Protein found in Sydney rock oysters’ haemolymph can kill bacteria and boost some antibiotics’ effectiveness, scientists discover
An antimicrobial protein found in the blood of an Australian oyster could help in the fight against superbugs, new research suggests.
Australian scientists have discovered that a protein found in the haemolymph – the equivalent of blood – of the Sydney rock oyster, Saccostrea glomerata, can kill bacteria itself and increase the effectiveness of some conventional antibiotics.
Antimicrobial resistance has been described as a “looming global health crisis” that – without urgent action – could render critical drugs ineffective and result in declines in lifespan and life quality by 2050.
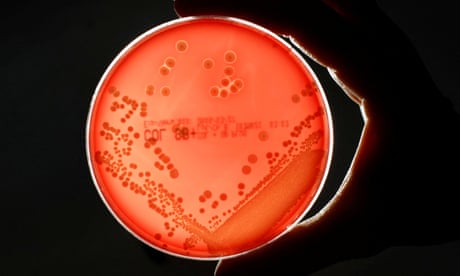
In lab tests, the haemolymph protein alone was effective at killing the bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae, which mainly causes pneumonia, and Streptococcus pyogenes, the culprit for strep throat and scarlet fever. It has not yet been tested in animals or humans.
When used in combination with antibiotics, including ampicillin and gentamicin, it improved their effectiveness from two- to 32-fold against bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus (golden staph) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which often infects immunocompromised people.
The study’s co-author Prof Kirsten Benkendorff, of Southern Cross University, estimated that about two dozen oysters would contain enough haemolymph to provide an active dose of the protein for an average person, but she emphasised that more research was needed to purify the protein and understand how it works.

“We found that heating [the protein] does actually reduce the antimicrobial activity, so cooking would reduce the effect,” Benkendorff said.
It is uncertain, however, whether eating the protein would be effective, as unlike many conventional antibiotics, antimicrobial proteins can be broken down by the digestive system before they reach their target site.
“I definitely would not suggest that people ate oysters instead of taking antibiotics if they have got a serious infection,” Benkendorff said.
She said “oysters as filter feeding organisms are sucking bacteria in through their bodies all the time”, making them good candidates in which to look for new antimicrobial drugs – but also means that in places such as near stormwater drains, they can accumulate substances that can be harmful to humans if consumed.
Benkendorff said the protein could help treat respiratory infections that are resistant to regular antibiotics because of biofilms.
To protect themselves, infectious bacteria often aggregate into biofilms – sticky communities that enable them to better evade antibiotics and the human immune system.
The oyster haemolymph protein was effective against Streptococcus biofilms, the scientists found.
“We often think about bacteria just floating around in the blood. But in reality, a lot of them actually adhere to surfaces,” Benkendorff said. “The advantage of having something that disrupts the biofilm is … it’s stopping all of those bacteria from attaching to the surfaces. It’s releasing them back out into the blood, where then they can be attacked by antibiotics.”
Prof Jonathan Iredell, an infectious diseases physician and clinical microbiologist at the University of Sydney, who was not involved in the research, said the oyster protein belonged to a class of compounds called antimicrobial peptides. “There is a lot of excitement about their discovery because they often contain interesting kinds of mechanisms that we haven’t seen before.”
The study, he said, added “to an exciting field where we’re looking to naturally occurring antimicrobials of a different type to try and provide new prospects in the face of advancing adaptation by bacteria”.
Prof Branwen Morgan, who leads the CSIRO’s minimising antimicrobial resistance mission, described the protein’s properties as a “really interesting discovery, given biofilms are so problematic”.
Morgan, who was not involved in the research, said any potential treatment that reduced the reliance on traditional antibiotics was worth pursuing, in light of the increase in drug-resistant infections around thee world.
“Given the significant costs in developing new medicines, the idea of using excess and/or imperfect oysters to generate a sustainable supply of antimicrobial proteins … should be investigated further,” she said.
The study was published in the journal Plos One.
News
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]





















