This uncommon process is more frequently observed in neurodegenerative diseases and could offer insights into disease mechanisms.
According to a new study published in PLOS Biology by Kim Hai-Man Chow and colleagues from the Chinese University of Hong Kong, neurons in the brain that re-enter the cell cycle after mitosis are prone to quick senescence, a process observed more frequently in Alzheimer’s disease. This discovery provides insight into neurodegeneration and suggests that the methods used can be applied to study other unique cell populations in the brain.
Most neurons in the brain are post-mitotic, meaning they have ceased to divide. For many years, it had been assumed that this post-mitotic state was permanent. Recent discoveries have shown that a small proportion of neurons re-enter the cell cycle, but little is known about their fate after they do.
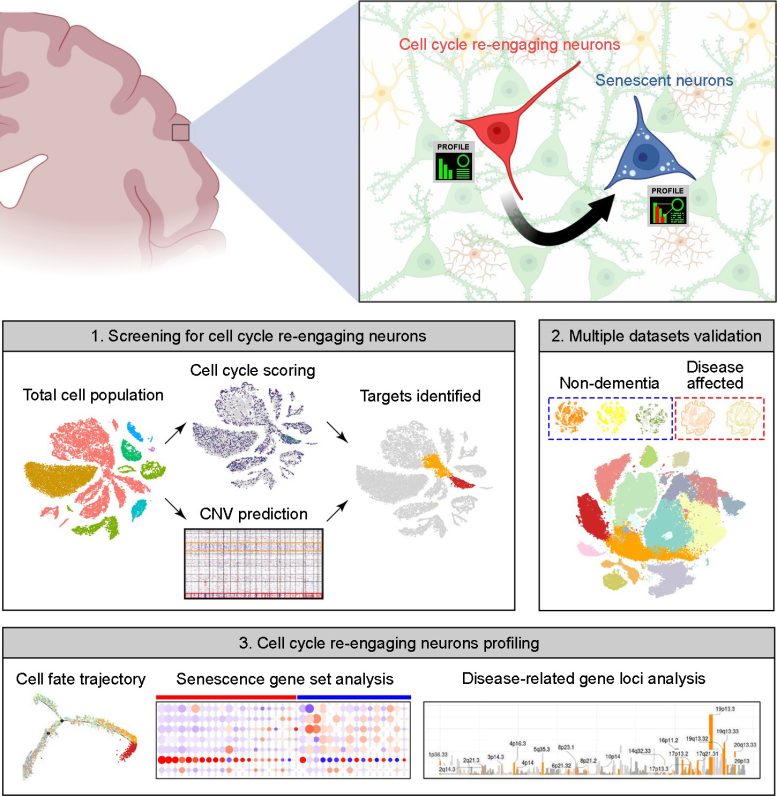
Summary image of the article. The upper part highlights neuronal cell cycle re-engagement is a stage proceeding neuronal senescence and that their full molecular profiles can now be identified by the bioinformatics pipeline we reported in the accepted manuscript. The bottom part is a simplified version of Figure 1A from the paper. The upper panel is created by the BioRender application. Credit: Kim Hei-Man Chow (CC-BY 4.0)
To address this question, the authors turned to publicly accessible databases of “snRNA-seq” data, in which individual single nuclei are isolated and their RNA is sequenced, providing a snapshot of what a cell was doing at the time of isolation. The cell cycle proceeds through distinct phases, including growth, DNA synthesis, division-specific growth, and mitosis, and each phase is characterized by a specific set of proteins required to carry it out. This allowed the authors to use the set of RNAs to tell them which phase of the cycle any specific nucleus was in.
Their data included information on over 30,000 nuclei, each of which was assigned a score based on the level of expression of a set of about 350 cell cycle-related genes. They found that small populations of excitatory neurons had indeed re-entered the cell cycle. These cells did not, for the most part, continue successfully through the cell cycle to produce daughter neurons, however. Instead, cells undergoing re-entry also had elevated expression of genes associated with senescence; in effect, the cells had reawakened only to enter senescence.
Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Intriguingly, the authors found that neurons in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients reentered the cell cycle at a higher rate, and that those neurons that had reentered the cell cycle and aged had increased expression of multiple genes associated with a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease, including those that contribute directly to the production of amyloid, the sticky protein that aggregates in the AD brain. Similarly, brains from patients with Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia had an increase in the proportion of re-entering neurons compared to healthy brains.
The neurobiological significance of this heightened re-entry for the diseased brain is still unclear, but the analytical approach taken here may offer deeper insights into neuronal subpopulations within the brain, as well as shedding light on disease mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases.
“Because of the rare existence and random localization of these cells in the brain, their molecular profiles and disease-specific heterogeneities remain unclear,” Chow said. “While experimental validations of these findings in relevant human samples will be conducted in the future, the applicability of this analytical approach in different diseases and cross-species settings offers new opportunities and insights to supplement mainstay histological-based approaches in studying the roles of these cells in brain aging and disease pathogenesis.”
The authors add, “This bioinformatics analytical pipeline demonstrated will offer the field a new tool to unbiasedly dissect cell cycle re-engaging and senescent neurons, and to dissect their heterogeneities in healthy versus disease-affected brains.”
Reference: “Neuronal cell cycle reentry events in the aging brain are more prevalent in neurodegeneration and lead to cellular senescence” by Deng Wu, Jacquelyne Ka-Li Sun and Kim Hei-Man Chow, 23 April 2024, PLOS Biology.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002559
The work was supported, in part, by grants from the following: The Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC)-General Research Fund (GRF) (PI: ECS24107121, GRF16100219 and GRF16100718) (all to K.H-M.C) and the RGC- Collaborative Research Fund (CRF) (Co-I: C4033-19EF) (K.H-M.C); the National NaturalScience Foundation-Excellent Young Scientists Fund 2020 (Ref: 32022087) (K.H-M.C); Alzheimer’s Association Research Fellowship (PI: AARF-17-531566) (K.H-M.C).
News
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]