal, the [...]