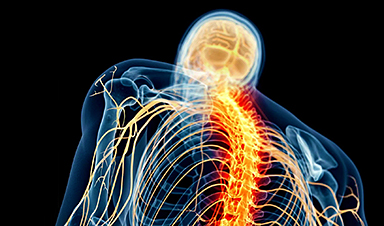
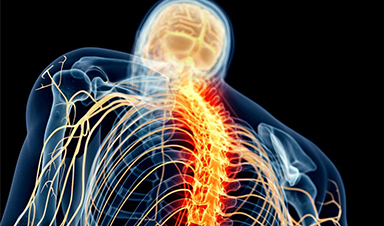
A new electrical stimulation therapy for spinal muscle atrophy (SMA) has shown promise in reactivating motor neurons and improving movement. In a pilot clinical trial, three patients who received spinal cord stimulation for one month experienced increased strength, reduced fatigue, and improved walking ability.
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have developed a new, drug-free, minimally invasive treatment that addresses the underlying cause of progressive neural function loss in spinal muscle atrophy (SMA), a genetic neuromuscular disease. This approach involves electrically stimulating sensory spinal nerves to gradually reactivate dormant motor neurons in the spinal cord. The treatment has been shown to improve leg muscle strength and walking ability in adults with SMA. These findings were published in Nature Medicine.
Early results from a pilot clinical trial involving three individuals with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) indicate that one month of regular neurostimulation sessions led to improved motor neuron function, reduced fatigue, and enhanced strength and walking ability in all participants, regardless of symptom severity. This study is the first to demonstrate that a neurotechnology can be specifically designed to reverse neural circuit degeneration and restore cell function in a human neurodegenerative disease.
“To counteract neurodegeneration, we need two things – stop neuron death and restore the function of surviving neurons,” said co-corresponding author Marco Capogrosso, Ph.D., assistant professor of neurosurgery at Pitt. “In this study we proposed an approach to treat the root cause of neural dysfunction, complementing existing neuroprotective treatments with a new approach that reverses nerve cell dysfunction.”
Understanding SMA and Its Impact
SMA is a genetic neurodegenerative disease that manifests in progressive death and functional decline of motor neurons — nerve cells that control movement by transmitting signals from the brain and the spinal cord to the muscles. Over time, the loss of motor neurons causes gradual muscle weakness, and leads to a variety of motor deficits, including for the participants in this trial, difficulty in walking, climbing stairs, and standing up from chairs.
While there is no cure for SMA, several promising neuroprotective treatments have become available in the last decade. These include gene replacement therapies and medications, both of which stimulate the production of motoneuron-supporting proteins that prevent neuronal death and that slow down – though do not reverse – disease progression.
Studies show that movement deficits in SMA emerge before widespread motoneuron death, suggesting that underlying dysfunction in spinal nerve circuitry may contribute to disease onset and symptom development. According to earlier research on animal models of SMA by study co-author George Mentis, Ph.D., at Columbia University, surviving motor neurons receive fewer stimulation inputs from sensory nerves – fibers that return the information from skin and muscles back to the central nervous system. Compensating for this deficit in neural feedback could, therefore, improve communication between the nervous system and the muscles, aid muscle movement, and combat muscle wasting.
Pitt researchers hypothesized that a targeted epidural electrical stimulation therapy could be used to rescue lost nerve cell function by amplifying sensory inputs to the motor neurons and engaging the degenerated neural circuits. These cellular changes could, in turn, translate into functional improvements in movement capacity.
How the Study Was Conducted
The Pitt study was conducted as part of a pilot clinical trial that enrolled three adults with milder forms of SMA (Type 3 or 4 SMA). During a study period of 29 days, participants were implanted with two spinal cord stimulation (SCS) electrodes that were placed in the lower back region on each side of the spinal cord, directing the stimulation exclusively to sensory nerve roots. Testing sessions lasted four hours each and were conducted five times a week for a total of 19 sessions, until the stimulation device was explanted.
After confirming that the stimulation worked as intended and engaged spinal motor neurons, researchers performed a battery of tests to measure muscle strength and fatigue, changes in gait, range of motion, and walking distance, as well as motoneuron function.
“Because SMA is a progressive disease, patients do not expect to get better as time goes on. But that is not what we saw in our study. Over the four weeks of treatment, our study participants improved in several clinical outcomes with improvements in activities of daily living. For instance, toward the end of the study, one patient reported being able to walk from their home to the lab without becoming tired,” said co-corresponding author Elvira Pirondini, Ph.D., assistant professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Pitt.
All participants increased their 6-Minute Walk Test score – a measure of muscle endurance and fatigue – by at least 20 meters, compared to a mean improvement of 1.4 meters over three months of comparable exercise regimen unaided by SCS and a median increase of 20 meters after 15 months of SMA-specific neuroprotective pharmacologic therapy.
These functional gains were mirrored by improved neural function, including a boost in motoneurons’ capacity to generate electrical impulses and transmit them to the muscles.
“Our results suggest that this neurostimulation approach could be broadly applied to treat other neurodegenerative diseases beyond SMA, such as ALS or Huntington’s disease, as long as appropriate cell targets are identified in the course of future research,” said co-corresponding author Robert Friedlander, M.D., chair of neurosurgery at Pitt and co-director of the UPMC Neurological Institute. “We are hoping to continue working with SMA patients and launch another clinical trial to test the long-term efficacy and safety of electrical spinal cord stimulation.”
Reference: “First-in-human study of epidural spinal cord stimulation in individuals with spinal muscular atrophy” by Genís Prat-Ortega, Scott Ensel, Serena Donadio, Luigi Borda, Amy Boos, Prakarsh Yadav, Nikhil Verma, Jonathan Ho, Erick Carranza, Sarah Frazier-Kim, Daryl P. Fields, Lee E. Fisher, Doug J. Weber, Jeffrey Balzer, Tina Duong, Steven D. Weinstein, Mikael J. L. Eliasson, Jacqueline Montes, Karen S. Chen, Paula R. Clemens, Peter Gerszten, George Z. Mentis, Elvira Pirondini, Robert M. Friedlander and Marco Capogrosso, 5 February 2025, Nature Medicine.
DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03484-8
Genis Prat-Ortega, Ph.D., Scott Ensel, B.S., and Serena Donadio, B.S., all of Pitt, are co-first authors of the study. Other authors of the study are Amy Boos, M.S., Jacqueline Ho, M.D., Sarah Frazier-Kim, Daryl Fields, M.D., Ph.D., Lee Fisher, Ph.D., Paula Clemens, M.D., and Peter Gerszten, M.D., all of Pitt; Luigi Borda, B.S., Prakarsh Yadav, B.S., Nikhil Verma, B.S., and Douglas Weber, Ph.D., all of Carnegie Mellon University; Tina Duong, Ph.D., of Stanford University; Jacqueline Montes, P.T., Ed.D., and George Mentis, Ph.D., of Columbia University; Steven Weinstein, Mikael Eliasson, of Genentech Roche; and Karen S. Chen, of the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Foundation.
This research was supported by an exploratory research grant from F. Hoffmann–La Roche. Genentech, Inc. (a member of the Roche Group) and the University of Pittsburgh hold rights to IP related to this study. Marco Capogrosso, Genis Prat-Ortega and Mikael Eliasson hold patent applications that relate to this work.
News
Specially engineered antibody delivers RNA therapy to treatment-resistant tumors
Elias Quijano, PhD; Diana Martinez-Saucedo, PhD; Zaira Ianniello, PhD; and Natasha Pinto-Medici, PhD, there are 25 other contributors, most from Yale's Department of Therapeutic Radiology and from the departments of genetics, molecular biophysics and [...]
Vaccinated women face fewer cervical cancer risks
New data from Denmark shows the HPV vaccine’s powerful long-term impact, while also revealing why cervical cancer screening is still essential. A Danish study published in the journal Eurosurveillance reports that women who received the human [...]
3D-printed implant offers a potential new route to repair spinal cord injuries
A research team at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences has developed a 3-D printed implant to deliver electrical stimulation to injured areas of the spinal cord, offering a potential new route to [...]
Nanocrystals Carrying Radioisotopes Offer New Hope for Cancer Treatment
The Science Scientists have developed tiny nanocrystal particles made up of isotopes of the elements lanthanum, vanadium, and oxygen for use in treating cancer. These crystals are smaller than many microbes and can carry isotopes of [...]
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]