Gold particles of the size of billionths of a meter are lethal to cancer cells. This fact has been known for a long time, as has a simple correlation: The smaller the nanoparticles used to fight the cancer cells, the faster they die. However, a more interesting, more complex picture of these interactions is emerging from the latest research, conducted at the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences, using a novel microscopic technique.
Smaller kills faster—this is what was previously thought about gold nanoparticles used to fight cancer cells. Scientists thought that small nanoparticles would simply find it easier to penetrate the interior of a cancer cell, where their presence would lead to metabolic disturbances and ultimately cell death.
The reality, however, turns out to be more complex, as demonstrated by research carried out by scientists from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IFJ PAN) in Cracow, supported by theoretical analysis performed at the University of Rzeszow (UR) and Rzeszow University of Technology.
“Our institute operates a state-of-the-art medical and accelerator center for proton radiotherapy. So when reports emerged a few years ago that gold nanoparticles could be good radiosensitizers and enhance the effectiveness of this sort of therapy, we started to synthesize them ourselves and test their interaction with cancer cells. We quickly found out that the toxicity of nanoparticles was not always as expected,” says Dr. Joanna Depciuch-Czarny (IFJ PAN), initiator of the research and first author of an article discussing the results, published in the journal Small.
Nanoparticles can be produced using a variety of methods, yielding particles of different sizes and shapes. Shortly after starting their own experiments with gold nanoparticles, the IFJ PAN physicists noticed that biology does not follow the popular rule that their toxicity is greater the smaller they are.
Spherical nanoparticles of 10 nanometers in size, produced in Cracow, turned out to be practically harmless to the glioma cell line studied. However, high mortality was observed in cells exposed to nanoparticles as large as 200 nanometers, but with a star-shaped structure.
Elucidation of the stated contradiction became possible thanks to the use of the first holotomographic microscope in Poland, at IFJ PAN.
A typical CT scanner scans the human body using X-rays, and reconstructs its spatial internal structure section by section. In biology, a similar function has recently been performed by the holotomographic microscope. Here, cells are also swept by a beam of radiation, though not high-energy radiation, but electromagnetic radiation. Its energy is chosen so that the photons do not disturb cell metabolism.
The result of the scan is a set of holographic cross-sections containing information about the distribution of refractive index changes. Since light refracts differently on the cytoplasm and differently on the cell membrane or nucleus, it is possible to reconstruct a three-dimensional image of both the cell itself and its interior.
“Unlike other high-resolution microscopy techniques, holotomography does not require the preparation of samples or the introduction of any foreign substances into the cells. The interactions of gold nanoparticles with cancer cells could therefore be observed directly in the incubator, where the latter were cultured, in an undisturbed environment–what’s more, with nanometric resolution–from all sides simultaneously and practically in real time,” enumerates Dr. Depciuch-Czarny.
The unique features of holotomography allowed the physicists to determine the causes of the unexpected behavior of cancer cells in the presence of gold nanoparticles. A series of experiments was conducted on three cell lines: two glioma and one colon. Among others, it was observed that although the small, spherical nanoparticles easily penetrated the cancer cells, the cells regenerated and even started to divide again, despite the initial stress.
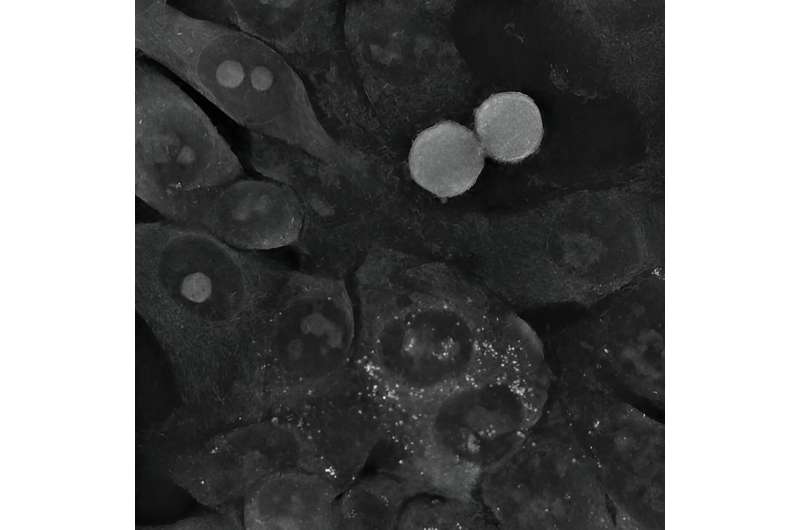
In the case of colon cancer cells, the gold nanoparticles were quickly pushed out of them. The situation was different for the large star-shaped nanoparticles. Their sharp tips perforated the cell membranes, most likely resulting in increasing oxidative stress inside the cells. When these cells could no longer cope with repairing the increasing damage, the mechanism of apoptosis, or programmed death, was triggered.
“We used the data from the Cracow experiments to build a theoretical model of the process of nanoparticle deposition inside the cells under study. The final result is a differential equation into which suitably processed parameters can be substituted—for the time being only describing the shape and size of nanoparticles—to quickly determine how the uptake of the analyzed particles by cancer cells will proceed over a given period of time,” says Dr. Pawel Jakubczyk, professor at the UR and co-author of the model.
He emphasizes, “Any scientist can already use our model at the design stage of their own research to instantly narrow down the number of nanoparticle variants requiring experimental verification.”
The ability to easily reduce the number of potential experiments to be carried out means a reduction in the costs associated with the purchase of cell lines and reagents, as well as a marked reduction in research time (it typically takes around two weeks just to culture a commercially available cell line). In addition, the model can be used to design better-targeted therapies than before—ones in which the nanoparticles will be particularly well absorbed by selected cancer cells, while maintaining relatively low or even zero toxicity to healthy cells in the patient’s other organs.
The Cracow-Rzeszow group of scientists is already preparing to continue their research. New experiments should soon make it possible to extend the model of the interaction of nanoparticles with cancer cells to include further parameters, such as the chemical composition of the particles or further tumor types. Later plans also include supplementing the model with mathematical elements to optimize the efficacy of photo- or proton therapy for indicated combinations of nanoparticles and tumors.
More information: Joanna Depciuch et al, Modeling Absorption Dynamics of Differently Shaped Gold Glioblastoma and Colon Cells Based on Refractive Index Distribution in Holotomographic Imaging, Small (2024). DOI: 10.1002/smll.202400778
Journal information: Small
Provided by Polish Academy of Sciences
News
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]





















