A study forecasts that by mid-2024, bad actors are expected to increasingly utilize AI in their daily activities. The research, conducted by Neil F. Johnson and his team, involves an exploration of online communities associated with hatred. Their methodology includes searching for terminology listed in the Anti-Defamation League Hate Symbols Database, as well as identifying groups flagged by the Southern Poverty Law Center.
From an initial list of "bad-actor" communities found using these terms, the authors assess communities linked to by the bad-actor communities. The authors repeat this procedure to generate a network map of bad-actor communities—and the more mainstream online groups they link to.
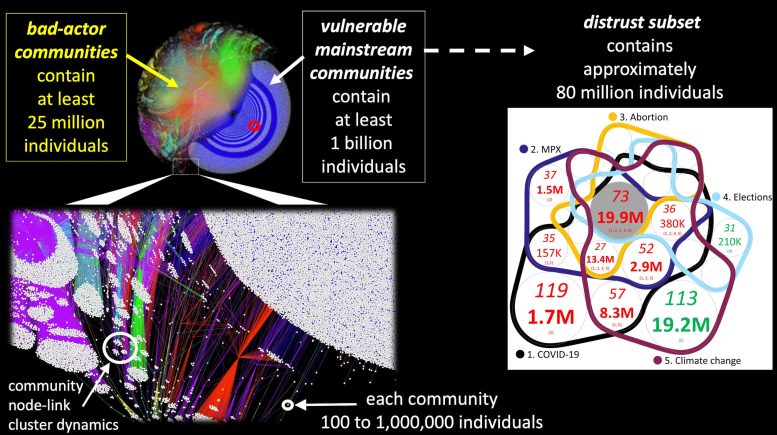
Mainstream Communities Categorized as "Distrust Subset"
Some mainstream communities are categorized as belonging to a "distrust subset" if they host significant discussion of COVID-19, MPX, abortion, elections, or climate change. Using the resulting map of the current online bad-actor "battlefield," which includes more than 1 billion individuals, the authors project how AI may be used by these bad actors.
The bad-actor–vulnerable-mainstream ecosystem (left panel). It comprises interlinked bad-actor communities (colored nodes) and vulnerable mainstream communities (white nodes, which are communities to which bad-actor communities have formed a direct link). This empirical network is shown using the ForceAtlas2 layout algorithm, which is spontaneous, hence sets of communities (nodes) appear closer together when they share more links. Different colors correspond to different platforms. Small red ring shows 2023 Texas shooter's YouTube community as illustration. Right panel shows Venn diagram of the topics discussed within the distrust subset. Each circle denotes a category of communities that discuss a specific set of topics, listed at bottom. The medium size number is the number of communities discussing that specific set of topics, and the largest number is the corresponding number of individuals, e.g. gray circle shows that 19.9M individuals (73 communities) discuss all 5 topics. Number is red if a majority are anti-vaccination; green if majority is neutral on vaccines. Only regions with > 3% of total communities are labeled. Anti-vaccination dominates. Overall, this figure shows how bad-actor-AI could quickly achieve global reach and could also grow rapidly by drawing in communities with existing distrust. Credit: Johnson et al.
The authors predict that bad actors will increasingly use AI to continuously push toxic content onto mainstream communities using early iterations of AI tools, as these programs have fewer filters designed to prevent their usage by bad actors and are freely available programs small enough to fit on a laptop.
AI-Powered Attacks Almost Daily by Mid-2024
The authors predict that such bad-actor-AI attacks will occur almost daily by mid-2024—in time to affect U.S. and other global elections. The authors emphasize that as AI is still new, their predictions are necessarily speculative, but hope that their work will nevertheless serve as a starting point for policy discussions about managing the threats of bad-actor-AI.
Reference: "Controlling bad-actor-artificial intelligence activity at scale across online battlefields" by Neil F Johnson, Richard Sear and Lucia Illari, 23 January 2024, PNAS Nexus.
DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae004
News
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]