Researchers in Germany and Japan have been able to increase the diffusion of magnetic whirls, so-called skyrmions, by a factor of ten.
In today's world, our lives are unimaginable without computers. Up until now, these devices process information using primarily electrons as charge carriers, with the components themselves heating up significantly in the process. Active cooling is thus necessary, which comes with high energy costs. Spintronics aims to solve this problem: Instead of utilizing the electron flow for information processing, it relies on their spin or their intrinsic angular momentum. This approach is expected to have a positive impact on the size, speed, and sustainability of computers or specific components.
Magnetic Whirls Store and Process Information
Science often does not simply consider the spin of an individual electron, but rather magnetic whirls composed of numerous spins. These whirls called skyrmions emerge in magnetic metallic thin layers and can be considered as two-dimensional quasi-particles. On the one hand, the whirls can be deliberately moved by applying a small electric current to the thin layers; on the other hand, they move randomly and extremely efficiently due to diffusion. The feasibility of creating a functional computer based on skyrmions was demonstrated by a team of researchers from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), led by Professor Dr. Mathias Kläui, using an initial prototype. This prototype consisted of thin, stacked metallic layers, some only a few atomic layers thick.
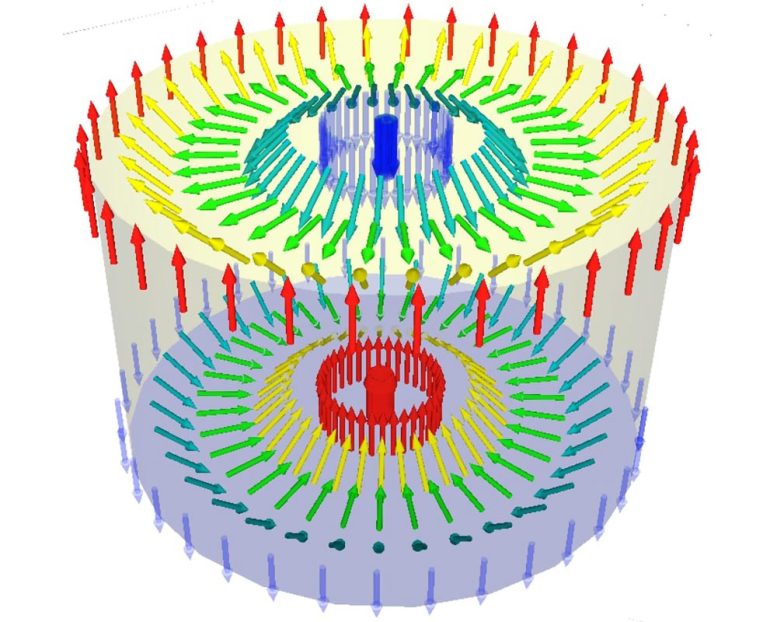
Two skyrmions antiferromagnetically coupled: The spin in the center and the outside spins are antiparallel to each other. Credit: ill./©: Takaaki Dohi / Tohoku University
Boosting Energy Efficiency
In collaboration with the University of Konstanz and Tohoku University in Japan, researchers of Mainz University have now achieved another step towards spin-based, unconventional computing: They were able to increase the diffusion of skyrmions by a factor of about ten using synthetic antiferromagnets, which drastically reduces the energy consumption and increases the speed of such a potential computer. "The reduction of energy usage in electronic devices is one of the biggest challenges in fundamental research," emphasized Professor Dr. Ulrich Nowak, who led the theoretical part of the project in Konstanz.
The Power of Antiferromagnets
But what is an antiferromagnet and what is it used for? Normal ferromagnets consist of many small spins, all coupled together to point in the same direction, thereby creating a large magnetic moment. In antiferromagnets, the spins are aligned alternatingly antiparallel, i.e., a spin and its direct neighbors point in the opposite direction. As a result, there is no net magnetic moment, even though the spins remain antiferromagnetically well-ordered. Antiferromagnets have significant advantages, such as three magnitudes of faster dynamics for switching, better stability, and the potential for higher storage densities. These properties are intensively studied in multiple research projects.
In order to understand why these antiferromagnets are useful in this context, we need to delve a bit deeper. When skyrmions move very rapidly, an additional force component arises in ferromagnetic layers perpendicular to the direction of motion. This force component pushes the skyrmions off course. Consequently, they end up colliding with the wall, getting stuck, and obstructing the path for others. At higher speeds, they can even be destroyed. However, it is theoretically known that this effect either does not occur in antiferromagnets or it occurs to a very limited extent.
Advancements in Synthetic Antiferromagnets
To create such an antiferromagnet artificially, the researchers coupled two of their ferromagnetic layers in a way that the magnetization in the two layers is precisely aligned in opposite directions, canceling out their magnetic fields. This provides two advantages: They reduce the force pushing the whirls off their path and thus increase the diffusion. "With this, we have created a synthetic antiferromagnet in which the diffusion of skyrmions is approximately ten times higher than in the individual layers," said Klaus Raab, a physicist at JGU. "This diffusion can be implemented to realize stochastic computing – a form of computing where stochastic processes like the random motion of particles are utilized."
The team of researchers investigated the effects of the compensation of the magnetic layers in addition to the influence of temperature and size of the skyrmions on diffusion and consequently on the motion of the skyrmions, both experimentally and through simulations. Intricate connections have been found: As temperature rises, the skyrmions have more energy to diffuse faster. The heat also reduces the size of the skyrmions, which positively affects their mobility. The compensation of the vertical force component also has a positive impact on diffusion. All these effects are difficult to disentangle from each other. "The increasing diffusion seems to be attributable not only to the pure compensation of the magnetic fields but also to the associated reduction in the size of the skyrmions," summarized Raab.
Professor Mathias Kläui, who led the study, is pleased with the fruitful collaboration with Tohoku University: "We have been working with this leading Japanese university for about ten years and there are even joint study programs. With the support of the German Academic Exchange Service – the DAAD – and other research funders, over a dozen students from Mainz University have already participated in exchanges with Tohoku University. I am delighted that this collaborative effort has been made possible through this cooperation."
The research results have been published recently in the journal Nature Communications.
Reference: "Enhanced thermally-activated skyrmion diffusion with tunable effective gyrotropic force" by Takaaki Dohi, Markus Weißenhofer, Nico Kerber, Fabian Kammerbauer, Yuqing Ge, Klaus Raab, Jakub Zázvorka, Maria-Andromachi Syskaki, Aga Shahee, Moritz Ruhwedel, Tobias Böttcher, Philipp Pirro, Gerhard Jakob, Ulrich Nowak and Mathias Kläui, 11 September 2023, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40720-0
News
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]