The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don’t have a good grasp on the metal’s chemistry. That’s because actinium is only available in extremely small amounts and working with the radioactive material requires special facilities. But to improve emerging cancer treatments using actinium, researchers will need to better understand how the element binds with other molecules.
In a study led by the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), researchers grew crystals containing actinium and studied the compound’s atomic structure. While elements often behave similarly to their lighter cousins on the periodic table, researchers were surprised to find that the actinium behaved differently than predicted by looking at its counterpart, lanthanum.
“There’s a breadth of applications for these elements, from nuclear energy to medicine to national security, but if we don’t know how they behave, that inhibits the progress we can make,” said Jen Wacker, first author of the paper published in Nature Communications and a chemist at Berkeley Lab.
“We’re seeing that this work is necessary to really understand the complexity of these radioactive elements, because in a lot of cases, using their surrogates is not sufficient to understand their chemistry.”
One area of interest is in using an isotope of actinium (actinium-225) in a cancer treatment method called targeted alpha therapy (TAT), which has shown promise in clinical trials. The TAT method uses biological delivery systems such as peptides or antibodies to move the radioactive element to the cancer site.
When the actinium decays, it releases energetic particles that travel a short distance, destroying the nearby cancer cells but sparing healthy tissue further away.

“There’s a movement to design better delivery systems to get the actinium to particular cells and keep it there,” said Rebecca Abergel, a UC Berkeley associate professor of nuclear engineering and of chemistry who leads the Heavy Element Chemistry Group at Berkeley Lab.
“If we can engineer proteins to bind the actinium with a really high affinity, and either be fused with an antibody or serve as the targeting protein, that would really enable new ways to develop radiopharmaceuticals.”
Researchers used a novel approach to grow the crystals using only 5 micrograms of pure actinium—roughly one tenth the weight of a grain of salt, and invisible to the naked eye. They first purified the actinium through a complex filtration process that removed other elements and chemical impurities.
They then bound the actinium to a metal-trapping molecule called a ligand and enveloped the bundle inside of a protein isolated and purified by Roland Strong’s team at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, building a “macromolecular scaffold.”
The crystals, grown over a week inside of the Heavy Element Research Laboratory, were then cryocooled in liquid nitrogen and illuminated with X-rays at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (ALS). The X-rays revealed the compound’s 3D structure and showed how actinium interacted with surrounding atoms. It is the first single-crystal X-ray structure reported for actinium
“I’ve been working in crystallography for 40 years and seen a lot of things, and the method the team is using is unique and provides details we couldn’t get in the past,” said Marc Allaire, a scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging Division and head of the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology team at the ALS.
“To the best of my knowledge, Berkeley Lab is the only place in the world where we do this kind of study and measure radioactive protein crystals.”
-
Joshua Woods and Appie Peterson measure a small sample of actinium. Credit: Marilyn Sargent/Berkeley Lab -
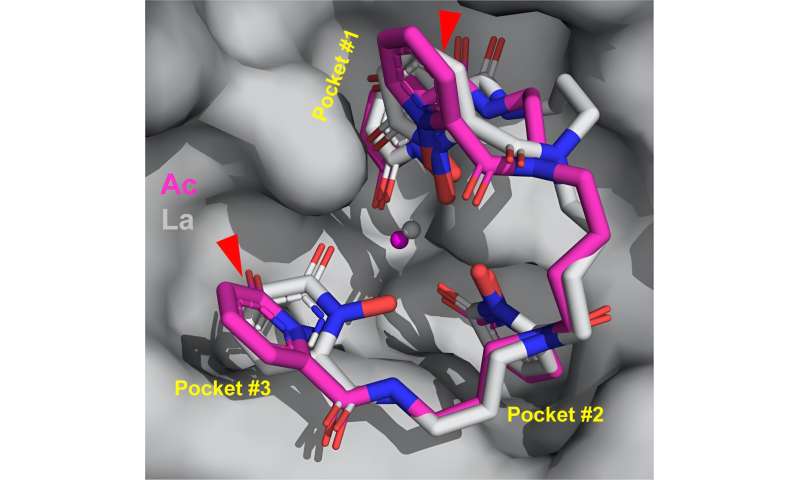
This rendering shows the structure of how actinium (magenta) binds with other molecules. Red triangles point out how the arrangement differs from actinium’s lighter counterpart, lanthanum (gray). The stick structure of the binding molecule (the ligand) is surrounded by pockets in the protein. Credit: Jen Wacker/Berkeley Lab
In this work, scientists used actinium-227, the longest-lived isotope of the element. Future studies will explore actinium-225 (the preferred isotope for targeted alpha therapy) to look for other changes in how the metal binds. Researchers are also interested in pairing actinium with different proteins to learn more about the structures it forms.
“This is very fundamental science that is part of our core program in understanding the chemistry of heavy elements,” Abergel said.
“We’ve achieved a really technically difficult experimental method that pushes the boundaries of isotope chemistry and lets us gain a better understanding of this element. It hopefully will enable us and others to develop better systems that are useful for targeted alpha therapy.”
More information: Jennifer N. Wacker et al, Actinium chelation and crystallization in a macromolecular scaffold, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50017-5
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
News
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]