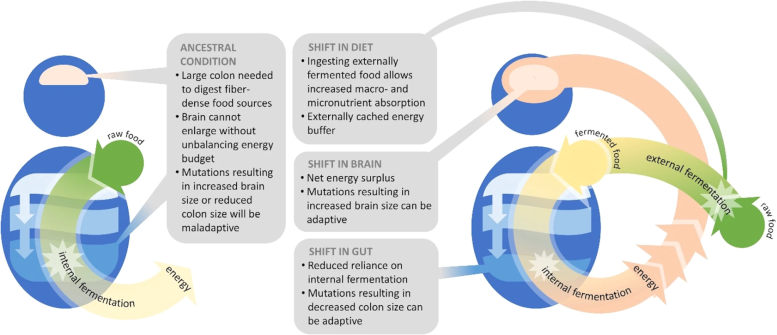
The study hypothesizes that 'pre-digested' foods contributed to the development of larger brains.
The large, capable human brain is a marvel of evolution, but how it evolved from a smaller primate brain into the creative, complex organ of today is a mystery. Scientists can pinpoint when our evolutionary ancestors evolved larger brains, which roughly tripled in size as human ancestors evolved from the bipedal primates known as Australopithecines.
But why it happened when it did – what spurred that change – has remained elusive. While some have theorized that the use of fire, and the subsequent invention of cooking, gave our ancestors enough nourishment for our larger-brained ancestors to become dominant, a new theory points to a different spark: fermentation.
The Role of Diet in Brain Evolution
The key to understanding how our brains grew is most likely rooted in what – and how – we eat, said Erin Hecht, one of the authors of the study which was recently published in Nature Communications Biology.
"Brain tissue is metabolically expensive," said the Human Evolutionary Biology assistant professor. "It requires a lot of calories to keep it running, and in most animals, having enough energy just to survive is a constant problem." For larger-brained Australopiths to survive, therefore, something must have changed in their diet. Theories put forward have included changes in what these human ancestors consumed or, most popularly, that the discovery of cooking allowed them to garner more usable calories from whatever they ate.
But the problem with this theory is that the earliest evidence places the use of fire at approximately 1.5 million years ago – significantly later than the development of the hominid brain. "Our ancestors' cranial capacity began increasing 2.5 million years ago, which conservatively gives us about a 1-million-year gap in the timeline between brain size increasing and the possible emergence of cooking technology," explained Katherine L. Bryant, one of the paper's co-authors and currently a researcher at the Institute for Language, Communication, and the Brain at Aix-Marseille Université in France. "Some other dietary change must have been releasing metabolic constraints on brain size, and fermentation seems like it could fit the bill."
Added Hecht: "Whatever changed in their diets had to have happened before brains started getting bigger."
Fermentation: A New Perspective on Brain Growth
She continued, noting that during the last few years, researchers have postulated other options, such as the consumption of rotting meat. In this new paper, Hecht and her team offer a different hypothesis: that cached (or saved) food fermented, and that this "pre-digested" food provided a more accessible form of nourishment, fueling that bigger brain and allowing our larger-brained ancestors to survive and thrive through natural selection.
The shift was probably a happy accident. "This was not necessarily an intentional endeavor," Hecht posited. "It may have been an accidental side effect of caching food. And maybe, over time, traditions or superstitions could have led to practices that promoted fermentation or made fermentation more stable or more reliable."
This hypothesis is supported by the fact that the human large intestine is proportionally smaller than that of other primates, suggesting that we adapted to food that was already broken down by the chemical process of fermentation. In addition, fermented foods are found in all cultures and across food groups, from Europe's wine and cheese to Asia's soy sauce and natto, or soybeans.
Hecht suggested that an additional study of brain responses to fermented and non-fermented foods might be useful, as might one of olfactory and taste receptors, perhaps using ancient DNA. For the evolutionary biologist, these are all fertile areas for other researchers to pick up on. (Hecht's focus is more on "how brain circuits have evolved to support complex behaviors" with research on both living humans and dogs.)
As research progresses, Bryant sees possibilities for a wide range of benefits. "This hypothesis also gives us as scientists even more reasons to explore the role of fermented foods on human health and the maintenance of a healthy gut microbiome," she said. "There have been a number of studies in recent years linking gut microbiome to not only physical but mental health."
Reference: "Fermentation technology as a driver of human brain expansion" by Katherine L. Bryant, Christi Hansen and Erin E. Hecht, 23 November 2023, Communications Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-05517-3
News
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]