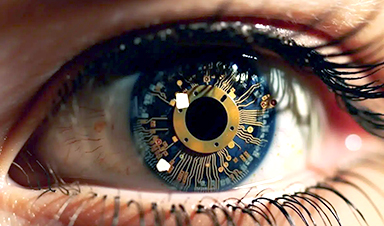
Summary: Researchers developed a single-chip device that mimics the human eye’s capacity to capture, process, and store visual data.
This groundbreaking innovation, fueled by a thin layer of doped indium oxide, could be a significant leap towards applications like self-driving cars that require quick, complex decision-making abilities. Unlike traditional systems that need external, energy-intensive computation, this device encapsulates sensing, information processing, and memory retention in one compact unit.
As a result, it enables real-time decision-making without being hampered by processing extraneous data or being delayed by transferring information to separate processors.
Key Facts:
- The neuromorphic device uses a single layer of doped indium oxide, which is thousands of times thinner than a human hair, to mimic the human eye’s ability to capture, process, and store visual information.
- The device can retain information for more extended periods without the need for frequent electric signals to refresh the memory, significantly reducing energy consumption and improving performance.
- The scientists behind the device envisage a wide range of applications, from self-driving cars to bionic vision and advanced forensics. Future work includes extending the technology for visible and infrared light detection.
Source: RMIT University
Researchers have created a small device that ‘sees’ and creates memories in a similar way to humans, in a promising step towards one day having applications that can make rapid, complex decisions such as in self-driving cars.
The neuromorphic invention is a single chip enabled by a sensing element, doped indium oxide, that’s thousands of times thinner than a human hair and requires no external parts to operate.
RMIT University engineers in Australia led the work, with contributions from researchers at Deakin University and the University of Melbourne.
The team’s research demonstrates a working device that captures, processes and stores visual information. With precise engineering of the doped indium oxide, the device mimics a human eye’s ability to capture light, pre-packages and transmits information like an optical nerve, and stores and classifies it in a memory system like the way our brains can.
Collectively, these functions could enable ultra-fast decision making, the team says.
Team leader Professor Sumeet Walia said the new device can perform all necessary functions – sensing, creating and processing information, and retaining memories – rather than relying on external energy-intensive computation, which prevents real-time decision making.
“Performing all of these functions on one small device had proven to be a big challenge until now,” said Walia from RMIT’s School of Engineering.
“We’ve made real-time decision making a possibility with our invention, because it doesn’t need to process large amounts of irrelevant data and it’s not being slowed down by data transfer to separate processors.”
What did the team achieve and how does the technology work?
The new device was able to demonstrate an ability to retain information for longer periods of time, compared to previously reported devices, without the need for frequent electrical signals to refresh the memory. This ability significantly reduces energy consumption and enhances the device’s performance.
Their findings and analysis are published in Advanced Functional Materials.
First author and RMIT PhD researcher Aishani Mazumder said the human brain used analog processing, which allowed it to process information quickly and efficiently using minimal energy.
“By contrast, digital processing is energy and carbon intensive, and inhibits rapid information gathering and processing,” she said.
“Neuromorphic vision systems are designed to use similar analog processing to the human brain, which can greatly reduce the amount of energy needed to perform complex visual tasks compared with today’s technologies
What are the potential applications?
The team used ultraviolet light as part of their experiments, and are working to expand this technology even further for visible and infrared light – with many possible applications such as bionic vision, autonomous operations in dangerous environments, shelf-life assessments of food and advanced forensics.
“Imagine a self-driving car that can see and recognise objects on the road in the same way that a human driver can or being able to able to rapidly detect and track space junk. This would be possible with neuromorphic vision technology.”
Walia said neuromorphic systems could adapt to new situations over time, becoming more efficient with more experience.
“Traditional computer vision systems – which cannot be miniaturised like neuromorphic technology – are typically programmed with specific rules and can’t adapt as easily,” he said.
“Neuromorphic robots have the potential to run autonomously for long periods, in dangerous situations where workers are exposed to possible cave-ins, explosions and toxic air.”
The human eye has a single retina that captures an entire image, which is then processed by the brain to identify objects, colours and other visual features.
The team’s device mimicked the retina’s capabilities by using single-element image sensors that capture, store and process visual information on one platform, Walia said.
“The human eye is exceptionally adept at responding to changes in the surrounding environment in a faster and much more efficient way than cameras and computers currently can,” he said.
“Taking inspiration from the eye, we have been working for several years on creating a camera that possesses similar abilities, through the process of neuromorphic engineering.”
Support for the research
The team used the Micro Nano Research Facility and the Microscopy and Microanalysis Research Facility at RMIT.
Funding: The work was also supported by the Australian Research Council and the National Computational Infrastructure.
News
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]