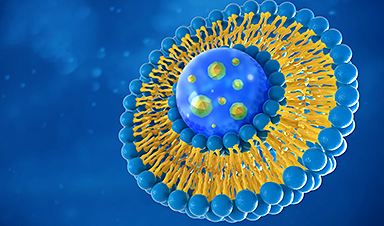
Breakthrough medical technology like mRNA vaccines rely on tiny nanoparticles to deliver medicine to cells. A new device will help drug manufacturers and evaluators like the FDA more precisely measure genetic payloads to evaluate drug effectiveness.
An important component of the vaccines protecting people against SARS-CoV-2 virus and its variants are lipid nanoparticles, or LNPs. These circular particles carry therapeutic mRNA payloads, the snippets of genetic material that trigger our immune systems to defend against COVID-19. Even with their success, certain characteristics about the particles, such as payload distribution, are unknown. Researchers and the Food and Drug Administration want more insights about these characteristics to improve metrics reporting in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
A new molecular detection platform developed by two Whiting School of Engineering professors is answering the FDA’s call. Hai-Quan Mao and Tza-Huei (Jeff) Wang want to address how many mRNA molecules an LNP can carry and whether the mRNA is uniformly packed inside the particle to help researchers design more efficient and effective treatments and vaccines.
“Our platform processes molecules at the single nanoparticle level, but unlike the current imaging methods for mRNA LNPs, our approach is based on fluorescent spectroscopy and gives us the ability to see through the particles,” said Wang, a professor in the departments of Mechanical Engineering and Biomedical Engineering at the Whiting School, and a core researcher at the Institute for NanoBioTechnology.
The ability to peer inside the nanoparticles allows the researchers to differentiate between and measure empty LNPs that do not contain mRNA, LNPs with mRNA, and free-floating mRNA in a sample.
Their platform, called cylindrical illumination confocal spectroscopy, or CICS, works by tagging mRNA and LNP components with fluorescent signals of up to three colors and passing the sample through a detection plane. The detection plane reads the fluorescent signals and measures their intensity before comparing the strength of the intensities with that of a single mRNA molecule. The data analysis with an algorithm called deconvolution tells the team both how many mRNA copies are inside the LNP—if any—and their distribution in the sample. The team’s platform overcomes contrast limitations and increases the sample analysis throughput, that are seen in cryo-transmission electron microscopy, the current gold standard for imaging mRNA LNPs.
Tests conducted using this sensing platform revealed that from a benchmark solution of mRNA LNP used in academic research studies, over 50% of the LNPs are not loaded with mRNA molecules, and of the mRNA-filled LNPs, most of them contained two to three mRNA molecules per particle.
“Being able to quantitatively resolve payload characteristics of mRNA LNPs at the single particle level has never been done before. We are intrigued by the substantial presence of empty LNPs, and by altering formulation conditions, a single nanoparticle can load as few as one to as many as ten mRNA molecules.” said Mao, professor in the departments of Materials Science and Engineering and Biomedical Engineering at the Whiting School and director of the Institute for NanoBioTechnology.
The team’s results are published in Nature Communications.
“There are a lot of groups doing LNP research,” Wang said. “However, when they discover a formula that might work well, it has been hard to associate those discoveries back to the composition and payload distribution of the nanoparticles. With this platform we can provide a more comprehensive understanding on what is happening at the single particle level.”
More research is needed to learn how many mRNA molecules per LNP capsule is optimal for the most effective treatment. However, the empty LNPs revealed by the new platform show there is a need to improve methods for packaging the mRNA inside the LNPs.
Mao and Wang say that their platform shows that it has the potential to not only be used at all stages of LNP-related research and development, but also in the development of other drug delivery systems and quality control measures at the manufacturing stage. The team has filed a patent application covering the technique and is working with collaborators to use the platform to analyze other types of therapeutic cargos in diverse nanoparticle systems for treating different diseases.
“The FDA has recently addressed the need for better quality metrics in nanoparticle design in the pharmaceutical industry,” said Michael J. Mitchell, a leading scientist in the field of LNP research and Skirkanich Assistant Professor of Innovation in the Department of Bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania. “This will become increasingly more important as mRNA LNP technology expands beyond vaccines into new therapeutics that are administered into the bloodstream, which have very stringent requirements. The new detection platform developed by Drs. Mao and Wang’s team is a potentially important step forward in addressing needs at the research and regulatory phase, and can potentially aid in the development of mRNA LNP technology beyond vaccines.”
News
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]