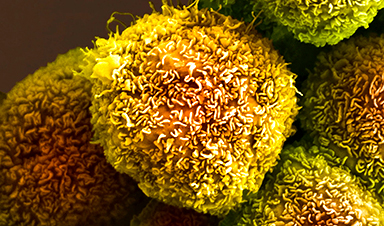
Using mRNA tailored to each patient’s tumor, the vaccine may have staved off the return of one of the deadliest forms of cancer in half of those who received it.
Five years ago, a small group of cancer scientists meeting at a restaurant in a deconsecrated church hospital in Mainz, Germany, drew up an audacious plan: They would test their novel cancer vaccine against one of the most virulent forms of the disease, a cancer notorious for roaring back even in patients whose tumors had been removed.
The vaccine might not stop those relapses, some of the scientists figured. But patients were desperate. And the speed with which the disease, pancreatic cancer, often recurred could work to the scientists’ advantage: For better or worse, they would find out soon whether the vaccine helped.
On Wednesday, the scientists reported results that defied the long odds. The vaccine provoked an immune response in half of the patients treated, and those people showed no relapse of their cancer during the course of the study, a finding that outside experts described as extremely promising.
The study, published in Nature, was a landmark in the yearslong movement to make cancer vaccines tailored to the tumors of individual patients.
Researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, led by Dr. Vinod Balachandran, extracted patients’ tumors and shipped samples of them to Germany. There, scientists at BioNTech, the company that made a highly successful Covid vaccine with Pfizer, analyzed the genetic makeup of certain proteins on the surface of the cancer cells.
“This is the first demonstrable success — and I will call it a success, despite the preliminary nature of the study — of an mRNA vaccine in pancreatic cancer,” said Dr. Anirban Maitra, a specialist in the disease at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, who was not involved in the study. “By that standard, it’s a milestone.”
The study was small: Only 16 patients, all of them white, were given the vaccine, part of a treatment regimen that also included chemotherapy and a drug intended to keep tumors from evading people’s immune responses. And the study could not entirely rule out factors other than the vaccine having contributed to better outcomes in some patients.
“It’s relatively early days,” said Dr. Patrick Ott of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
Beyond that, “cost is a major barrier for these types of vaccines to be more broadly utilized,” said Dr. Neeha Zaidi, a pancreatic cancer specialist at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. That could potentially create disparities in access.
Since the beginning of the study, in December 2019, BioNTech has shortened the process to under six weeks, said Dr. Ugur Sahin, a co-founder of the company, who worked on the study. Eventually, the company intends to be able to make cancer vaccines in four weeks.
And since it first began testing the vaccines about a decade ago, BioNTech has lowered the cost from roughly $350,000 per dose to less than $100,000 by automating parts of production, Dr. Sahin said.
A personalized mRNA cancer vaccine developed by Moderna and Merck reduced the risk of relapse in patients who had surgery for melanoma, a type of skin cancer, the companies announced last month. But the latest study set the bar higher by targeting pancreatic cancer, which is thought to have fewer of the genetic changes that would make it ripe for vaccine treatments.
In patients who did not appear to respond to the vaccine, the cancer tended to return around 13 months after surgery. Patients who did respond, though, showed no signs of relapse during the roughly 18 months they were tracked.
Intriguingly, one patient showed evidence of a vaccine-activated immune response in the liver after an unusual growth developed there. The growth later disappeared in imaging tests.
“It’s anecdotal, but it’s nice confirmatory data that the vaccine can get into these other tumor regions,” said Dr. Nina Bhardwaj, who studies cancer vaccines at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
Scientists have struggled for decades to create cancer vaccines, in part because they trained the immune system on proteins found on tumors and normal cells alike.
Tailoring vaccines to mutated proteins found only on cancer cells, though, potentially helped provoke stronger immune responses and opened new avenues for treating any cancer patient, said Ira Mellman, vice president of cancer immunology at Genentech, which developed the pancreatic cancer vaccine with BioNTech.
“Just establishing the proof of concept that vaccines in cancer can actually do something after, I don’t know, thirty years of failure is probably not a bad thing,” Dr. Mellman said. “We’ll start with that.”
News
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]