The rising concern of plastic pollution and the increase in nanoplastics, which are small plastic debris particles with nanoscale sizes between 1 and 1000 nm, have become a field of research that has garnered popularity over recent years. Innovative research published in the journal, ACS Omega, has investigated the effect of nanoplastics on developing zebrafish embryos.
Nanoplastic Pollution
Nanoplastic pollution is a significant rising concern for public health and the environment.
Plastics, which have become a ubiquitous waste material found in landfills and the oceans, have been a growing concern due to their lack of biodegradability. Additionally, the eroding of large plastics into nanosize can be more detrimental for the environment and human health, with nanosized particles causing more damage.
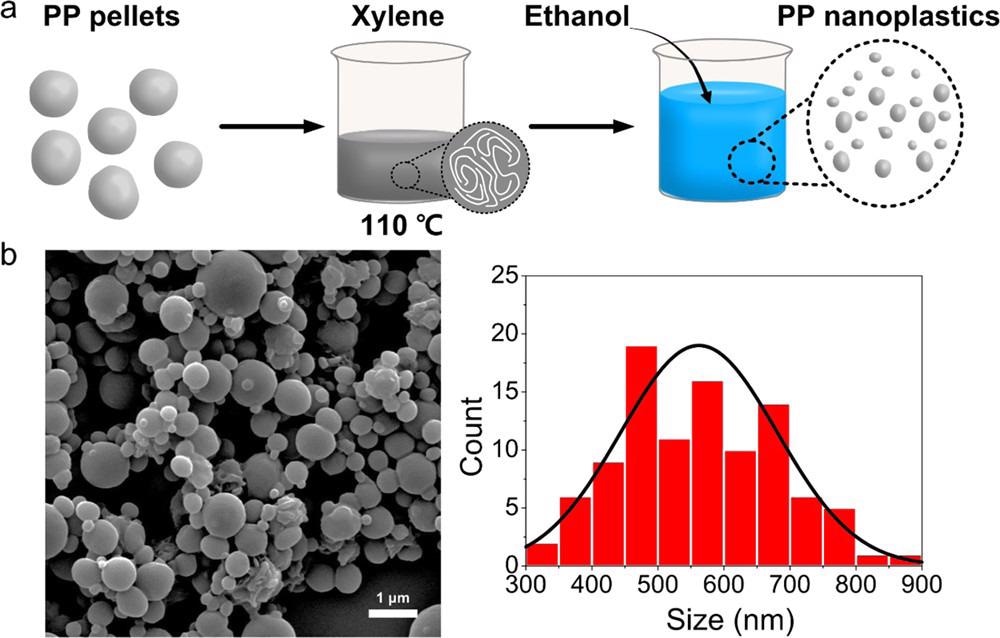
(a) Scheme for preparation of the polypropylene nanoplastics (PPNPs) using a modified nonsolvent-induced phase separation (NIPS) method. (b) SEM images and the size distribution (n = 100). © Lee, W., Kim, H., Sim, Y., Kang, T. and Jeong, J., (2022)
With physiochemical properties associated with nanosized plastics, they can interact with biological systems, leading to disastrous effects. Additionally, nanoplastic pollution may not be purified by wastewater treatment systems.
It can be found in drinking water, causing them to be ingested; resultant oxidative stress and inflammation have been reported in diverse organisms. This can also occur through its ability to penetrate human tissue by crossing the lungs, skin and gastrointestinal barriers – which can be deleterious for health.
Plastic types that are a risk and constitute plastic debris include polystyrene, polyethylene, and polypropylene (PP). Polystyrene has largely been responsible for the risk that nanoplastics hold due to its commercial availability of various sizes and surface charges; however, while this plastic has high usage, polyethylene and polypropylene are ubiquitously detected in plastic debris in the environment.
While polypropylene is abundant in the environment, there are limited studies on this plastic type. Regardless, its incorporation as the most used plastic, such as within food packaging, automotive components, and even personal protective equipment (PPE), including masks that have increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, raises the concern for plastic pollution.
The accumulation of PP into microplastics such as UV radiation, oxidation, and biofilms can be a health risk with the detection of PP being found gastrointestinal tracts of sea turtles on the Atlantic coastline of Florida after only being post-hatched for 96 hours. Additionally, PP microplastics were found to induce cytotoxicity, proinflammatory cytokine production, oxidative stress and intestinal damage in human-derived cell and animal models such as zebrafish.
With the disastrous effect of microplastics on both the environment and human health, fragmentation into nanosized particles could be potentially further hazardous. This plastic pollution, which is a major concern due to associated plastic manufacturing, requires further research to understand the effects of polypropylene nanoplastics.
Innovative Nanoplastic Research
The researchers of this innovative study aimed to investigate the biological effects of nanoscale polypropylene in an animal model utilizing developing zebrafish embryos.
The team produced PPNPs utilizing a high yield method, including nonsolvent-induced phase separation; they fabricated PPNPs within a spherical shape with an average diameter of 562.15 ± 118.47 nm. They were then fluorescently labeled utilizing the combined swelling-diffusion method to investigate and observe the biodistribution of these particles after being exposed to developing zebrafish embryos.
Interestingly, the researchers found the fluorescent-labeled polypropylene nanoplastics internalized through ingestion and found even in the intestines of developing zebrafish embryos before being eventually excreted.
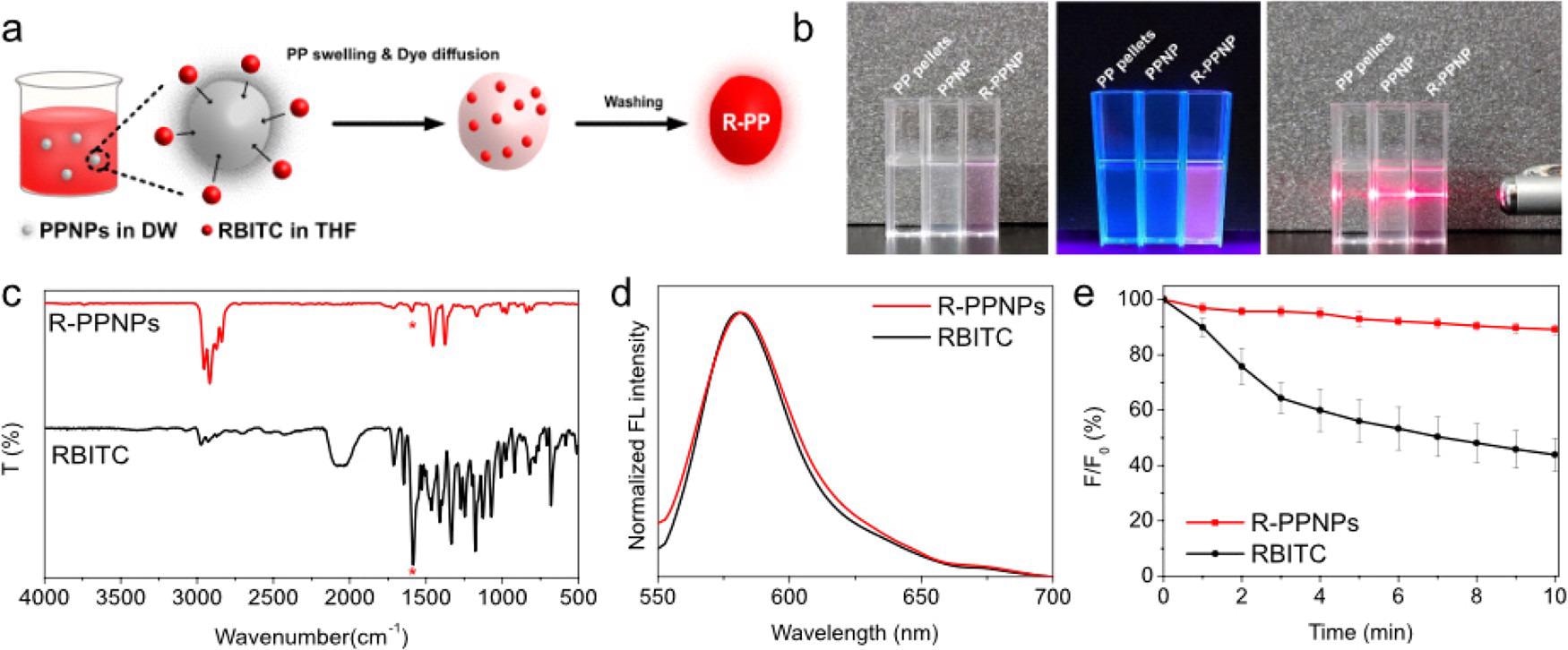
(a) Scheme of fluorescence labeling of PPNPs by the CSD method. (b) Photographs of PP pellets, PPNPs, and R-PPNP suspension in DW under visible light (left), UV light (365 nm, middle), and visible light with laser beam (right). (c) FT-IR spectra, (d) fluorescence spectra, and (e) fluorescence stability of RBITC and R-PPNPs. © Lee, W., Kim, H., Sim, Y., Kang, T. and Jeong, J., (2022)
Significant Implications for Environmental and Human Health
Overcoming the limitations of prior investigations into polypropylene plastic pollution, this novel research has uncovered the significant effect that nanoplastics can have on biological systems.
The team has raised awareness of the biodistribution of nanoplastics, especially polypropylene, which is found significantly in plastic debris within the environment. This study can be a basis for further research into the effect that nanoplastics can have on biological systems, such as focusing on oxidative stress and potential interactions that may cause harm for human health if ingested.
The research team can also aid in bringing awareness to the significance of nanoplastic pollution and its effects on the environment, with microplastic awareness being provided with traction. This can translate to reducing the manufacturing of polypropylene-based plastics, including finding other biodegradable plastics for applications, including PPE, which has become an increasing concern for plastic pollution.
Creating biodegradable plastics can ease plastic pollution and advancement in wastewater treatments can reduce any harmful effects these plastics can have on animal and human health.
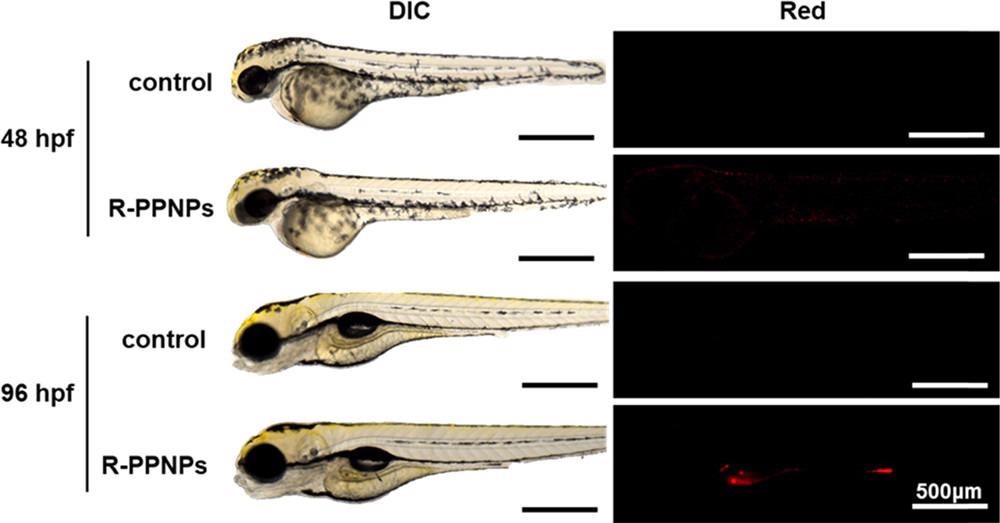
Optical and fluorescence images of zebrafish embryos with or without R-PPNP treatments at 24 and 72 hpf. These images were taken after 24 h exposure. © Lee, W., Kim, H., Sim, Y., Kang, T. and Jeong, J., (2022)
News
Specially engineered antibody delivers RNA therapy to treatment-resistant tumors
Elias Quijano, PhD; Diana Martinez-Saucedo, PhD; Zaira Ianniello, PhD; and Natasha Pinto-Medici, PhD, there are 25 other contributors, most from Yale's Department of Therapeutic Radiology and from the departments of genetics, molecular biophysics and [...]
Vaccinated women face fewer cervical cancer risks
New data from Denmark shows the HPV vaccine’s powerful long-term impact, while also revealing why cervical cancer screening is still essential. A Danish study published in the journal Eurosurveillance reports that women who received the human [...]
3D-printed implant offers a potential new route to repair spinal cord injuries
A research team at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences has developed a 3-D printed implant to deliver electrical stimulation to injured areas of the spinal cord, offering a potential new route to [...]
Nanocrystals Carrying Radioisotopes Offer New Hope for Cancer Treatment
The Science Scientists have developed tiny nanocrystal particles made up of isotopes of the elements lanthanum, vanadium, and oxygen for use in treating cancer. These crystals are smaller than many microbes and can carry isotopes of [...]
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]