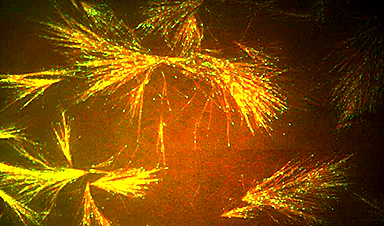
Princeton researchers have learned to harness the gossamer scaffolding that maintains the structure of living cells and used it to develop a nanotechnology platform. The technique eventually could lead to advances in soft robotics, new medicines, and the development of synthetic systems for high-precision biomolecular transport.
Inside cells, tubulin proteins form long, incredibly thin rods called microtubules. Networks of microtubules grow like tree roots into branching systems that form a primary element of the cytoskeleton, which gives cells their shape and enables them to divide.
Besides helping to maintain a cell’s shape, the microtubular scaffolding also works like a molecular railway. Specialized motor proteins carry molecular loads along the microtubule filaments. Slight changes in the microtubules’ molecular makeup act like signposts to adjust the chemical carriers’ courses, sending molecular payloads to their destinations.
At Princeton, questions about these intracellular networks led to a collaboration between Sabine Petry, an associate professor of molecular biology, and Howard Stone, a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering who specializes in fluid mechanics.
“The biological systems we were inspired by were axons,” said Meisam Zaferani, one of the lead researchers. “Axons are long protrusions coming out of a neuron that allow for directed molecular transport.”
In the nervous system, microtubule networks work both as structures connecting nerve cells and as a means for the nervous system to transmit chemical signals that produce sensation. Zaferani said scientists are still working to understand elements of microtubule growth and chemical properties. But he said the research team wanted to know if they could harness the networks for practical applications.
“Engineers and physicists have started to study microtubules as components to build novel materials and technologies,” he said. “There are many mysteries about their fundamental properties, but we know enough to start to think about how we could engineer these systems.”
With co-researcher Ryungeun Song, Zaferani worked to create a system to control the growth of microtubules in the cleanroom labs at the Princeton Materials Institute.
Using specialized equipment in micro/nanofabrication and microfluidics, the researchers precisely controlled the growth of the microtubule branches. They were able to adjust the angle and direction of growth and were able to create microstructures in which growth direction of microtubules was regulated.
Zaferani said the Materials Institute offered a unique mix of equipment and expertise that would be difficult to find anywhere else.
The researchers plan to follow up by directing chemical cargo along the microtubule branches. The goal is to build a controllable chemical transport system. In a related effort, they are also examining the use of microtubule networks as a tool like microtweezers that exert physical force on incredibly tiny objects.
Petry’s research group has long collaborated with Stone, the Donald R. Dixon ’69 and Elizabeth W. Dixon Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, at the intersection of biology and fluid dynamics. They hired Song, a mechanical engineer who had focused on microfluidics in his graduate work; and Zaferani, a biophysicist who had studied the cues that help mammalian sperm cells navigate toward an egg.
Stone, who frequently collaborates with colleagues in engineering and the natural sciences, said mixing expertise from varied disciplines often leads to remarkable results.
“I find it very interesting to find problems that involve fluid mechanics in other fields,” he said. “Often I find a topic that is poorly understood to the scientists on the other side and poorly understood by myself, and together we work to figure it out.”
More information: Meisam Zaferani et al, Building on-chip cytoskeletal circuits via branched microtubule networks, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2315992121
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
News
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]