| A research team headed by chemist Prof Bart Jan Ravoo and biochemist Prof Volker Gerke has designed nanocontainers made of sugar and protein components. These containers are taken up by cells through natural processes and can thereby transport substances that normally cannot penetrate the cell membrane – such as drugs or labelled substances for the investigation of cell functions – into cells. | |
| The study was published in Advanced Science (“Biodegradable and Dual-Responsive Polypeptide-Shelled Cyclodextrin-Containers for Intracellular Delivery of Membrane-Impermeable Cargo”). | |
 |
|
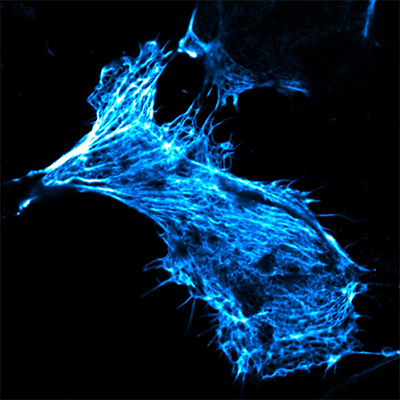
| Living human cancer cell in cell culture, its actin skeleton stained with fluorescent phalloidin. This toxic substance was only able to enter the cell by means of the newly developed nanocontainers. (Image: Kudruk & Pottanam Chali et al./Adv Sci 2021 (modified colours)) | |
| Nanocontainers can transport substances into cells where they can then take effect. This is the method used in, for example, the mRNA vaccines currently being employed against Covid-19 as well as certain cancer drugs. In research, similar transporters can also be used to deliver labelled substances into cells in order to study basic cellular functions. | |
| To take advantage of their full potential, scientists are conducting intensive research into how nanocontainers interact with biological environments and how they have to be chemically constructed to deliver cargo into cells in the gentlest and most controllable way possible. | |
| Scientists at the University of Münster have recently developed a new type of nanocontainer that is constructed entirely from biological components. Unlike other cargo transporters, these are not based on lipids but on sugar compounds which are sealed with a shell of protein structures – so-called polypeptides – the thickness of which is precisely tailored. | |
| “We do produce the components of our nanocontainers synthetically, but they are taken up by cells and – due to the overall structure we have developed – also degraded by them just like naturally occurring substances,” explains chemist Prof Bart Jan Ravoo. | |
| “For the degradation of the container shell inside the cell, we make use of two naturally occurring mechanisms – as a result, the transported substances are released rapidly, as soon as they arrive in the cell,” adds biochemist Prof Volker Gerke. | |
| The scientists want to use the tiny nanocontainers, which are about 150 nanometers in diameter, to load cells with labelled biologically relevant lipids that can be used to study transport processes occurring within the cell membrane. In addition, they plan to further develop the chemical design of the containers in such a way that they are, for example, only taken up by certain types of cells or only release their cargo when stimulated by external light. | |
| In the future, transport systems built from sugar and protein components might also be suitable for applications in living organisms to deliver drugs specifically into certain tissues and cells. | |
| Details on methods and results: | |
Bioinspired materials organize themselves, forming cargo-carrying containers |
|
| To synthesize the new cargo transporters, the scientists used sugar compounds (modified cyclodextrins) that are similar in structure – and thus behaviour – to certain lipids naturally found in every cell. Similar to the protective cell membrane lipids, the sugar structures arrange themselves, forming a shell in which they enclose the substances to be transported. However, because the resulting container is still leaky and would lose its cargo over time, the scientists added protein structures (polypeptides) that form a sealing layer around the container. | |
| “To test how thick the sealing layer needed to be, we varied the length of the peptide sequences and tailored them so that the containers stably encapsulated their cargo,” explains Sharafudheen Pottanam Chali, a chemistry doctoral student and one of the study’s two lead authors. | |
Nanocontainers that use a natural pathway into cells |
|
| In the next step, the scientists investigated whether and how the newly developed nanocontainers were taken up by cells. Their hypothesis was that this happens via so-called endocytosis. In this process, the cells internalize a part of their cell membrane and pinch it off, creating small vesicles called endosomes in which extracellular material is transported into the cell. To test this, the scientists used a sugar compound (dextran) known to be taken up by endocytosis. They treated their cell cultures with red fluorescent dextran and, at the same time, added nanocontainers filled with a green fluorescent cargo (pyranine). | |
| “In the fluorescence microscope, it became visible that both substances were taken up into the cells equally and their fluorescence overlapped visibly – therefore we could conclude that the nanocontainers, just like the dextran, were efficiently taken up by the cells through the endosomal transport process,” explains Sergej Kudruk, a biochemistry doctoral student and also a lead author of the study. | |
| The scientists confirmed this for two different cell types – human blood vessel cells and cancer cells. | |
Container shell is degraded by enzymes in the cells’ endosomes |
|
| Conditions inside the endosomes differ from those of the cellular environment, something which the scientists already were considering when designing their nanocontainers. They constructed the containers in such a way that the altered environment in the endosomes destabilizes and partially degrades the polypeptide shell – the nanocontainers thus become leaky and release their cargo into the inside of the cell. | |
| “When the containers are taken up into endosomes, two types of enzymes, which we knew to be present in endosomes and which can contribute to the degradation of the shell at specific sites, come into play,” explains Sergej Kudruk. | |
| “So-called reductases degrade the disulfide bridges that were previously established to crosslink the peptide molecules of our nanocontainers – in addition, peptidases cleave the peptide molecules themselves,” adds Sharafudheen Pottanam Chali. | |
| The scientists also tested the degradability of the container shell outside the cell. To do so, they loaded the containers with a fluorescent dye and simulated part of the complex endosomal microenvironment by using the enzyme trypsin as well as reducing agents. After treatment, the dye leaked out immediately. |
News
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]






















