A new drug, donanemab, is being hailed as a turning point in the fight against Alzheimer’s, after a global trial confirms it slows cognitive decline.
The antibody medicine helps in the early stages of the disease by clearing a protein that builds up in the brains of people with this type of dementia.
Although not a cure, charities say the results in the journal JAMA mark a new era where Alzheimer’s can be treated.
The UK’s drugs watchdog has started assessing it for possible NHS use.
The drug works in Alzheimer’s disease, not in other types of dementia, such as vascular dementia.
In the trials, it appears to have slowed the pace of the disease by about a third, allowing people to retain more of their day-to-day lives and tasks, such as making meals and enjoying a hobby.
Mike gets an infusion each month at a clinic in London and says he is “one of the luckiest people you’ll ever meet”.

Mike and his family noticed he was having problems with memory and decision-making, not long before he started on the trial.
His son, Mark, said it was very hard to watch at the beginning: “Seeing him struggle with processing information and solving problems was very hard. But I think the decline is reaching a plateau now.”
Mike, who is from Kent, said: “I feel more confident every day.”
Donanemab, made by Eli Lilly, works in the same way as lecanemab – developed by companies Eisai and Biogen – which created headlines around the world when it was proven to slow the disease.
Brain swelling was a common side-effect in up to a third of patients in the donanemab trial. For most, this resolved without causing symptoms. However, two volunteers, and possibly a third, died as a result of dangerous swelling in the brain.
Another antibody Alzheimer’s drug, called aducanumab, was recently rejected by European regulators over safety concerns and a lack of evidence that it was effective enough for patients.
What is dementia and what can be done about it?
In the donanemab trial, researchers examined 1,736 people aged 60 to 85 with early-stage Alzheimer’s.
Half of them received a monthly infusion of the treatment and the other half were given a dummy drug, also known as a placebo, over 18 months.
The findings show:
- The drug seems to have a meaningful benefit, at least for some patients
- Those who had earlier disease and less brain amyloid at baseline derived greater benefit, in terms of clearance seen on brain scans
- Those given the drug also retained more of their day-to-day lives such as being able to discuss current events, answer the phone or pursue hobbies
- The pace of the disease, judged by what people could still do day-to-day, was slowed by about 20-30% overall – and by 30-40% in a set of patients who researchers thought more likely to respond
- There were significant side-effects and patients will need to be aware of risks of treatment
- Half of patients on donanemab were able to stop the treatment after a year, because it had cleared sufficient brain deposits
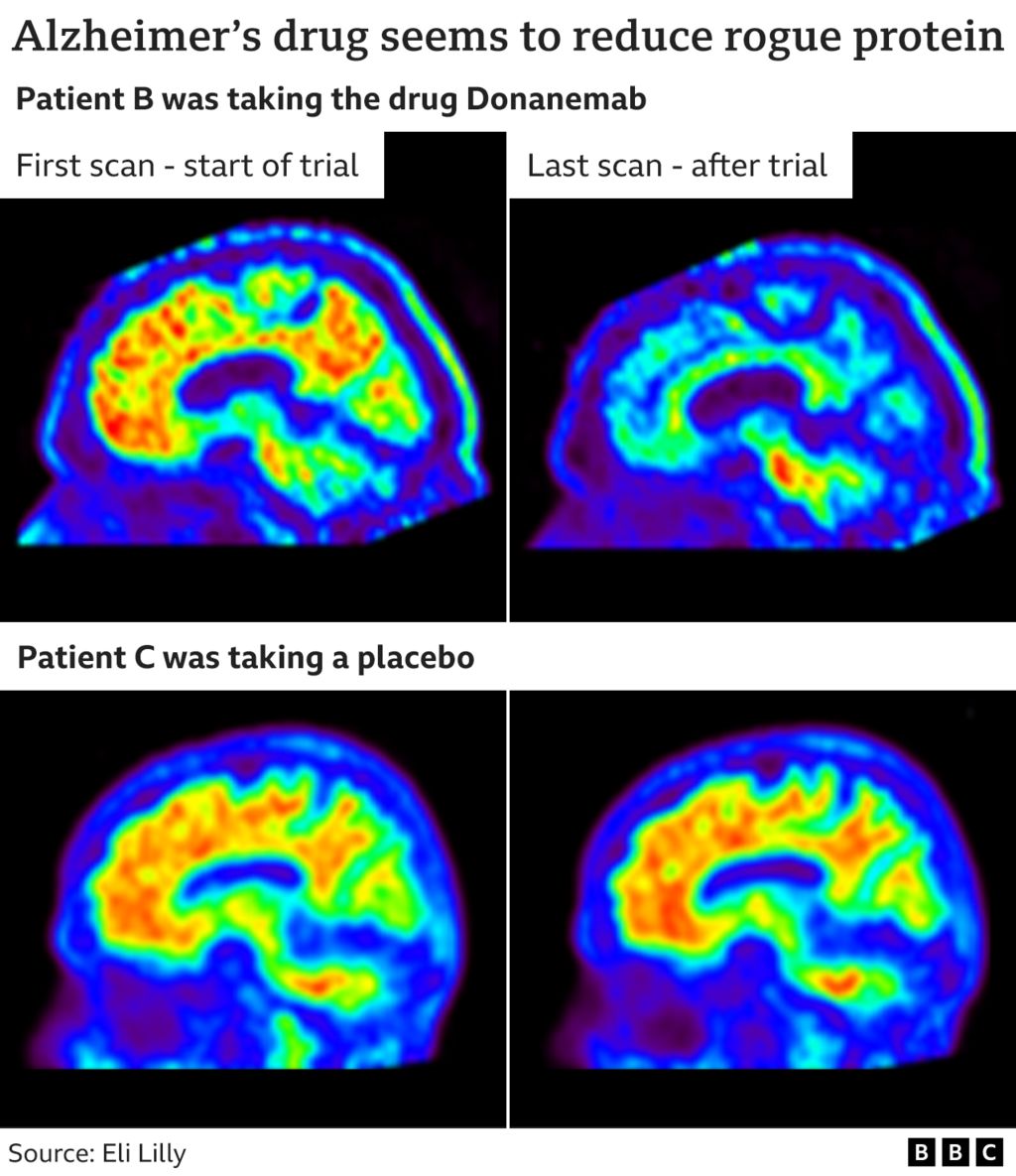
The drug’s effects may be modest, but the results provide further confirmation that removing amyloid from the brain may change the course of Alzheimer’s, and help people affected by this devastating disease if they’re treated at the right time, they say.
Prof Giles Hardingham from the UK Dementia Research Institute said: “It is terrific to see these results published in full today.
“We have waited a long time for Alzheimer’s treatments, so it’s really encouraging to see tangible progress continuing to gather pace in the field.”
Dr Susan Kohlhaas, from Alzheimer’s Research UK, said: “Today’s announcement marks another milestone.
“Thanks to decades of research, the outlook for dementia and its impact on people and society is finally changing, and we’re entering a new era where Alzheimer’s disease could become treatable.”
Speaking to BBC Radio 4’s PM programme, former Prime Minister David Cameron said resources should be put towards further research into what he called a “statin for the brain”.
“We want a pill that people who have the build-up of these proteins in the brain can take every day or every week in order to clear those proteins out of the brain and therefore reduce your chances of getting a disease that causes dementia,” he said.
Asked if the government were prepared to invest where needed to roll out new treatments, Mr Cameron said there was a real incentive to do so: “We’re a country of sixty million people, with a million people with dementia, many of them in very expensive residential care settings and so there is a lot of savings to be had from effectively treating people….I’m hopeful that our system can deliver.”
Lecanemab costs around $27,500 (£21,000) in the US, where it is licensed.
It is not clear how much donanemab may cost and how long it might take to get approval in the UK, but Alzheimer’s experts said having two drugs would help promote competition on price.
The UK’s drug’s watchdog NICE says it has already started work on its appraisal of donanemab for treating mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia caused by Alzheimer’s disease.
“Our aim is to produce recommendations on its use in the NHS as close as possible to it receiving its UK licence,” said a spokesperson.
Mike Colley turned 80 in April. At his birthday party, he surprised his family by singing My Way in front of 40 guests.
He told BBC News: “That’s the confidence I have now. I’d never have done that even 12 months ago.”
His son Mark added: “I never thought I would see my dad so full of life again. It was an incredible moment.”
Dr Emer MacSweeney, consultant neuroradiologist and medical director at Re:Cognition Health, led the trials of donanemab in the UK.
She said: “This is really significant and one of the biggest breakthroughs.”
The Alzheimer’s Society said: “This is truly a turning point in the fight against Alzheimer’s and science is proving that it is possible to slow down the disease.”
Around 720,000 people in the UK might potentially benefit from these emerging new Alzheimer’s disease treatments if they’re approved for use, but the Alzheimer’s Society said the NHS is “simply not ready to deliver them”.
Kate Lee, CEO for the charity, said: “Timely, accurate diagnosis is key, and currently only 2% of people in England and Wales receive their diagnosis through the specialist investigations needed to be eligible for these treatments.
“Alongside this, these emerging Alzheimer’s disease drugs require regular infusions and monitoring, and the NHS is not yet equipped to do this at scale.”
News
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]