A study reveals that a protein called RPA is essential for maintaining chromosome stability by stimulating telomerase.
New findings from the University of Wisconsin-Madison suggest that problems with a key protein that helps preserve chromosome stability may contribute to the development of severe, and sometimes fatal, diseases.
The study, published in Science, offers new clues for identifying mutations in this protein that could help doctors screen for certain cancers and disorders affecting bone marrow.
Chromosomes (bundles of proteins and DNA that hold our genetic blueprint) are shielded from damage by telomeres, the protective caps made of repeating DNA sequences and proteins at each chromosome's end. Although telomeres naturally shorten as we age, disruptions in how they are formed or maintained can destabilize DNA, potentially triggering premature aging and disease.
Researchers in the laboratory of Ci Ji Lim, a biochemistry professor at UW–Madison, worked with colleagues in the university's Department of Chemistry to search for proteins that interact with telomerase, the enzyme that maintains telomeres. They suspected that defects in these associated proteins might contribute to certain illnesses that arise when telomeres become abnormally short.
"This line of research goes beyond a biochemical understanding of a molecular process. It deepens clinical understanding of telomere diseases," says Lim, whose work is supported by the National Institutes of Health.
Discovering RPA's Hidden Role
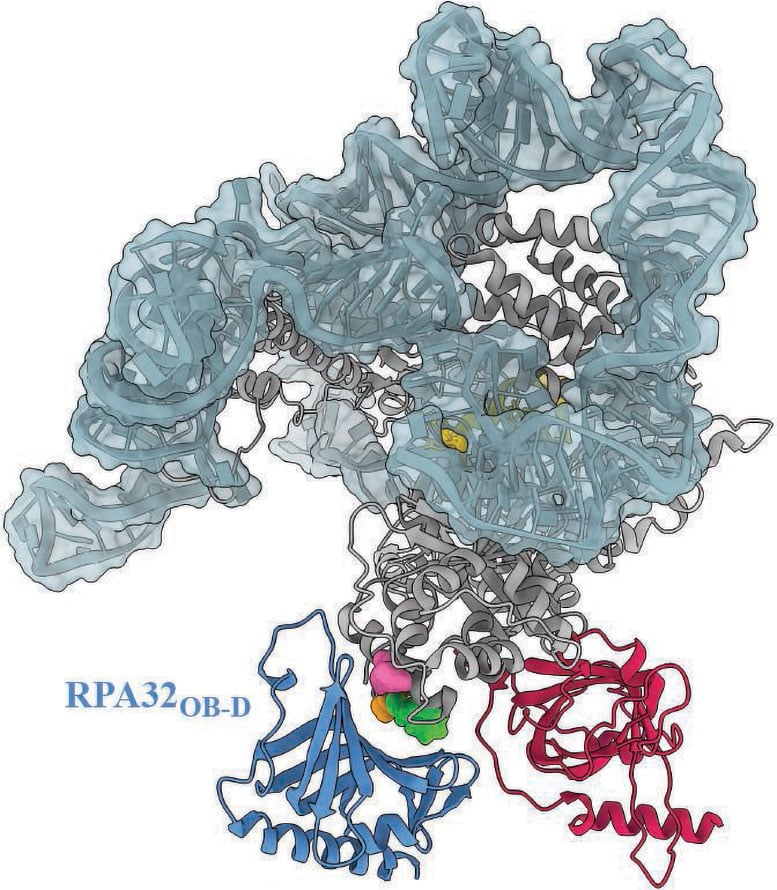
The researchers, led by graduate student Sourav Agrawal, research scientist Xiuhua Lin, and postdoctoral researcher Vivek Susvirkar, searched for proteins likely to interact with telomerase using AlphaFold, a machine learning tool that predicts the 3D structure of proteins and protein-protein interactions. They found that a molecule called replication protein A (RPA) plays an essential role in maintaining telomeres by stimulating telomerase. RPA's role in DNA replication and repair has long been understood, but its role in maintaining long, healthy telomeres in humans was previously unconfirmed. Guided by their findings from AlphaFold, the team experimentally validated that, in humans, RPA is required to stimulate telomerase and help maintain telomeres.
Their findings, Lim says, have immediate implications for some patients with often fatal illnesses resulting from shortened telomeres, including aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia.
"There are some patients with shortened telomere disorders that couldn't be explained with our previous body of knowledge," explains Lim. "Now we have an answer to the underlying cause of some of these short telomere disease mutations: it is a result of RPA not being able to stimulate telomerase."
A Global Impact and Future Testing
Lim and his team have received inquiries from clinicians and scientists around the world asking if their patients' diseases could be the result of genetic mutations inhibiting RPA's newfound function.
"There are colleagues reaching out from France, Israel, and Australia. They just want to give a cause for their patients' short telomere disease so that the patients and their families can understand what is happening and why," says Lim. "With biochemical analysis, we can test their patients' mutation to see if it impacts how RPA interacts with telomerase, and give the doctors insights into possible causes of their patients' diseases."
Reference: "Human RPA is an essential telomerase processivity factor for maintaining telomeres" by Sourav Agrawal, Xiuhua Lin, Vivek Susvirkar, Michael S. O'Connor, Bianca L. Chavez, Victoria R. Tholkes, Grace P. Tauber, Qixiang He, Kaitlyn M. Abe, Xuhui Huang and Ci Ji Lim, 30 October 2025, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.ads5297
This research was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health (R01GM153806 and DP2GM150023), the UW–Madison Office of the Vice Chancellor for Research, the Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation and UW–Madison Department of Biochemistry.
News
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]