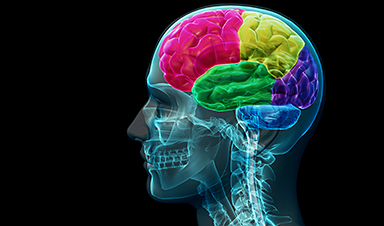
Researchers have created nanoscale robots which could be used to manage bleeds in the brain caused by aneurysms. The development could enable precise, relatively low-risk treatment of brain aneurysms, which cause around 500,000 deaths globally each year. The medical condition—a blood-filled bulge on a brain artery that can rupture and cause fatal bleeds—can also lead to stroke and disability.
The study points to a future where tiny robots could be remotely controlled to carry out complex tasks inside the human body—such as targeted drug delivery and organ repair—in a minimally invasive way, researchers say.
Swarming bots
The team, involving researchers from the University of Edinburgh, engineered magnetic nanorobots—about a twentieth the size of a human red blood cell—comprising blood-clotting drugs encased in a protective coating, designed to melt at precise temperatures. The work is published in the journal Small.
In lab tests, several hundred billion such bots were injected into an artery and then remotely guided as a swarm, using magnets and medical imaging, to the site of an aneurysm.
Magnetic sources outside the body then cause the robots to cluster together inside the aneurysm and be heated to their melting point, releasing a naturally occurring blood-clotting protein, which blocks the aneurysm to prevent or stem bleeding into the brain.
Lab trials
The international team, co-led by clinicians from Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in China, successfully tested their devices in model aneurysms in the lab and in a small number of rabbits.
The team says that nanorobots show potential for transporting and releasing drug molecules to precise locations in the body without risk of leaking into the bloodstream—a key test of the technology’s safety and efficacy.
The study could pave the way for further developments towards trials in people.
Promising potential
Their advancement could improve on current treatments for brain aneurysms. Typically, doctors thread a tiny microcatheter tube along blood vessels before using it to insert metal coils to stem the aneurysm blood flow, or a mesh tube called a stent, to divert the bloodstream in the artery.
Researchers say their new technique could decrease the risk that the body will reject implanted materials, and curb reliance on anti-blood-clotting drugs, which can cause bleeding and stomach problems.
The method also avoids the need for doctors to manually shape a microcatheter to navigate a complex network of small blood vessels in the brain to reach the aneurysm—a painstaking task which may take hours during surgery, researchers say.
Larger brain aneurysms—which can be difficult to stem quickly and safely using metal coils or stents—could potentially be treated using the new technique too.
The study was led by a team from the UK and China who have also developed nanorobots to remove blood clots, which show potential in treating stroke.
“Nanorobots are set to open new frontiers in medicine—potentially allowing us to carry out surgical repairs with fewer risks than conventional treatments and target drugs with pinpoint accuracy in hard-to-reach parts of the body. Our study is an important step towards bringing these technologies closer to treating critical medical conditions in a clinical setting,” Dr. Qi Zhou.
More information: Jienan Wang et al, Nanoarchitectonic Engineering of Thermal‐Responsive Magnetic Nanorobot Collectives for Intracranial Aneurysm Therapy, Small (2024). DOI: 10.1002/smll.202400408
Journal information: Small
Provided by University of Edinburgh
News
Specially engineered antibody delivers RNA therapy to treatment-resistant tumors
Elias Quijano, PhD; Diana Martinez-Saucedo, PhD; Zaira Ianniello, PhD; and Natasha Pinto-Medici, PhD, there are 25 other contributors, most from Yale's Department of Therapeutic Radiology and from the departments of genetics, molecular biophysics and [...]
Vaccinated women face fewer cervical cancer risks
New data from Denmark shows the HPV vaccine’s powerful long-term impact, while also revealing why cervical cancer screening is still essential. A Danish study published in the journal Eurosurveillance reports that women who received the human [...]
3D-printed implant offers a potential new route to repair spinal cord injuries
A research team at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences has developed a 3-D printed implant to deliver electrical stimulation to injured areas of the spinal cord, offering a potential new route to [...]
Nanocrystals Carrying Radioisotopes Offer New Hope for Cancer Treatment
The Science Scientists have developed tiny nanocrystal particles made up of isotopes of the elements lanthanum, vanadium, and oxygen for use in treating cancer. These crystals are smaller than many microbes and can carry isotopes of [...]
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]