A novel freeze-dissolving approach has been devised that offers greater efficiency and sustainability compared to the classic freeze-drying process to make superfine powder or nanoparticles.
In the research published in the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, sphere-shaped ice particles were formed in an aqueous mixture of NH4H2PO4 or NaHCO3 to produce their respective nanoparticles.
What is the Freeze-Drying Method?
Due to their significant specific areas and strong reactivity, nanomaterials and superfine powders are gaining popularity in fields such as sustainable and environmental applications.
Nanoparticles (NPs) and superfine powders are often produced using freeze-drying techniques. The initial stage in the freeze-drying technique is a cryogenic procedure that freezes target particles or molecules in an aqueous mixture.
In the aqueous mixture, water molecules solidify quickly via the fast-freeze stage, generating a framework of crystallized ice. This step is also referred to as ice templating or freeze-casting. The crystallized ice framework forces the targeted dissolved molecules or components to produce a nanoscale scaffolding architecture, which results in substances with nanoscale or microscale pores.
The freezing stage defines the architecture of the scaffolding and the ice template, as well as the crystal architecture of the targeted substances inside the ice templates or scaffolds, based on the freezing settings.
The second phase is a drying procedure that uses the process of sublimation to separate water as ice templates. The ice melts throughout the drying phase, but the targeted substances, particles, or molecules stay within the ice. From inside the ice, freeze-cast NPs or porous substances with identical architecture and characteristics may be retrieved.
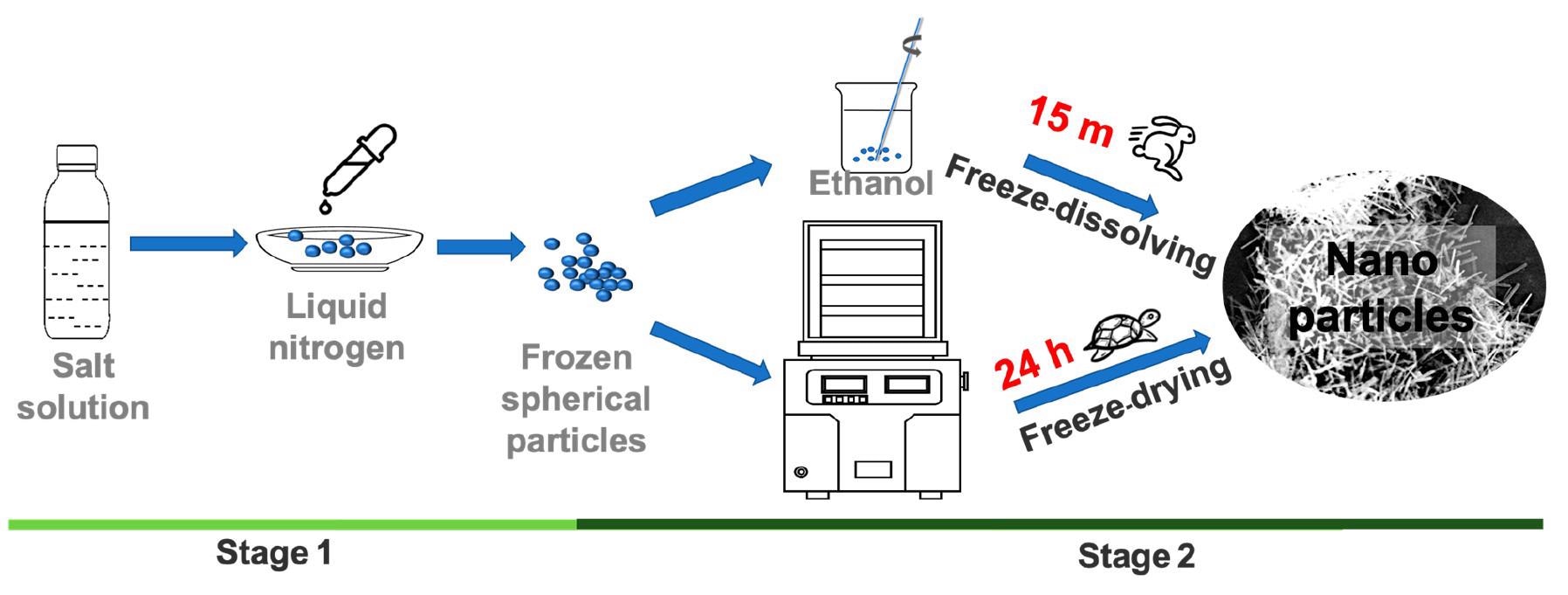
Schematic diagram of experimental setup for the freeze-dissolving method (top) and the freeze-drying method (bottom). © Yu, Q., Wang, Y., Luo, J., & Yang, H. (2022).
Limitations of Freeze-Drying
Due to the cooler temperatures employed in the drying phase, sublimation speeds are sluggish, and batch drying periods for common pharmacological items can take up to multiple days. The production speeds of such batch-based technologies are constrained by poor freeze-drying speeds and extended cycle operation durations.
Some drawbacks may be mitigated by purchasing a bigger freeze-dryer. Unfortunately, it takes much more time to establish perfect vacuum settings, and temperature and pressure are less consistent throughout the container, which could influence output quality. As a result of the cold temperatures and the vacuum arrangement, the drying phase consumes a lot of energy.
How is the Freeze-Dissolving Method Better?
The initial stage in freeze-dissolving is identical to that of freeze-drying, that is, freeze-casting to create ice containing the target components within and build an ice scaffold target architecture.
The ice is then dissolved at a cold temperature, such as a sub-zero temperature in an additional solvent having a low freezing point in the subsequent phase of the freeze-dissolving process. This additional solvent, like ethanol, acts as an antisolvent for the targeted components yet shows miscibility with water.
As a result, the ice scaffold will dissipate fast in the additional solvent, leaving just the targeted components in a solid-state in the mixture, and the architecture of the targeted components produced within the ice will be conserved.
Fire suppression chemicals, baking soda, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (NH4H2PO4), and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) are water-soluble but do not dissolve in ethanol.
In this work, various quantities of sodium bicarbonate or ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, dissolved in water, were employed to manufacture NPs via the freeze-dissolving technique, which were then evaluated against NPs produced by freeze-drying.
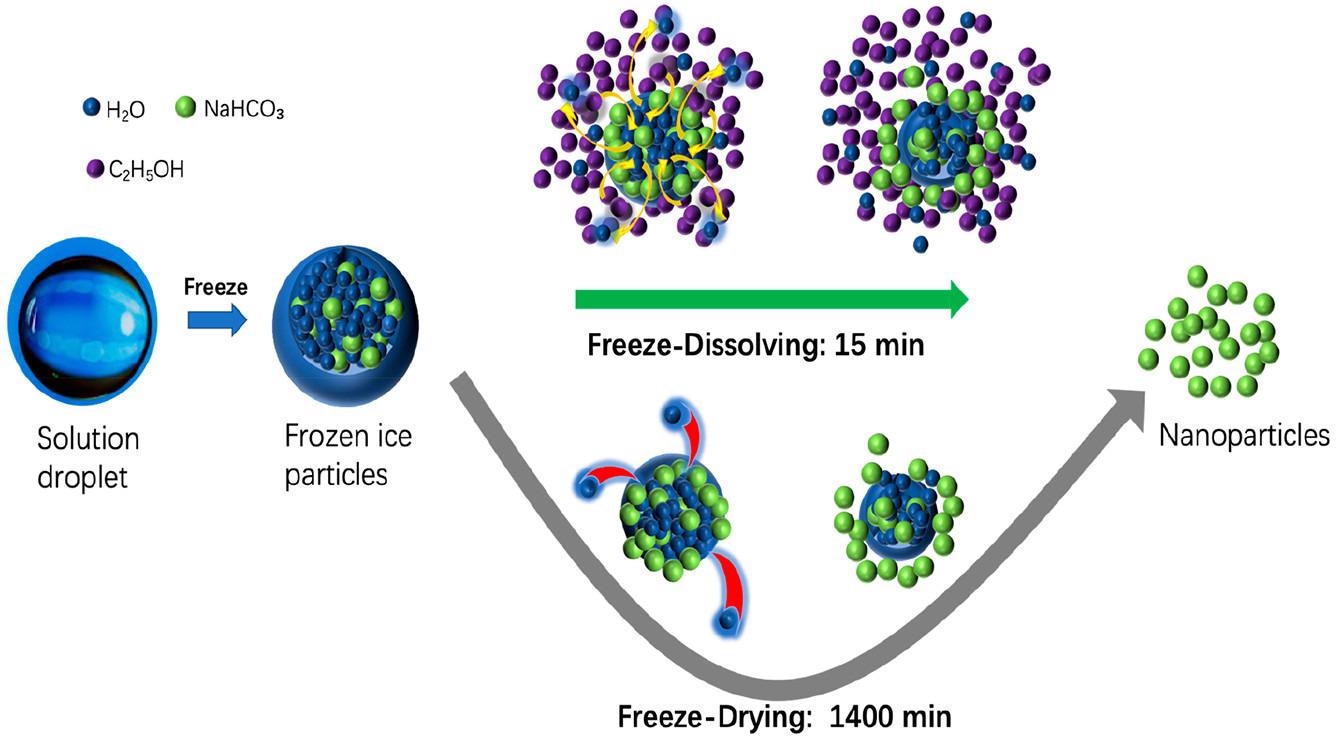
Schematic diagram of the freeze-dissolving and freeze-drying mechanisms for the formation and isolation of NaHCO3 nanoparticles. © Yu, Q., Wang, Y., Luo, J., & Yang, H. (2022).
Important Findings
To extract superfine powder and NPs from ice templates within frozen particles, the proposed freeze-dissolving process offers greater efficiency and sustainability compared to the conventional freeze-drying approach.
Particles of sodium bicarbonate and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate aqueous mixtures were quickly frozen to produce sphere-shaped ice particles, which were then filled with NPs and superfine powder of NaHCO3 or NH4H2PO4.
The frozen components were dispersed in ethanol for 5 minutes at 10 °C using the freeze-dissolving procedure to separate the ice scaffold. The freeze-drying approach, on the other hand, needed 1400 minutes to separate the ice scaffold via the process of sublimation. In identical experimental settings, the dimensions of the end products generated by the freeze-dissolving approach were comparatively small as opposed to those produced by the freeze-drying approach.
The freezing-dissolving approach reported in this study is approximately 100 times quicker and consumes roughly 100 times lesser energy as compared to the freeze-drying approach, without the need for a large facility or a vacuum. As a result, the freeze-dissolving process is likely to be used on an industrial scale with less time, energy, and footprint.
News
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]





















