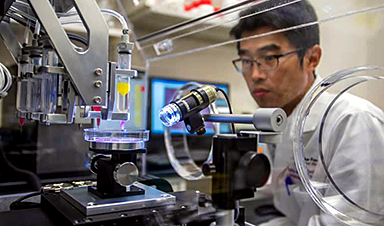
Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) scientists have improved upon the 3D bioprinting technique they developed to engineer skeletal muscle as a potential therapy for replacing diseased or damaged muscle tissue, moving another step closer to someday being able to treat patients.
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and are responsible for the body’s movement. When they are damaged, there is often loss of muscle function because the nerves are no longer sending signals to the brain.
Treatment of extensive muscle defect injuries like those caused by improvised explosive devices (IEDs) on the battlefield, for instance, is difficult and often requires reconstructive surgery with muscle grafts. Effective nerve integration of bioengineered skeletal muscle tissues has been a challenge.
“Being able to bioengineer implantable skeletal muscle constructs that mimics the native muscle to restore function represents a significant advance in treating these types of injuries,” said lead author Ji Hyun Kim, PhD, of WFIRM. “Our hope is to develop a therapeutic option that will help heal injured patients and give them back as much function and normalcy as possible.”
The work is detailed in a paper published online today by the journal Nature Communications.
Institute scientists previously demonstrated that the Integrated Tissue and Organ Printing System (ITOP), developed in house over a 14-year period, can generate organized printed muscle tissue that is robust enough to maintain its structural characteristics.
Since then, the WFIRM researchers have been developing and testing different types of skeletal muscle tissue constructs to find the right combination of cells and materials to achieve functional muscle tissue. In the current study, they investigated the effects of neural cell integration into the bioprinted muscle construct to accelerate functional muscle regeneration.
“These constructs were able to facilitate rapid nerve distribution and matured into organized muscle tissue that restored normal muscle weight and function in a pre-clinical model of muscle defect injury,” said Sang Jin Lee, PhD., co-senior author, also of WFIRM.
Image Credit: Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine/WFIRM.
Thanks to Heinz V. Hoenen. Follow him on twitter: @HeinzVHoenen
News This Week
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]