Longer-Term Projects
Vascular Cartographic Scanning Nanodevice (VCSN)
Frank Boehm’s book Nanomedical Device and Systems Design, Challenges, Possibilities, Visions endeavors to explore and present concepts for advanced nanomedical components, devices, and systems that may emerge over the next ~10-30 years. One of these nanodevices is called the Vascular Cartographic Scanning Nanodevice (VCSN) (Figure 1), which would be manifest as an autonomous, ~1 micron in diameter nanomedical device.
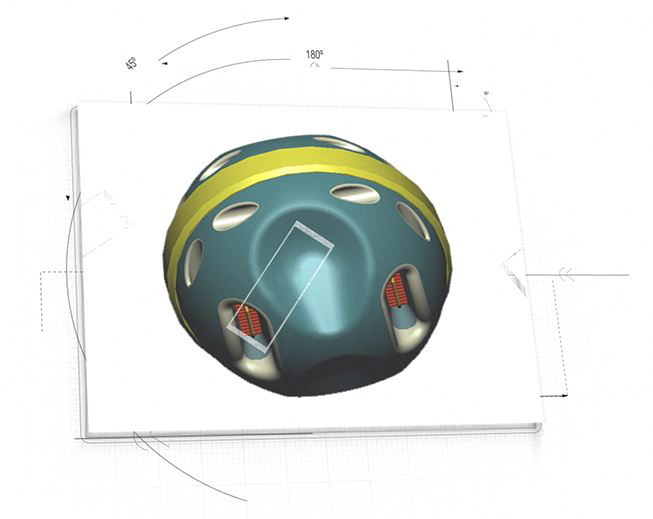
Figure 1: Artistic representation of conceptual Vascular Cartographic Scanning Nanodevice (VCSN)
Up to perhaps many thousands, or tens of thousands of VCSN nanodevices might be introduced into the patient intravenously, via ingestion as a pill, through inhalation, transdermally using a patch, or migrate in vivo utilizing a topical gel. Once within the patient their purpose would be to rapidly scan the entire human vasculature down to the smallest capillary lumen (~3 microns in diameter) in ultrahigh-resolution (sub-micron) three-dimensional (3D) digitized format. At all times they would be under the complete control of the surgeon or physician via “outbody” computer commands. Some of the capabilities of the VCSN are listed below:
- Capable of generating a very high-resolution (under 1 micron) 3D rendering of the complete human vasculature down to the smallest capillaries. It may also be applied to the imaging of the lymphatic system, and in a simplified form, the gastrointestinal tract, using a Gastrointestinal Micro Scanning Device (GMSD), (see description below).
- Ability to distinguish vascular and neurological plaque deposits and lesions with high accuracy.
- Capacity to determine vascular wall thicknesses, along with the identification and highlighting of any “hot spot” sites within the vasculature, such as imminent blockages or aneurysms that are at risk of rupturing.
- Surgeon and physicians would be able to “fly-through” all scanned areas via a joystick and computer display for the highly detailed inspection of any desired site within the system. The acquired spatial data from the VCSN may also enable holographic rendering and virtual travel through all imaged systems.
- Ability to facilitate the targeting of tumors by revealing sites of angiogenesis in close proximity to tumor growth sites.
A number of advantages of the VCSN include:
- High compactness and portability as its operation will require a relatively small footprint. This would enable a simple and quick setup and power-up procedures, which will be a boon for applications in developing countries and remote terrestrial environments.In aerospace, it might be utilized as an element of an on board medical diagnostics suite on military and medical aircraft.
- For space travel, it may be reconfigured for integration into spacesuits and spacecraft, and provide a compact yet very powerful medical imaging capability for future Moon and Mars habitats.
- Frugal energy consumption.
- Inexpensive administration and operation
- Rapid scanning time (~5 minutes).
- Ultrahigh resolution digital imagery and inherent flexibility for display across several formats and ease of file transmission to medical personnel globally via secure telecommunications connectivity
- Potential for enabling the significant reduction or elimination of long waiting queues for critical imaging technologies.
Gastrointestinal Micro Scanning Device (GMSD)
The Gastrointestinal Micro Scanning Device (GMSD) (Figure 2) will serve as far less complex precursor to the VCSN as it will not have the capacity for propulsion or navigation. It might, however, employ nascent forms of quantum computing, nanoelectronics, spatial data acquisition, and Pixel Matrix (see below) technologies that are envisaged for the VCSN. Hence, in addition to serving as formative in vivo spatial data acquisition device, the GMSD may also have utility as a test bed of sorts that is employed to identify and resolve technical, integrative, and functional issues toward the development of the VCSN.
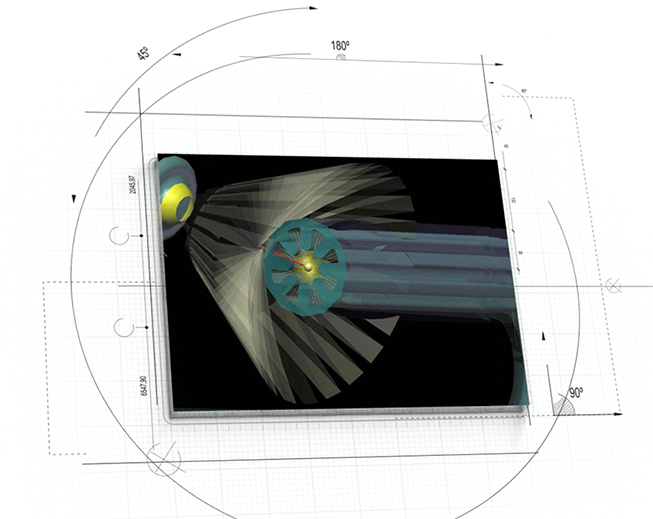
![]()
Figure 2: Artistic representation of conceptual Gastrointestinal Micro Scanning Device (GMSD)
The GMSD system will consist of three distinct components that work in unison to generate very high-resolution 3D topography of the entire internal surface of the GIT. The GMSD would accomplish this task by utilizing:
- Bright Ball (BB) scanning device, which would have a smooth spherical morphology of ~3 mm in diameter
- Pulse Generator/Data Transfer (PGDT) unit would trigger the activity of the internalized BB device via a specifically encrypted signal. The BB would be activated to scan subsequently to receiving this specific signal only. Once activated, the BB would commence to transmit a constant spatial data stream to the PGDT, which would serve as a data transfer device when linked to a computer and the Pixel Matrix (see below) software. The PGDT would be securely affixed to the patient’s abdominal surface and would stay in place for the duration of the scan.
- The Pixel Matrix display would process the PGDT supplied spatial data toward the reconstruction a high resolution “pixel per hit” 3D rendering of the total scanned area of the GIT that has been traversed by the BB. This software would enable “fly-through” and cross-sectional capabilities, allowing medical personnel to traverse the entire GIT (using a joystick, computer mouse, or touch screen display) to investigate any potential problem areas in great detail. The spatial data might also be converted to holographic and virtual reality formats. Using this procedure, the physician and/or surgeon would thus recognize any anomalous topography that is associated with tumor growth, lesions, and other abnormal features that may exist within the GIT.
The operational procedure for the GMSD would be relatively simple to implement, as the BB would be introduced orally to the patient in the same manner as a pill. Subsequently, an adhesive waterproof thin film PGDT patch would be affixed to the skin of patient’s abdomen. At this juncture, a system calibration would be performed to ensure that the communication link between the BB and the PGDT is functioning properly. An initial test scan would also be conducted in order to configure the image resolution. The PGDT would emit a unique pulsed signal (e.g., ultrasonic, near-infrared), which when received by sensors embedded within the surface of the BB would trigger all of the embedded emitters/receivers to fire and emit their scanning beams simultaneously in every direction. Once these procedures are completed the patient would be allowed to leave the physician’s office, clinic, or hospital to go about his/her normal routine. The internalized BB would now move along with the natural peristaltic rhythms of the GIT and be naturally eliminated at the conclusion of the transit duration. The patient would then return to the facility in two or three days (contingent on the assessed GIT transit time) to have the PGDT patch removed.
During the designated scanning period, the PGDT will have been continuously uploading spatial data provided by the BB, which would then be interfaced with a computer via a USB port to stream all of this data to the PM software housed within the computer. The data would now be translated to high-resolution 3D imagery on a display. The PM software would calculate BB orientation and would correlate the interrogating hits obtained within predetermined parameters to construct a cross section of the GIT to depict its internal topography. These digitized fragments would then be sequentially pieced together to form a seamless spatially accurate rendering of the system.
News
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]



















