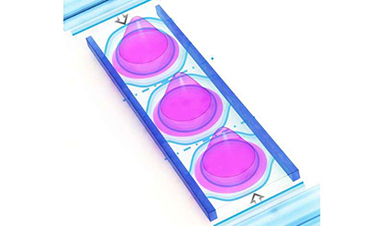
Engineers at Duke University have developed a device that uses sound waves to separate and sort the tiniest particles found in blood in a matter of minutes. The technology is based on a concept called “virtual pillars” and could be a boon to both scientific research and medical applications.
The results appeared online November 23 in the journal Science Advances.
“These nanoparticles have significant potential in medical diagnosis and treatment, but the current technologies for separating and sorting them take several hours or days, are inconsistent, produce low yield or purity, suffer from contamination and sometimes damage the nanoparticles,” said Tony Jun Huang, the William Bevan Distinguished Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science at Duke.
“We want to make extracting and sorting high-quality sEVs as simple as pushing a button and getting the desired samples faster than it takes to take a shower,” Huang said.
Recent research indicates that sEVs are comprised of several subgroups with distinct sizes (e.g., smaller than 50 nanometers, between 60 and 80 nanometers, and between 90 and 150 nanometers). Each size is believed to have different biological properties.
The recent discovery of sEV subpopulations has excited researchers because of their potential to revolutionize the field of non-invasive diagnostics, such as the early detection of cancer and Alzheimer’s disease. But the particles haven’t found their way into clinical settings yet.
Huang said this is largely due to the difficulties associated with separating and isolating these nano-sized sEV subpopulations. To meet this challenge, Huang, his doctoral student Jinxin Zhang, and collaborators at UCLA, Harvard, and Magee-Womens Research Institute, developed the ANSWER platform.
The device uses a single pair of transducers to generate a standing sound wave that envelops a narrow, enclosed channel filled with fluid. The sound wave “leaks” into the liquid center through the channel walls and interacts with the original standing sound wave. With careful design of the wall thickness, channel size and sound frequency, this interaction creates a resonance that forms “virtual pillars” along the center of the channel.
“The ANSWER EV fractionation technology is the most advanced capability for precise EV fractionation, and it will significantly impact the horizon of EV diagnostics, prognostics and liquid biopsy,” said David Wong, director for UCLA Center for Oral/Head & Neck Oncology Research.
In the new paper, the researchers demonstrate that their ANSWER platform can successfully sort sEVs into three subgroups with 96% accuracy for nanoparticles on the larger end of the spectrum and 80% accuracy for the smallest. They also show flexibility in their system, adjusting the number of groupings and ranges of sizes with simple updates to the sound wave parameters. Each of the experiments only took 10 minutes to complete, whereas other methods such as ultra-centrifugation can take several hours or days.
“Due to its contact-free nature, ANSWER offers a biocompatible approach for the separation of biological nanoparticles.” Zhang said. “Unlike mechanical filtration methods, which have fixed separation cutoff diameters, ANSWER offers a tunable approach to nanoscale separation, and the cutoff diameter can be precisely modified by varying the input acoustic power.”
Moving forward, the researchers will continue improving the ANSWER technology so that it can be efficient in purifying other biologically relevant nanoparticles such as viruses, antibodies and proteins.
News
3D-printed implant offers a potential new route to repair spinal cord injuries
A research team at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences has developed a 3-D printed implant to deliver electrical stimulation to injured areas of the spinal cord, offering a potential new route to [...]
Nanocrystals Carrying Radioisotopes Offer New Hope for Cancer Treatment
The Science Scientists have developed tiny nanocrystal particles made up of isotopes of the elements lanthanum, vanadium, and oxygen for use in treating cancer. These crystals are smaller than many microbes and can carry isotopes of [...]
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]