Artificial intelligence facilitates the visualization of neural connections in the brains of mice.
Scientists from Johns Hopkins have leveraged artificial intelligence to create a technique that allows for the visualization and monitoring of alterations in the strength of synapses — the connection points through which nerve cells in the brain communicate — in living organisms. The technique, as outlined in Nature Methods, could, according to the researchers, pave the way for an improved comprehension of how these connections in human brains evolve with learning, age, trauma, and disease.
"If you want to learn more about how an orchestra plays, you have to watch individual players over time, and this new method does that for synapses in the brains of living animals," says Dwight Bergles, Ph.D., the Diana Sylvestre and Charles Homcy Professor in the Solomon H. Snyder Department of Neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University (JHU) School of Medicine.
Bergles co-authored the study with colleagues Adam Charles, Ph.D., M.E., and Jeremias Sulam, Ph.D., both assistant professors in the biomedical engineering department, and Richard Huganir, Ph.D., Bloomberg Distinguished Professor at JHU and Director of the Solomon H. Snyder Department of Neuroscience. All four researchers are members of Johns Hopkins' Kavli Neuroscience Discovery Institute.
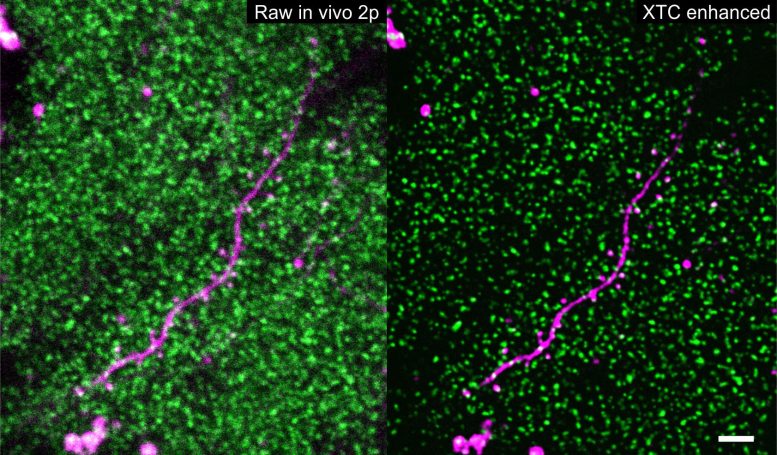
Thousands of SEP-GluA2 tagged synapses (green) surrounding a sparsely labeled dendrite (magenta) before and after XTC image resolution enhancement. Scale bar 5 microns. Credit: Xu, Y.K.T., Graves, A.R., Coste, G.I. et al. Nat Methods
Nerve cells transfer information from one cell to another by exchanging chemical messages at synapses ("junctions"). In the brain, the authors explain, different life experiences, such as exposure to new environments and learning skills, are thought to induce changes at synapses, strengthening or weakening these connections to allow learning and memory. Understanding how these minute changes occur across the trillions of synapses in our brains is a daunting challenge, but it is central to uncovering how the brain works when healthy and how it is altered by disease.
To determine which synapses change during a particular life event, scientists have long sought better ways to visualize the shifting chemistry of synaptic messaging, necessitated by the high density of synapses in the brain and their small size — traits that make them extremely hard to visualize even with new state-of-the-art microscopes.
"We needed to go from challenging, blurry, noisy imaging data to extract the signal portions we need to see," Charles says.
To do so, Bergles, Sulam, Charles, Huganir, and their colleagues turned to machine learning, a computational framework that allows the flexible development of automatic data processing tools. Machine learning has been successfully applied to many domains across biomedical imaging, and in this case, the scientists leveraged the approach to enhance the quality of images composed of thousands of synapses. Although it can be a powerful tool for automated detection, greatly surpassing human speeds, the system must first be "trained," teaching the algorithm what high-quality images of synapses should look like.
In these experiments, the researchers worked with genetically altered mice in which glutamate receptors — the chemical sensors at synapses — glowed green (fluoresced) when exposed to light. Because each receptor emits the same amount of light, the amount of fluorescence generated by a synapse in these mice is an indication of the number of synapses, and therefore its strength.
As expected, imaging in the intact brain produced low-quality pictures in which individual clusters of glutamate receptors at synapses were difficult to see clearly, let alone to be individually detected and tracked over time. To convert these into higher-quality images, the scientists trained a machine learning algorithm with images taken of brain slices (ex vivo) derived from the same type of genetically altered mice. Because these images weren't from living animals, it was possible to produce much higher quality images using a different microscopy technique, as well as low-quality images — similar to those taken in live animals — of the same views.
This cross-modality data collection framework enabled the team to develop an enhancement algorithm that can produce higher-resolution images from low-quality ones, similar to the images collected from living mice. In this way, data collected from the intact brain can be significantly enhanced and able to detect and track individual synapses (in the thousands) during multiday experiments.
To follow changes in receptors over time in living mice, the researchers then used microscopy to take repeated images of the same synapses in mice over several weeks. After capturing baseline images, the team placed the animals in a chamber with new sights, smells, and tactile stimulation for a single five-minute period. They then imaged the same area of the brain every other day to see if and how the new stimuli had affected the number of glutamate receptors at synapses.
Although the focus of the work was on developing a set of methods to analyze synapse level changes in many different contexts, the researchers found that this simple change in environment caused a spectrum of alterations in fluorescence across synapses in the cerebral cortex, indicating connections where the strength increased and others where it decreased, with a bias toward strengthening in animals exposed to the novel environment.
The studies were enabled through close collaboration among scientists with distinct expertise, ranging from molecular biology to artificial intelligence, who don't normally work closely together. But such collaboration, is encouraged at the cross-disciplinary Kavli Neuroscience Discovery Institute, Bergles says. The researchers are now using this machine learning approach to study synaptic changes in animal models of Alzheimer's disease, and they believe the method could shed new light on synaptic changes that occur in other disease and injury contexts.
"We are really excited to see how and where the rest of the scientific community will take this," Sulam says.
Reference: "Cross-modality supervised image restoration enables nanoscale tracking of synaptic plasticity in living mice" by Yu Kang T. Xu, Austin R. Graves, Gabrielle I. Coste, Richard L. Huganir, Dwight E. Bergles, Adam S. Charles and Jeremias Sulam, 11 May 2023, Nature Methods.
DOI: 10.1038/s41592-023-01871-6
News
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]