Human fingers and toes don’t grow outward as you might expect. Instead, our dexterous digits are ‘sculpted’ within a larger foundational bud.
Now the first human cell atlas of early limb development has at last revealed in exquisite detail exactly how that happens.
Prior to this, our understanding of vertebrate limb development has been largely based on model organisms, such as mice and chicken embryos, and lab-grown stem cells.
Although humans share some similarities with other vertebrates, their biology obviously diverges from ours.
The details of early limb formation have also been rendered a little fuzzy by technological limitations, now surpassed, and restrictions on the use of human embryos for research beyond 14 days, a rule that has been relaxed under strict ethical provisions.
The picture constructed so far had limbs initially emerging as shapeless limb buds protruding from the sides of the embryonic body. Eight weeks later, if all goes to plan, those pouches have transformed into anatomically distinct, recognizable limbs, complete with fingers and toes.
It’s a remarkable process in early embryonic development that produces arguably one of our most defining human features: our long, slender, opposable thumbs.
In 2014, scientists described how specific molecules expressed at precise moments in embryonic development moulded the formation of fingers and toes, although those predictions were based on simulations of experimental data.
Now, an international team led by cell biologist Bao Zhang at Sun Yat-sen University in China, has colored in that process in exquisite detail, by analyzing thousands of single cells from donated embryonic tissues that were between 5 and 9 weeks of development.

“We identified 67 distinct cell clusters from 125,955 captured single cells, and spatially mapped them across four first trimester timepoints to shed new light on limb development,” the team writes in their published paper.
“In doing so, we uncovered several new cell states,” they add.
“What we reveal is a highly complex and precisely regulated process,” says Hongbo Zhang, senior author and cell biologist from Sun Yat-sen University in China.
“It is like watching a sculptor at work, chiseling away at a block of marble to reveal a masterpiece. In this case, nature is the sculptor, and the result is the incredible complexity of our fingers and toes.”
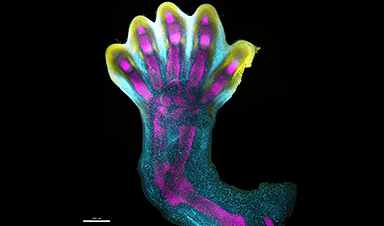
As you can see in the video below, the researchers mapped gene expression patterns to see how those genetic instructions shaped how digits formed.
From hazy beginnings, the expression of IRX1 (represented in aqua in the video below), a gene critical for digit formation, and SOX9 (represented in magenta in the video), a gene essential for skeletal development, overlap in five distinct lengths within the developing limb.
At around 7 weeks of development, programmed cell death instructions are switched on in the undifferentiated cells congregating between these lengths (associated with the expression of MSX1, represented in yellow in the video), and well-defined fingers and toes are revealed.
Like a block of marble being sculpted into a masterpiece by the expression of these genes, our fingers and toes are chiseled out from tip to base as unneeded cells recede.
Small irregularities in this process can lead to limb deformities, which 1 in 500 people are born with – making them some of the most frequently reported syndromes at birth.
The researchers also mapped the expression of genes linked with congenital conditions, such as short fingers (brachydactyly) or webbed digits (syndactyly), to get a better sense of where limb development gets off course.
“For the first time, we have been able to capture the remarkable process of limb development down to single-cell resolution in space and time,” says Sarah Teichmann, senior author and computational biologist at the Wellcome Sanger Institute.
She says creating single-cell atlases is “deepening our understanding of how anatomically complex structures form, helping us uncover the genetic and cellular processes behind healthy human development, with many implications for research and healthcare.”
Importantly, the researchers also showed that limb formation in humans and mice does follow similar trajectories, with some differences in activated genes and cell types.
The study has been published in Nature.
News
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]