Doxorubicin (DOX) is a powerful anti-cancer medication, and efforts have been made to design nanostructures for delivering it to cancerous cells. The nanostructures increase the cytotoxic effects of DOX on cancerous cells, while reducing the negative effects on healthy cells.
In a research paper published in the journal Scientific Reports, layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanostructures were developed to administer DOX effectively.
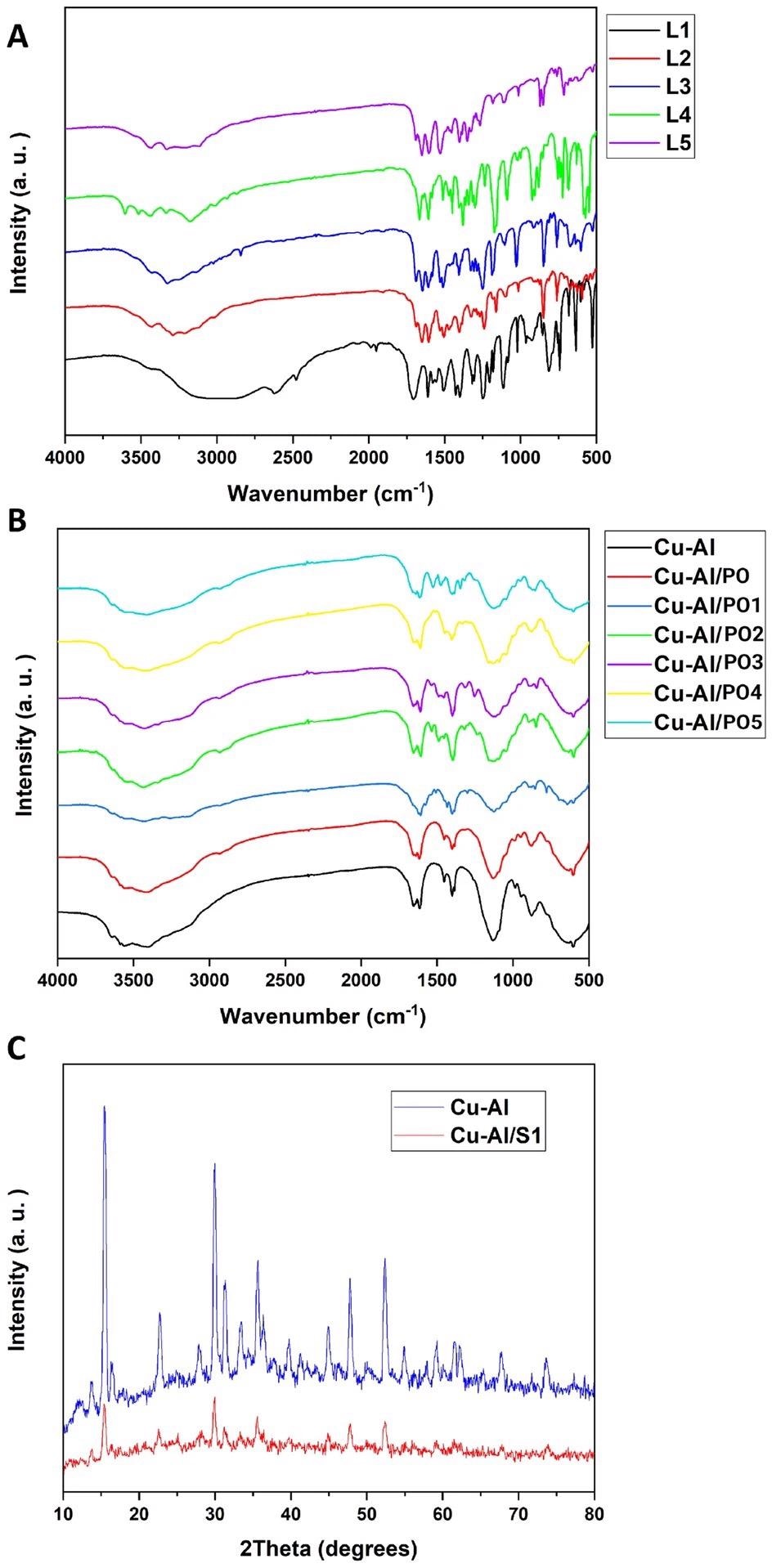
Figure 1. FTIR spectra of the synthesized nanomaterials (A,B). XRD results of the synthesized nanomaterials (C). S1 in part (C) stands for one of the PO’s. © Kiani, M., Bagherzadeh, M., Ghadiri, A. M., Makvandi, P., & Rabiee, N. (2022).
Cancer, and How Nanotechnology Can Help
Cancer accounts for the second-largest mortality rate after cardiac illnesses, with susceptibility to tumor development determined by multiple factors like age, family history and carcinogen exposure.
Chemotherapy is the most often used cancer treatment. However, complex encounters in the cancer microenvironment, as well as cancer cells’ capacity to proliferate and flip between molecular routes to guarantee their preservation, have led to the tumors developing resistance against treatments.
Doxorubicin (DOX) is widely used in tumor treatment because it may limit DNA replication by decreasing the action of topoisomerase enzymes, suppressing cell cycle progress and ultimately directing tumors towards cellular death.
Resistance against DOX has been caused by a range of factors, including discharge of doxorubicin by P-glycoprotein from tumor cells, Bcl-2 overexpression, apoptotic suppression, and abnormal expression of epigenetic and genetic variables. As a result, research has concentrated on developing nanostructured delivery mechanisms for doxorubicin to increase its cancer-suppressing effectiveness.
Benefits of LDH as Drug Deliver Systems
Nanotechnology offers fresh promise for reducing resistance against treatments and improving the efficacy of chemotherapy drugs in cancer treatment.
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) are multilayer nanoscale structures and anion clays having a hydrotalcite crystalline structure generated by two metallic ions, comprising a trivalent and a divalent metallic ion, an -OH group, an H2O molecule, and an interlayer anion.
Due to their distinctive multilayer architecture and interlayer anion exchanging capability, LDH nanostructures have paved the way in the biomedicinal domain. One of the most significant uses of LDH nanostructures in the administration of drugs is the incorporation of a specific chemical into LDHs through an interlayer anionic exchange.
LDHs have excellent drug loading capability, a large surface area, great durability, and anion exchanging ability. These properties make them preferable for drug administration, especially when compared to other nanostructures like polymer nanoparticles (NPs).
More significantly, as LDHs have a dissoluble bulk layer at pH 5.0 (around the acidity level of the cancer microenvironment), they are great contenders for drug administration against tumors.
Advantages of Plantago Ovata
Plantago ovata (PO) is a classic botanical remedy with bioactive polysaccharides. It is an organically produced substance with advantages such as sustainable production, low cost, availability, and a good safety profile.
PO was initially employed to treat wounds. Subsequent research revealed that PO extracts possess a variety of medicinal properties, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammation, immunomodulation, and pain-relieving properties.
Important Findings of the Study
PO was utilized to modify the surfaces of Cu–Al LDH nanoscale structures to boost their capability as nanoscale drug administration systems. Doxorubicin, an anti-cancer medication, was stacked onto NPs once they were prepared, and characterization procedures showed proper fabrication and drug content.
The drug discharge analysis indicated pH-sensitive discharge of doxorubicin from LDH NPs, with the largest discharge of anti-cancer medications occurring at pH 5.5 and the least amount of medication discharge occurring at pH 4.5, perhaps owing to the detrimental effect of lower and strongly acidic pH on NP architectures.
The MTT experiment exhibited great cytocompatibility of PO-incorporated Cu–Al LDH nanostructures, demonstrating partial and low cytotoxicity against HEK-293 and PC12 cells, while decreasing the viability of MCF-7 and HT-29 cells as cancerous cells.
Notably, the decrease in viability of HT-29 and MCF-7 cells was smaller in PO-incorporated LDH NPs than LDH nanoscale carriers without PO, which should be investigated further in future studies. The CLSM data demonstrated that LDH NPs delivered doxorubicin to the nucleus and cytoplasm of HEK-293 and MCF-7 cells.
Histological examination of renal tissue revealed no cellular deterioration, adequate cellular and tubular architecture, and zero bloodstream obstructions. This indicates the great cytocompatibility of PO-incorporated LDH nanostructures.
Antimicrobial testing revealed that Cu–Al LDH nanoparticles exhibited biotoxicity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, and they may be used in treating microbial illnesses in future trials.
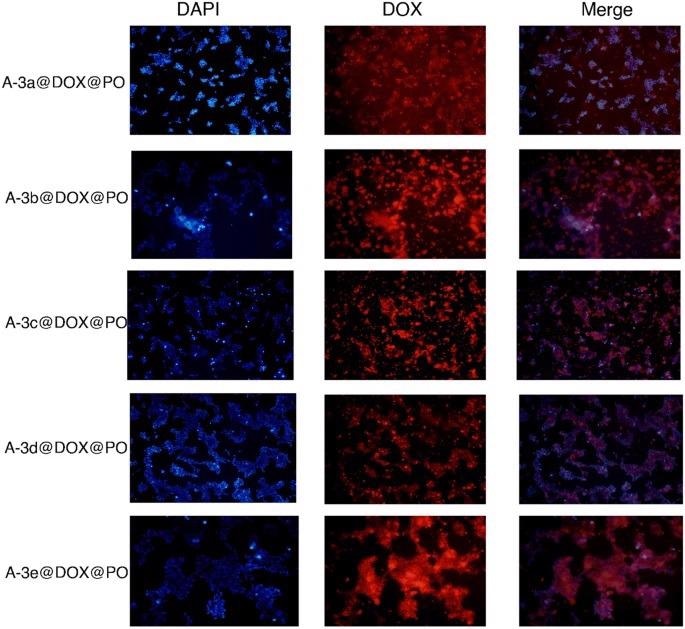
Figure 3. The CLSM images of the drug loaded nanocarriers-coated with leaf extracts treated with HEK-293 cell lines. The used concentration of the nanoparticles: 17.5 μg/mL. © Kiani, M., Bagherzadeh, M., Ghadiri, A. M., Makvandi, P., & Rabiee, N. (2022).
News
Nanocrystals Carrying Radioisotopes Offer New Hope for Cancer Treatment
The Science Scientists have developed tiny nanocrystal particles made up of isotopes of the elements lanthanum, vanadium, and oxygen for use in treating cancer. These crystals are smaller than many microbes and can carry isotopes of [...]
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]





















