Bacteria across our planet contain nanometer-sized factories that do many different things. Some make nutrients, others isolate toxic materials that could harm the bacteria. We have barely scratched the surface of their functional diversity.
But all share a common exterior, a shell made of protein tiles, that Michigan State University researchers are learning how to manipulate in the lab. This will allow them to build factories of their own design, using the natural building blocks. Indeed, scientists see the structures as a source of new technologies. They are trying to repurpose them to do things they don’t in nature.
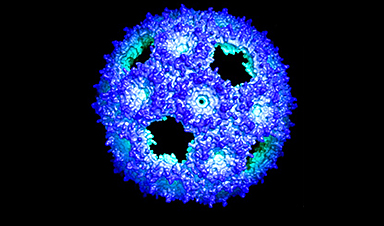
In a new study, the lab of Cheryl Kerfeld reports a new genetically engineered shell, based on natural structures and the principles of protein evolution. The new shell is simpler, made of only a single designed protein. It will be easier to work with and, perhaps, even evolve in the lab. The study is published in ACS Synthetic Biology.
Natural shells are made of up to three types of proteins. The most abundant is called BMC-H. Six BMC-H proteins come together to form a hexagon shape to tile the wall.
At some time in evolutionary history, some pairs of BMC-H proteins became joined together, in tandem. Three of these mergers, called BMC-T, join to also form a hexagon shape.
“The two halves of a BMC-T protein can evolve separately while staying next to each other, because they are fused together,” said Bryan Ferlez, a postdoc in the Kerfeld lab. “This evolution allows for diversity in the structures and functions of BMC-T shell proteins, something that we want to recreate by design in the lab.”
To take his fledgling lab to new heights, Liangfang Zhang hatched a plan that he considered brilliant in its simplicity. It involved procedures that many of his peers found a little out there. But if he could make his idea work, it would clear a major hurdle to safely ferry therapies through the body on nanoparticles one-thousandth the width of a human hair.
Yet back in 2010, the young nanoengineer could not convince the National Institutes of Health, the main funder of U.S. biomedical research, to support the project. Zhang applied for funding four or five times over several years, to no avail.
“It felt quite lonely,” he says. “But I just felt this is very unique stuff. And it may become a big thing.”
Pulling funds from other projects and from the start-up package he received to set up his lab at the University of California, San Diego, Zhang did the experiments for his breakthrough paper, published in 2011 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. He and coworkers created a new class of nanoparticles, made from carbon-containing polymers, that could slip through blood vessels in a mouse without triggering an immune reaction. While immune responses are important for killing disease-causing pathogens, the same reactions are a nuisance when they clear out molecules made to deliver lifesaving drugs.
Then, instead of just viewing their particles as a drug-delivery system, which most other researchers were focused on, Zhang and his team made a surprising pivot. They repurposed the particles to act as “nanosponges” that trap and remove toxins from the blood. In lab experiments, the nanosponges worked against toxins unleashed by E. coli and some of the harder-to-fight bacteria. Nanosponges also slowed harmful inflammation in mice with a form of rheumatoid arthritis and diverted HIV and Zika from the cells those viruses normally infect, the researchers reported last year.
Image Credit: MSU
News This Week
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]





















Leave A Comment