The findings could potentially improve the success rate of cancer drug development.
Approximately 90% of drugs don't reach the market, highlighting the clear need for increased efficiency in drug development. The story isn't different for drugs aimed at treating cancer, with many failing due to various reasons. Now, researchers have revealed one reason why certain anti-cancer compounds can cause unexpected side effects. This research could help guide an understanding of why some drugs show more promise than others, providing a new tool that can be used to identify those drugs and drug candidates.
One of the most essential and energy-consuming cellular processes is ribosome biogenesis, the formation of the cellular machines that manufacture all proteins. For cancer cells, this process is paramount. A recent study published in the journal eLife from the Stowers Institute for Medical Research screened over 1,000 existing anti-cancer drugs to assess how they impact the structure and function of the nucleolus, the ubiquitous cellular organelle where ribosomes are made.
"All cells must make proteins to function, so they have to make ribosomes, which are also protein complexes themselves," said lead author Tamara Potapova, Ph.D., a research specialist in the lab of Investigator Jennifer Gerton, Ph.D. "In cancer cells, ribosome production must be in overdrive to compensate for high proliferation rates requiring even more proteins."
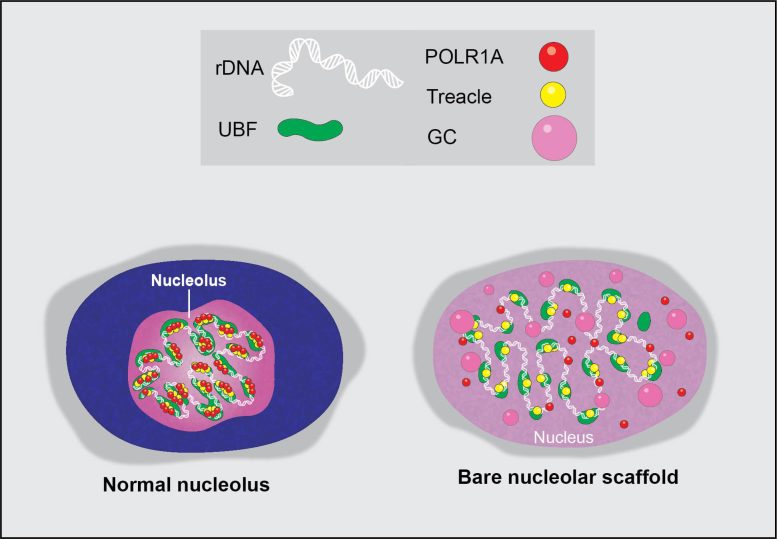
Graphical illustration of a normal nucleolus and its extreme stress state following transcriptional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibition by chemotherapy agents. Credit: Image courtesy of Mark Miller and Tamara Potapova, Stowers Institute for Medical Research
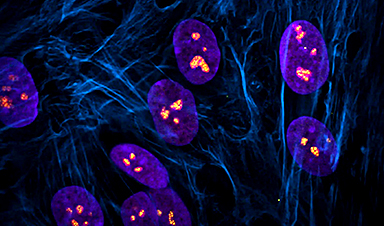
The nucleolus is a special part of the cell nucleus that houses ribosomal DNA, and where ribosomal RNA production and ribosome assembly largely takes place. Nucleoli can vary greatly in appearance, serving as visual indicators of the overall health of this process. Thus, the team found a way to capitalize on this variation and asked how chemotherapy drugs impact the nucleolus, causing nucleolar stress.
"In this study, we not only evaluated how anti-cancer drugs alter the appearance of nucleoli but also identified categories of drugs that cause distinct nucleolar shapes," said Gerton. "This enabled us to create a classification system for nucleoli based on their appearance that is a resource other researchers can use."
Because cancer's hallmark is unchecked proliferation, most existing chemotherapeutic agents are designed to slow this down. "The logic was to see whether these drugs, intentionally or unintentionally, are affecting ribosome biogenesis and to what degree," said Potapova. "Hitting ribosome biogenesis could be a double-edged sword—it would impair the viability of cancer cells while simultaneously altering protein production in normal cells."
Different drugs impact different pathways involved in cancer growth. Those that influence ribosome production can induce distinct states of nucleolar stress that manifest in easily seen morphological changes. However, nucleolar stress can be difficult to measure.
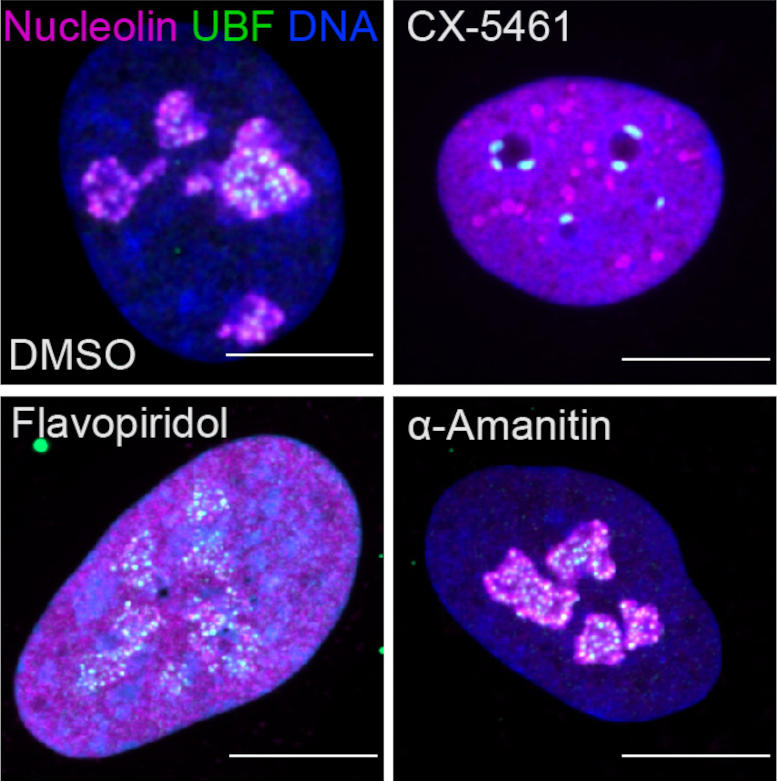
Fluorescent images showing nucleolar stress induced by drugs that inhibit transcriptional enzymes, or cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK). The upper left panel shows a normal cell with two important nucleolar proteins stained (magenta and green) and DNA (blue). The remaining panels show the impact of CDK or transcription-inhibitory drugs on nucleoli. Credit: Image courtesy of Tamara Potapova, Gerton Lab, Stowers Institute for Medical Research
"This was one of the issues that impeded this field," said Potapova. "Cells can have different numbers of nucleoli with different sizes and shapes, and it has been challenging to find a single parameter that can fully describe a "normal" nucleolus. Developing this tool, which we termed "nucleolar normality score," allowed us to measure nucleolar stress precisely, and it can be used by other labs to measure nucleolar stress in their experimental models."
Through the comprehensive screening of anti-cancer compounds on nucleolar stress, the team identified one class of enzymes in particular, cyclin-dependent kinases, whose inhibition destroys the nucleolus almost completely. Many of these inhibitors failed in clinical trials, and their detrimental impact on the nucleolus was not fully appreciated previously.
Drugs often fail in clinical trials due to excessive and unintended toxicity that can be caused by their off-target effects. This means that a molecule designed to target one pathway may also be impacting a different pathway or inhibiting an enzyme required for cellular function. In this study, the team found an effect on an entire organelle.
"I hope at a minimum this study increases awareness that some anti-cancer drugs can cause unintended disruption of the nucleolus, which can be very prominent," said Potapova. "This possibility should be considered during new drug development."
News
One Nasal Spray Could Protect Against COVID, Flu, Pneumonia, and More
A single nasal spray vaccine may one day protect against viruses, pneumonia, and even allergies. For decades, scientists have dreamed of creating a universal vaccine capable of protecting against many different pathogens. The idea [...]
New AI Model Predicts Cancer Spread With Incredible Accuracy
Scientists have developed an AI system that analyzes complex gene-expression signatures to estimate the likelihood that a tumor will spread. Why do some tumors spread throughout the body while others remain confined to their [...]
Scientists Discover DNA “Flips” That Supercharge Evolution
In Lake Malawi, hundreds of species of cichlid fish have evolved with astonishing speed, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study how biodiversity arises. Researchers have identified segments of “flipped” DNA that may allow fish to adapt rapidly [...]
Our books now available worldwide!
Online Sellers other than Amazon, Routledge, and IOPP Indigo Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artifcial Intelligence Global Health Care Equivalency In The Age Of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine And Artificial [...]
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]