The impact of different kinds of commercial metallic nanoparticles (nanosized zero valent iron (nZVI), bimetal nZVI-Pd, and nano-magnetite (nFe3O4)) for the recovery of soil co-contaminated with Cr and PCBs are evaluated in a recent article published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The implementation of restoration solutions for soil degraded with a combination of pollutants (metal(loid)s and chemical products) has rarely been studied. The results suggest that the introduction of nZVI or nZVI-Pd, as well as pseudo-anaerobic settings, may well be employed to restore Cr and PCB-contaminated soil.
Soil Contamination Due to Chromium
Soil contamination is a global problem. It degrades the ecological functions supplied by the soil, reduces agricultural production, and has a negative influence on human health.
The bulk of contaminants come from man-made sources such as commercial activities, quarrying, public transit, and sewer waste treatment on soil.
The primary pollutants detected in European soils are metals and metalloids. As environmental pollutants, they are non-biodegradable and hence linger for long durations.
Due to its highly anti-corrosive characteristics, chromium (Cr) is extensively employed in a variety of industrial applications. Metallurgical operations, tanneries, wood processing, galvanizing, and petrochemical industries are just a few examples.
Cr (III), which presents as impermeable oxide and hydroxide cations, and Cr (VI), which emerges as oxyanion, are by far the most frequent types of Cr found as soil minerals.
Cr (III) is rejected by the electrostatic repulsion of soil and so stays in soil solution, accessible to crops and other creatures. As a result of its high mobility and bioavailability, Cr (VI) is 1000 times more hazardous than Cr (III).
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): A Major Soil Pollutant
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs), like metallic materials, are biological chemical compounds that are permanent, extremely poisonous, and micropollutants, posing a concern to the ecosystem.
PCBs are a class of synthetic organic chemicals classified as POPs by the Stockholm Convention of 2001 owing to their high public health hazard and breakdown resilience. PCBs may be created inadvertently as by-products in a variety of biochemical procedures that use chlorine and hydrocarbons.
PCBs have been linked to spillage from power equipment, waste distribution to soil, garbage furnace fumes, leaks during transportation, evaporation and sedimentation from surface waterways, and leakage from improper treatment and disposal.
Use of Nanoparticles for Soil Remediation
Compared to conventional physio-chemical approaches, nanoscience has recently allowed the development of new cost-effective and ecologically sound restoration solutions.
The increased particular surface area of nanoparticles leads to faster reaction kinetics with contaminants. Many distinct nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes, inorganic materials, and activated carbons, have been explored for cleanup purposes, but nano zero valent iron (nZVI) particulates are the most extensively deployed.
The application of magnetized nanomaterials, such as nano magnetite (nFe3O4), for the rehabilitation of metal(loid) contaminated streams has gained popularity in recent decades. This is because of their higher absorption capabilities and magnetic characteristics, which allow for better membrane separation from the solid material.
The major goal of this research was to compare the efficacy of three kinds of commercial magnetite nanoparticles (nZVI, nZVI-Pd, and nFe3O4) for the restoration of industrialized soil polluted with Cr and PCBs.
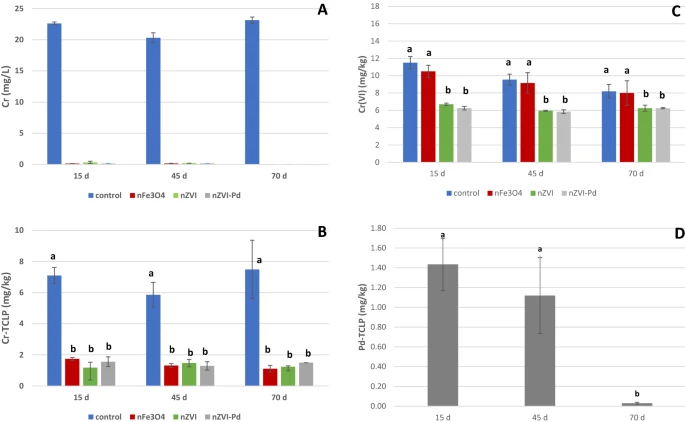
(A) Mean concentration of Cr (mg/L) in the aqueous extracts at the different sampling times. (B) Mean concentration of Cr (mg/kg) in TCLP extracts at the different sampling times. (C) Mean concentration of Cr(VI) (mg/kg) in soil samples at the different sampling times. For each sampling time, bars with the same letter do not differ significantly (p < 0.05). (D) Mean concentration of Pd (mg/kg) in TCLP extracts at the different sampling times for nZVI-Pd treated soils. Bars with the same letter do not differ significantly (p < 0.05). © Gil-Díaz, M., Pérez, R., Alonso, J., Miguel, E., Diez-Pascual, S. and Lobo, M., (2022)
Research Findings and Conclusion
When nZVI, nZVI-Pd, or nFe3O4 were added to soil polluted with Cr and PCBs, the leakage of Cr in the soil was greatly decreased, and the immobilization remained stable over a period of 70 days under the simulated conditions.
When contrasted to nFe3O4, Te nZVI and nZVI-Pd were more successful in converting Cr (VI) to Cr (III). The PCB levels in soils sprayed with the three kinds of iron nanoparticles fell considerably after 15 days of engagement between soil and nanoparticles.
Control soils demonstrated a drop in PCBs content during the 45-day sample period due to environmental remediation, reaching levels comparable to those seen in soil amended with nZVI and nZVI-Pd. In this case, biodegradation might be possible if the soil was just poisoned with PCBs, but not if it also included metals like Cr.
Tus, nZVI-based nanoparticles show modest performance in PCB-polluted soil cleanup. Both nZVI particles, on the other hand, achieved effective Cr absorption in soils.
The findings show that the introduction of nZVI or nZVI-Pd, as well as pseudo-anaerobic settings, might be employed to recover Cr and PCB-contaminated soils.
News
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]