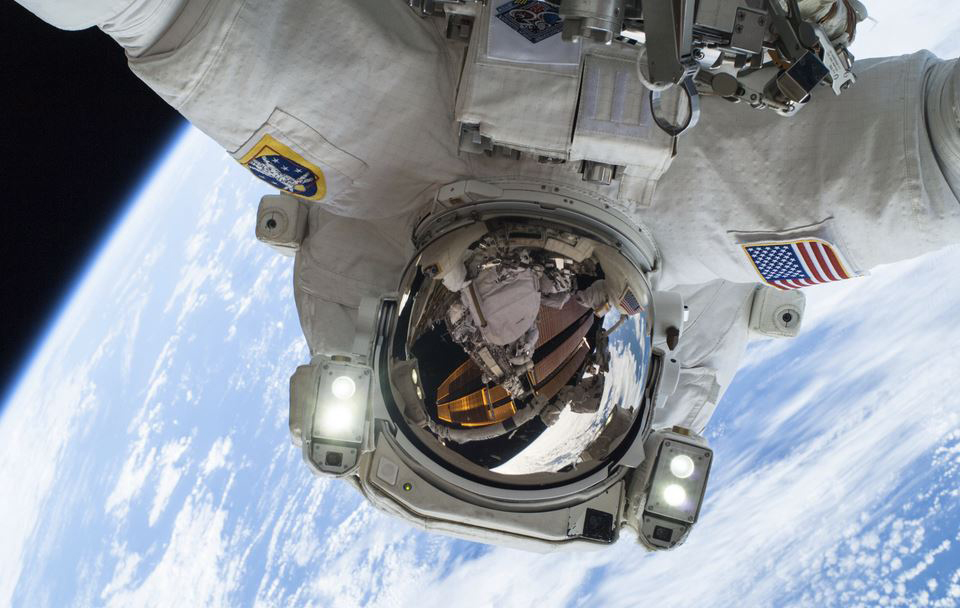
Detrimental Physiological Effects of Microgravity on the Brain and DNA


![]()
Microgravity imparts multiple deleterious effects on human physiology, which must be resolved as a prerequisite for enabling humans to engage in extended space expeditions. A summary of these negative impacts on various physiological systems is listed in Table 1 below. Nanomedicine might have the capacity to prevent or counteract the effects of microgravity (e.g., bone loss, neurological damage, soft tissue degradation, and detrimental ocular conditions to enable humans to endure prolonged missions to Mars and beyond, to the further reaches of deep space.![]()
| System | Microgravity Impact |
|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal System |
|
| Cardiovascular System |
|
| Sensory Motor System |
|
| Immune System |
|
| Wound Healing |
|
Table 1: Physiological impacts of microgravity (reconfigured from Blaber, et al.)
Here, we briefly articulate what might be possible through the application of advanced nanomedicine toward addressing the deleterious effects of microgravity on other critical soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, nervous system, and DNA. The functionality of degraded or destroyed populations of neurons and glial cells, as well as neuronal circuitry might be nanomedically restored through the use of targeted nanocarriers, which may precisely transport the appropriate molecules, biomaterials, and stem cells to any damaged sites of the nervous system to initiate efficacious repairs. Multilayered electrospun polymeric nanofiber scaffolds (Figure 1) may be self-assembled from constituent components in vivo and used to support the growth of stem cells. Nanofiber scaffolds comprised of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/chitosan nanofibers (~Ø 221 nm) were demonstrated by Alhosseini et al. to create microscale pores at their interstices, which facilitated cell tethering and migration, the proliferation of blood vessels, as well as to enable cellular nutrient and waste exchange.

![]()
Figure 1: Electrospun polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofiber scaffold (Image credit: Koh and Strange)
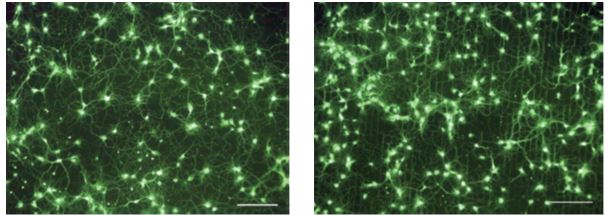
PC12 nerve cells from rat adrenal medulla were cultured on a PVA/chitosan nanofiber scaffold in vitro and observed to respond positively to the support. They also exhibited higher levels of attachment, propagation, migration, and viability in contrast to a pure PVA nanofiber scaffold. The presence of chitosan appeared to provide several physicochemical and biological factors that were amenable to the nerve cells including reduced nanofiber diameters, more surface resident amine and decreased water content. In a further neural engineering study by Jang et al., the growth of E18 rat hippocampal neurites traced the micropatterns of a substrate that were established by octadecyltrichlorosilane (OTS) and pristine carbon nanotubes (Figure 2), which biomimetically emulated extracellular matrices. It was suggested that a cell adhesion protein (poly-l-lysine (PLL)), which was coated onto the substrate, was a critical factor for attachment, guidance, and elongation.
![]()
Figure 2: Neuron networks (at seven divisions) shown on (a) carbon nanotube-only substrate and (b) patterned carbon nanotube/OTS substrate (Image credit: Jang et al.)
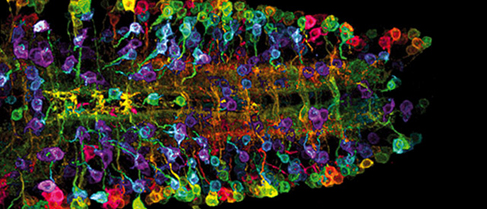
The nanomedical repair of the brain, at today’s level of sophistication, might involve the activation of renewable multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) (Figure 3), as described by Santos et al., which reside within two specific regions of the brain (germinal subventricular and hippocampal subgranular zones), to rejuvenate neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. The activation of NSCs might be initiated via the delivery of targeted nanoparticles that bear payloads of neurogenesis-inducing biomolecules to these sites, while imparting negligible side effects. (Reynolds and Weiss, Gage et al., Quadrato and Giovanni, Kazanis, Gage, Bible et al.)
![]()
Figure 3: Neural stems cells (Image credit: The New York Academy of Sciences)
Further in the future, with the advent of mature Molecular Manufacturing (MM), it might be possible to affect real time brain repairs almost instantaneously via sophisticated indwelling nanomedical devices. This strategy may sustainably negate the deleterious effects of both ionizing radiation and microgravity toward addressing the possibility of cumulative damage manifesting in the brain as the result of prolonged exposure to the space environment.
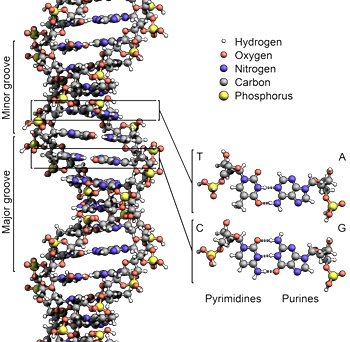
“A robust means for the preservation of the integrity and viability of DNA molecules and the proteins that they encode will be absolutely essential for long-haul human space travel and the eventual human habitation of the Moon, Mars, and beyond.” (Boehm) Within the nuclei of human cells (~Ø5-10 microns) there inherently exist a dozen species of protein based DNA repair mechanisms that are encoded by ~150 genes. Each of these self-assembling biological “nanomachines” is devoted to the repair of a specific type of damage to the DNA duplex. (Figure 4)
![]()
Figure 4: Illustration of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) (Image credit: Zephyris /Richard Wheeler)
In the space environment, microgravity in conjunction with ionizing radiation may negatively impact a number of DNA repair mechanisms. Subsequent to extensive studies of astronauts and cosmonauts it was revealed by Rowe that human exposure to microgravity induces a considerable decline in serum magnesium (Mg); an antioxidant and calcium blocker, which is critical for the binding of telomerase to DNA. Telomerase facilitates telomere elongation, chromosome stability, and the promotion of transcription and replication. Insufficient levels of magnesium results in oxidative stress, accelerated cell senescence, unstable DNA, as well as reduced protein synthesis and mitochondrial performance.
It was demonstrated that when human endothelial cells had no access to Mg for only two hours, they showed elevated levels of 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanine (in contrast to controls), which is a key DNA repair product that is generated in response to oxidative stress-induced DNA damage. To maintain ample concentrations of Mg under microgravity conditions, Mg loaded nanoparticles may have the capacity for the prolonged release of Mg ions, to sustain healthy plasma levels and those within intracellular compartments, which diminish over time and may not necessarily be related with concentrations in the plasma.
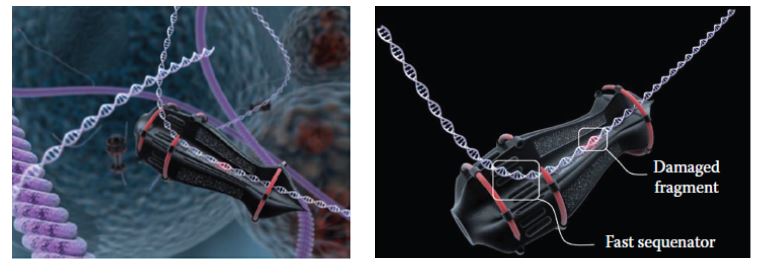
Svidinenko designed a conceptual sophisticated DNA repair nanorobot (Figure 5) that might transit along the duplex (similar to a bead on a chain). DNA damage would be detected immediately upon entering through the input port. When approaching the output port, the damaged DNA segment would be mechanically stabilized, where after the deficient base pairs would be removed and rapidly replaced by a dedicated “sequenator”, which could be considered as akin to the operation of a film-editing mechanism. The excised DNA segment would be then be discarded from a discharge port to be naturally degraded.
![]()
Figure 5: Conceptual DNA repair nanorobot (Image credit: Nanorobotmodels Medical Animation Studio)
News
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]











