Despite the end of the pandemic, COVID-19 continues to pose a serious health threat. Most individuals have established robust immune protection and do not develop severe disease but the infection can still lead to marked and sometimes long-lasting disease symptoms.
The researchers discovered that the pirola variant, in contrast the all previously circulating omicron variants, enters lung cells with high efficiency and uses the cellular enzyme TMPRss2 for entry, thereby exhibiting surprising parallels to variants alpha, beta, gamma and delta that circulated during the first years of the pandemic. The improved entry into lung cells might indicate that the virus is more aggressive but production of new, infectious viral particles in infected cells was reduced, which may limit spread and pathogenic potential.
The researchers report in the journal Cell that the pirola variant is resistant against all therapeutic antibodies and efficiently evades antibody responses in vaccinated individuals with and without breakthrough infection. However, the virus was appreciably inhibited by antibodies elicited by the new, XBB.1.5-adpated mRNA vaccine.
In summary, the results show that four years after the start of the pandemic the virus is still capable of profound changes and can reacquire properties that may promote the development of severe disease.
The spread of SARS-CoV-2 is associated with the constant emergence of new viral variants. These variants have acquired mutations in the spike protein, which allow evasion of neutralizing antibodies in vaccinated and convalescent individuals. The emergence of viral variants started with the alpha variant followed by the beta, gamma and delta variants.
At the end of the year 2021 the omicron variant became globally dominant, which, based on genome sequence, differed markedly from previously circulating variants. However, the virus had to pay a price for this massive change. Thus, the omicron variant evades neutralizing antibodies and is transmitted with high efficiency but has lost the ability to efficiently use a host cell enzyme, the protease TMPRSS2, for lung cell entry. As a consequence, the omicron variant induces pneumonia less frequently.
Pirola: A quantum leap in SARS-CoV-2 evolution
Descendants of the omicron variant dominated globally until the end of the year 2023. New variants frequently differed only by few mutations from their predecessors and there was evidence that viruses circulating in 2023 had only limited options to evade antibody pressure in the human population. Therefore, the discovery of a new SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant, pirola (BA.2.86), which, based on genome sequence, strongly differed from other circulating viruses drew a lot of attention.
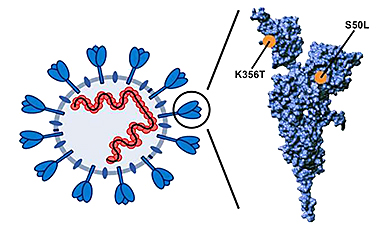
The pirola variant, analogous to the omicron variant, likely arose in immunocompromised patients and presents a quantum leap in SARS-CoV-2 evolution. The spike protein of the pirola variant harbors more than 30 mutations relative to its precursor variant, BA.2, and it is largely unknown how these mutations affect the biological properties of the virus.
A team of researchers from the German Primate Center (DPZ) led by Markus Hoffmann and Stefan Pöhlmann addressed this question jointly with the research groups of Christian Drosten (Charité, Berlin), Georg Behrens (Hannover Medical School), Luka Cicin-Sain (Helmholtz Center for Infection Research, Braunschweig) and Hans-Martin Jäck (Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen Nuremberg).
Pirola can infect lung cells more efficiently
The researchers discovered that the pirola variant, in contrast to all previously circulating omicron subvariants, enters lung cells with high efficiency and in a TMPRSS2-dependent manner. Further, they could demonstrate that mutations S50L and K356T in the spike protein of the pirola variant are important for the highly efficient lung cell entry.
“It is noteworthy that two years after the global dominance of the omicron variant, which fails to robustly enter lung cells, now a quite different virus is spreading and that this virus is able to again enter lung cells with high efficiency. If the augmented lung cell entry translates into more severe disease upon infection with the pirola variant remains to be investigated in animal models,” says Pöhlmann, head of the Infection Biology Unity of the German Primate Center.
Pirola replicates less well than its predecessors
SARS-CoV-2 infected cells produce new virus particles many of which, but not all, are able to infect new cells. The researchers provided evidence that cells infected by the pirola variant are less well able than cells infected with previous variants to produce intact viral particles. “The relatively inefficient production of infectious particles by cells infected with the pirola variant was surprising,” says Hoffmann, the lead contact of the study.
“It will be interesting to analyze which mechanism is responsible. Maybe the infected cells produce defective interfering particles, which regulate spread of the pirola variant and contribute to antibody evasion.”
Therapeutic antibodies are ineffective against pirola
Recombinantly produced neutralizing antibodies were successfully used for COVID-19 prophylaxis and therapy. However, due to the emergence of viral variants with mutations in the antibody binding sites most of those antibodies are not active against currently circulating variants. The present study shows that the pirola variant is no exception—none of the tested antibodies was able to neutralize the virus.
“These results show that the development of new, broad spectrum antibodies is an important task,” says Hoffmann.
New, adapted vaccine protects against pirola
The pirola variant was also able to evade antibodies induced by vaccination or infection but with less efficiency than the contemporaneously circulating Eris variant (EG.5.1). However, antibodies induced by vaccination with the new XBB.1.5-adapted vaccine were able to appreciably inhibit both the pirola and the Eris variant.
“These results suggest that the XBB.1.5-adpated vaccine might induce a robust, although likely short-lived, protection against infection with the pirola variant,” says Hoffmann.
“In this context it is interesting that subvariants of pirola are currently globally on the rise that harbor an additional mutation in the spike protein, which may increase antibody evasion. The virus is in the process of optimizing itself and the consequences of this optimization should be studied,” adds Lu Zhang, first author of the study.
More information: Lu Zhang et al, SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 enters lung cells and evades neutralizing antibodies with high efficiency, Cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.025
News
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]