Bird flu is transmitted mainly by wild birds, like these snow geese. The H5N1 avian influenza virus is causing the largest bird flu outbreak in history, infecting millions of birds and a growing range of mammal species. Though human infection is currently rare, efficient transmission between farmed minks in Spain raises concerns about potential human transmission. Just one or two mutations could make H5N1 more efficient at infecting humans.
Many virologists are concerned that this virus could spill over to humans and cause a new human pandemic. University of Colorado Boulder virologists Sara Sawyer, Emma Worden-Sapper and Sharon Wu summarize the compelling story of H5N1 and why scientists are closely watching the outbreak.
1. Is this virus a serious threat to humans?
H5N1 is a specific type of influenza virus, predominantly harbored by birds, that was first detected on a goose farm in China in 1996. Recently it has begun infecting an exploding diversity of bird and mammalian species around the globe.
The good news about H5N1 for humans is that it currently doesn’t spread well between people. Most people who have contracted H5N1 have gotten it directly from interacting with infected poultry – specifically chickens, turkeys, ducks and geese, which often are raised in close quarters on large commercial farms.
There are only a small handful of examples of human-to-human spread. Because H5N1 doesn’t spread well between people, and because direct infection of humans by infected birds is still relatively rare, H5N1 has not yet erupted into a human epidemic or pandemic.
2. Why is this outbreak suddenly getting so much attention?
The first reason that so much attention is being paid to bird flu right now is that currently H5N1 is causing the largest “bird pandemic” ever recorded. A certain viral variant that arose in 2020, called H5N1 2.3.4.4b, is driving this outbreak.
In agricultural poultry flocks, if a few birds test positive for H5N1, the whole flock is killed regardless of symptoms or infection status. Higher prices for eggs and poultry meat in the U.S. are one result. The Biden administration is considering vaccinating farmed poultry flocks, but the logistics could be quite complicated.
The second reason for increased attention is that H5N1 is now infecting more bird and mammalian species than ever before. The virus has been detected in a broad array of wild birds and in diverse mammals, including badgers, black bears, bobcats, coyotes, ferrets, fisher cats, foxes, leopards, opossums, pigs, skunks and sea lions.
As H5N1 infects more species, it also increases its geographical range and produces more viral variants that could have new biological properties.

Peru decreed a 90-day health emergency in December 2022 after more than 13,000 pelicans died on its beaches, possibly infected with H5N1.
The third and most worrisome reason that this virus is getting so much press is that H5N1 now seems to be transmitting well between individuals of at least one mammalian species. In late 2022, mammal-to-mammal spread occurred in Spain in farmed minks. H5N1 spread very efficiently between the minks and caused clinical signs of illness and death in the mink populations where it was detected.
Sea lions in Peru are also succumbing to H5N1 virus in massive numbers. It hasn’t been confirmed definitively whether the sea lions are spreading the virus to each other or are contracting it from birds or H5N1-infected water.
Here’s the key question: If H5N1 can achieve spread in minks and possibly sea lions, why not humans? We are also mammals. It is true that the farmed minks were confined in close quarters, like chickens on a poultry farm, so that may have contributed. But humans also live in high densities in many cities around the world, providing the virus similar tinder should a human-compatible variant arise.
The World Health Organization is closely monitoring and analyzing the spread of H5N1 in mammals.
3. What features could help H5N1 spread well in humans?
Birds experience influenza as a gastrointestinal infection and spread flu predominantly through defecating in water. By contrast, humans experience influenza as a respiratory infection and spread it by breathing and coughing.
Over the centuries, some of these avian influenza viruses have been passed from birds to humans and other mammalian species, although this is a relatively rare event.
This is because bird influenza viruses must mutate in several ways to infect mammals efficiently. The most important mutational changes affect the tissue tropism of the virus – its ability to infect a specific part of the body.
Avian flu viruses have evolved to infect cells of the intestine, while human flu viruses have evolved to infect cells of the respiratory tract. However, sometimes a flu virus can acquire mutations that allow it to infect cells in a different part of the body.
Which cells influenza infects is partially dictated by the specific receptor that it binds. Receptors are the molecules on the surface of host cells that a virus exploits to enter those cells. Once viruses are in cells, they may be able to produce copies of themselves, at which point an infection has been achieved.
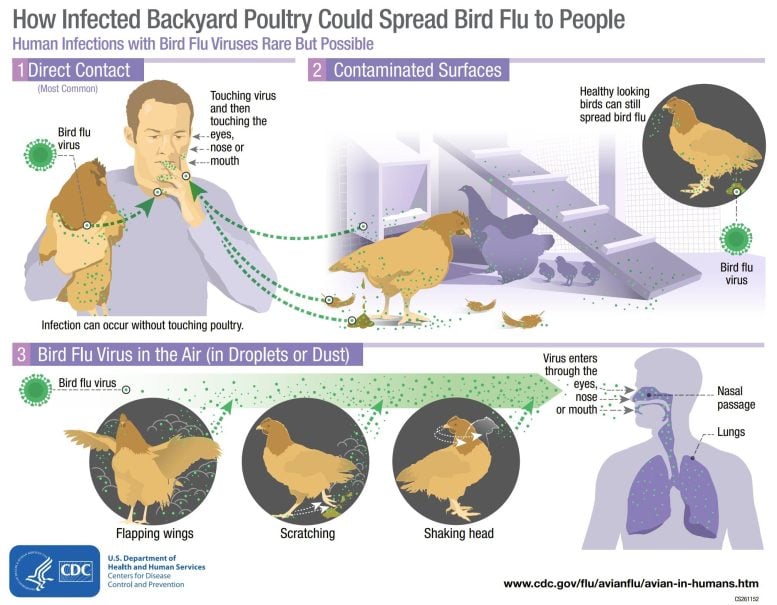
Bird flu infections in people are rare, but possible. Most reported bird flu infections in people have happened after unprotected contact with infected birds or contaminated surfaces. Credit: US CDC
This is a concern because studies have shown that only one or two mutations in the viral genome are enough to switch receptor binding from a2,3-linked sialic acid to the human a2,6-linked sialic acid. That doesn’t seem like much of a genetic obstacle.
4. Why don’t we make a vaccine just in case?
With avian influenza viruses, it is not possible to make effective human vaccines in advance, because we don’t know exactly what the genetics of the virus will be if it starts to spread well in humans. Remember that the seasonal flu vaccine must be remade every year, even though the general types of flu viruses that it protects against are the same, because the specific genetic variants that affect humans change from year to year.
Right now, the best way people can protect themselves from H5N1 is to avoid contact with infected birds. For more information about prevention, especially for people who keep domesticated birds or are bird-watching hobbyists, the Centers for Disease Control has a list of guidelines for avoiding H5N1 and other bird flu viruses.
Written by:
- Sara Sawyer, Professor of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology, University of Colorado Boulder
- Emma Worden-Sapper, PhD Student in Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology, University of Colorado Boulder
- Sharon Wu, PhD Student in Interdisciplinary Quantitative Biology and Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, University of Colorado Boulder
This article was first published in The Conversation.
News
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]





















