Japanese scientists detected all five nucleobases — building blocks of DNA and RNA — in samples returned from asteroid Bennu by NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission.
NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission brought back 121.6 grams of asteroid Bennu, unveiling nitrogen-rich organic matter, including DNA's essential bases. Scientists found differences between Bennu's chemistry and that of meteorites like Ryugu, suggesting diverse cosmic conditions shaped their molecular makeup.
Asteroids: Ancient Messengers of Life?
Asteroids, small rocky bodies in the inner Solar System, may have played a key role in delivering water and essential chemical ingredients for life to early Earth. While meteorites that fall to Earth come from asteroids, their exposure to the atmosphere and biological contamination makes them difficult to study. The best way to analyze asteroid material is by collecting pristine samples directly from space. So far, only two countries have successfully done this: Japan, with its Hayabusa and Hayabusa2 missions, and the United States, with OSIRIS-REx.
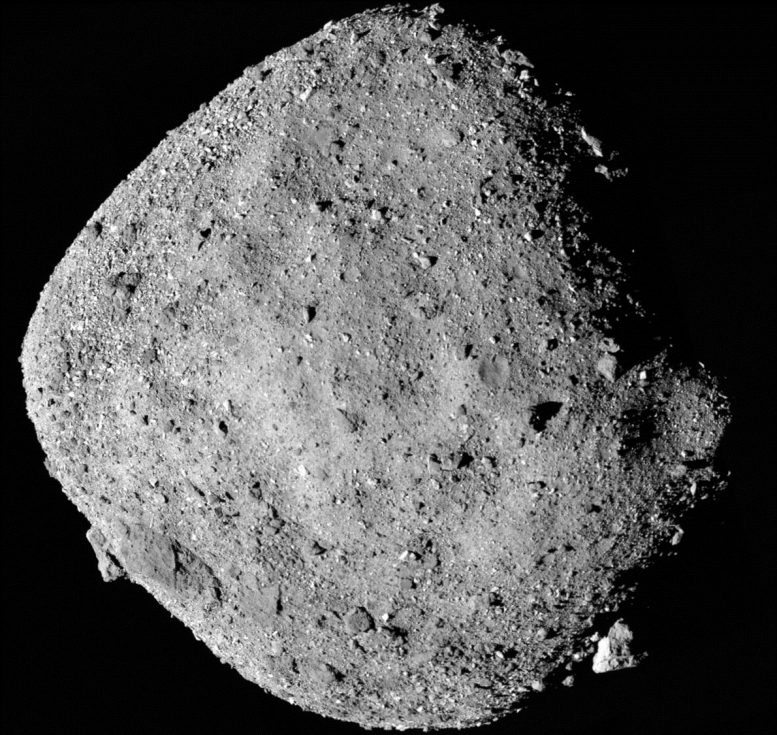

NASA's OSIRIS-REx Brings Bennu to Earth
In September 2023, NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission returned 121.6 grams of material from asteroid Bennu, the largest asteroid sample ever brought to Earth. Now, an international research team led by Dr. Daniel Glavin and Dr. Jason Dworkin at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center has made a groundbreaking discovery: ammonia and nitrogen-rich organic compounds in the Bennu samples.
Their findings, published today (January 29) in Nature Astronomy, add weight to the theory that asteroids may have helped kick-start life on Earth. Notably, Japanese researchers on the team detected all five nitrogenous bases — key molecules needed to form DNA and RNA — inside the asteroid sample, a discovery that strengthens the idea that life's building blocks may have originated in space.
The Bennu samples from NASA were handled under nitrogen to prevent contamination by Earth's atmosphere. A 17.75 mg sample was processed and analyzed for N-heterocycles—organic molecules with a ring structure containing carbon and nitrogen—using high-resolution mass spectrometry at Kyushu University.
The analysis was carried out by a research team, whose members are part of the OSIRIS-REx sample analysis team, consisting of Associate Professor Yasuhiro Oba of Hokkaido University, Principal Researcher Yoshinori Takano of JAMSTEC and Keio University, Dr. Toshiki Koga of JAMSTEC, Professor Hiroshi Naraoka of Kyushu University, and Associate Professor Yoshihiro Furukawa of Tohoku University.
The analysis revealed that the concentration of N-heterocycles is approximately 5 nmol/g, 5-10 times higher than that reported from Ryugu. In addition to the five nitrogenous bases — adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil — required for building DNA and RNA, the researchers also found xanthine, hypoxanthine, and nicotinic acid (vitamin B3).
"In previous research, uracil and nicotinic acid were detected in the samples from asteroid Ryugu, but the other four nucleobases were absent. The difference in abundance and complexity of N-heterocycles between Bennu and Ryugu could reflect the differences in the environment to which these asteroids have been exposed in space," Koga explains.

Clues from Other Space Rocks
Samples from the meteorites Murchison and Orgueil were also processed and analyzed previously under identical conditions for comparison. The research team observed that the ratio of purines (adenine and guanine) to pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil) was much lower in the Bennu samples compared to both Murchison and Orgueil.
"There are multiple possible reasons for this observed difference," Oba says. "They may be due to differences in parent bodies or formation pathways, or the Bennu asteroid was exposed to a cold molecular cloud environment where pyrimidine formation is more likely to occur."
"Our findings, which contribute to the larger picture painted by all the authors of the paper, indicate that nucleobase chemistry in the Bennu samples must be further studied," concluded Naraoka. Another important result of this study is that, by comparing meteorites with Bennu samples, a reference for the reanalysis of other meteorites in collections across the globe has been created.

Reference: "Abundant ammonia and nitrogen-rich soluble organic matter in samples from asteroid (101955) Bennu" by Daniel P. Glavin, Jason P. Dworkin, Conel M. O'D. Alexander, José C. Aponte, Allison A. Baczynski, Jessica J. Barnes, Hans A. Bechtel, Eve L. Berger, Aaron S. Burton, Paola Caselli, Angela H. Chung, Simon J. Clemett, George D. Cody, Gerardo Dominguez, Jamie E. Elsila, Kendra K. Farnsworth, Dionysis I. Foustoukos, Katherine H. Freeman, Yoshihiro Furukawa, Zack Gainsforth, Heather V. Graham, Tommaso Grassi, Barbara Michela Giuliano, Victoria E. Hamilton, Pierre Haenecour, Philipp R. Heck, Amy E. Hofmann, Christopher H. House, Yongsong Huang, Hannah H. Kaplan, Lindsay P. Keller, Bumsoo Kim, Toshiki Koga, Michael Liss, Hannah L. McLain, Matthew A. Marcus, Mila Matney, Timothy J. McCoy, Ophélie M. McIntosh, Angel Mojarro, Hiroshi Naraoka, Ann N. Nguyen, Michel Nuevo, Joseph A. Nuth III, Yasuhiro Oba, Eric T. Parker, Tanya S. Peretyazhko, Scott A. Sandford, Ewerton Santos, Philippe Schmitt-Kopplin, Frederic Seguin, Danielle N. Simkus, Anique Shahid, Yoshinori Takano, Kathie L. Thomas-Keprta, Havishk Tripathi, Gabriella Weiss, Yuke Zheng, Nicole G. Lunning, Kevin Righter, Harold C. Connolly Jr. and Dante S. Lauretta, 29 January 2025, Nature Astronomy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02472-9
News
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]





















