Exciting and novel research has investigated the internalization of nanoparticles by cells to optimize drug delivery into target cells. This research, published within the journal, Pharmaceutics, aims to analyze the simultaneous uptake of two different types of nanoparticles into cells.
Enhancing Drug Delivery Using Nanoparticles
Nanoparticles, sized within the nanoscale, between 1 and 100 nm, hold high efficacy for drug delivery due to their ability to interact with biological systems.
The use of nanocarriers to carry drugs to their target cells is one of the advantages of incorporating nanotechnology within medicine, especially with their surface functionalization ability which enables them to target cells more effectively. This allows them to be more beneficial than the conventional method of drug delivery which has a systemic effect and can cause adverse effects on all cells rather than just targeting specific cells.
Understanding how many carriers enter cells is critical for deciphering the intercellular dose that the target cells are provided to determine the efficacy of utilizing nanoparticles in this way and advancing drug delivery systems.
While this area of research has already been spearheaded with previous research with internalization pathways for particles being investigated, the effect of cell uptake when two different particles are exposed to the cell simultaneously is limited.
These investigations include reports of an increase in cell uptake of gold and iron nanoparticles when both particles were exposed to murine macrophages. However, another researcher has described changes to cellular function with simultaneous exposure, with carbon black and iron oxide particles exposed to human epithelial cells, possibly resulting in protein and lipid oxidation.
Interestingly, this novel research can be useful when enhancing drug delivery in the body by using two different particles that can be used for various applications to increase the efficacy of drug treatment for diseases and disorders.
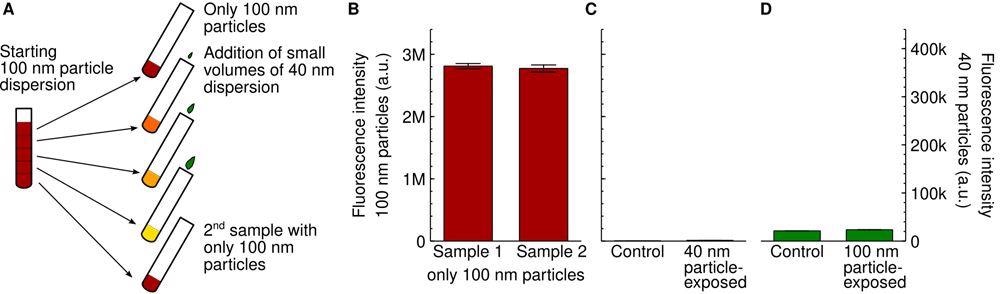
Experimental setup. (A) Schematic showing the dispersion procedure we used to ensure that the concentration of the 100 nm particles was the same for all samples. A first dispersion of the 100 nm particles was prepared and then divided up. To the resulting samples, different small volumes of a 40 nm particle dispersion were added. The first and last sample were left without 40 nm particles to serve as controls. Note that the colours are schematic only. (B) Nanoparticle fluorescence of cells exposed to the two different control dispersions of the 100 nm particles mentioned in panel A (first and last sample; 20 μg/mL or 0.060 nM). The similarity of the signal is consistent with the two control samples having the same nanoparticle concentration. (C,D) Lack of cross-talk between the two particle signals. (C) Cells were exposed to only the 40 nm particles (100 μg/mL; 4.7 nM) and the fluorescence intensity measured at the same wavelengths where researchers measured the 100 nm particles (left axis). There is a low background signal (right bar), but this is comparable to control cells not exposed to any particles at all (left bar). (D) Cells were exposed to only the 100 nm particles (80 μg/mL; 0.24 nM) and the fluorescence intensity measured at the same wavelengths where we measure the 40 nm particles (right axis). There is a low background signal (right bar), but this is comparable to control cells not exposed to any particles at all (left bar). © De Boer I, Richards CJ, Åberg C. (2022)
Innovative Research
The researchers of this study exposed HeLa (adenocarcinomic human cervical epithelial) cells to two different sized carboxylated polystyrene nanoparticles, including 40 nm and 100 nm diameter particles labeled with different fluorescent dyes to track the movement.
They observed that smaller particles had an increased cell uptake in the presence of larger-sized particles while larger particle uptake was impeded in the presence of smaller particles. This confirmed previous research on simultaneous cell uptake.
However, this increase was confirmed of cells within a medium with serum and the formation of a biomolecular corona on particles, which was not the same as previous research within a serum-free medium.
This research can enable the understanding of whether the competition between different concentrations of various sized particles is dependent on cell types; through the examination of 2D fluorescence distribution of the two measurable particles, the results have illustrated all cells take up both particles, but this may be within varying levels.
A limitation of this research is a lack of comprehension about the uptake mechanisms underlying the competitive nature of two various sized nanoparticles. With further research, the cellular mechanisms of this uptake can be clarified to understand these observations.
Significant Implications for Enhanced Drug Delivery
This research can be utilized to enhance drug delivery with the presence of a second nanoparticle, such as one of a larger size with the aim of increasing the cellular uptake of the first nanoparticle. The implications of this can be significant for increasing the intercellular drug dose found within cells and can be a start to advancing nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems.
With nanoparticles already being able to be functionalized through surface ligands, the use of these as nanocarriers for drug delivery as well as secondary particles can be an innovative approach to increasing the therapeutic selectivity of cells.
This can be utilized for diseases and even for cancer treatment to develop particles that work together for enhanced drug delivery into target cells, sustained delivery, and possibly the clearance of the drug from the body. Innovative drug delivery systems with more control through this approach may be a step towards personalized medicine that prioritizes patient care.
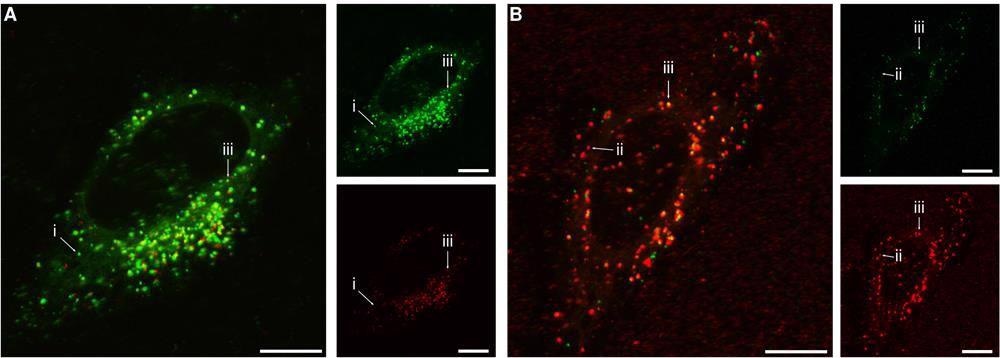
Subcellular distribution of the 40 nm and 100 nm particles. Cells were exposed for 24 h to both the 40 nm and 100 nm particles simultaneously and then observed using confocal fluorescence microscopy. (A) Concentration of 100 and 40 nm particles 20 and 100 μg/mL, respectively (0.060 nM and 4.7 nM; conditions correspond to the highest 40 nm particle concentration in Figures 2 and S3). (B) Concentration of 40 and 100 nm particles 6.25 and 80 μg/mL, respectively (0.30 and 0.24 nM; conditions correspond to the highest 100 nm particle concentration in Figures 4 and S4). The larger images show overlaps of both fluorescence colours, while the smaller images show the individual colours. (Green) 40 nm particles; (red) 100 nm particles. Arrows show examples of (i) 40 nm particle( s) (green) in the absence of 100 nm particles; (ii) 100 nm particle(s) (red) in the absence of 40 nm particles; (iii) 40 and 100 nm particles in the same location. The results show that the two particles often end up in the same location, but not always. All scale bars correspond to 10 μm. © De Boer I, Richards CJ, Åberg C. (2022)
News
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
Scientists Discover Simple Saliva Test That Reveals Hidden Diabetes Risk
Researchers have identified a potential new way to assess metabolic health using saliva instead of blood. High insulin levels in the blood, known as hyperinsulinemia, can reveal metabolic problems long before obvious symptoms appear. It is [...]
One Nasal Spray Could Protect Against COVID, Flu, Pneumonia, and More
A single nasal spray vaccine may one day protect against viruses, pneumonia, and even allergies. For decades, scientists have dreamed of creating a universal vaccine capable of protecting against many different pathogens. The idea [...]
New AI Model Predicts Cancer Spread With Incredible Accuracy
Scientists have developed an AI system that analyzes complex gene-expression signatures to estimate the likelihood that a tumor will spread. Why do some tumors spread throughout the body while others remain confined to their [...]
Scientists Discover DNA “Flips” That Supercharge Evolution
In Lake Malawi, hundreds of species of cichlid fish have evolved with astonishing speed, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study how biodiversity arises. Researchers have identified segments of “flipped” DNA that may allow fish to adapt rapidly [...]
Our books now available worldwide!
Online Sellers other than Amazon, Routledge, and IOPP Indigo Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artifcial Intelligence Global Health Care Equivalency In The Age Of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine And Artificial [...]
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]