Researchers succeeded for the first time in accelerating electrons using a nano device.
Particle accelerators are crucial tools in a wide variety of areas in industry, research, and the medical sector. The space these machines require ranges from a few square meters to large research centers. Using lasers to accelerate electrons within a photonic nanostructure constitutes a microscopic alternative with the potential of generating significantly lower costs and making devices considerably less bulky.
Until now, no substantial energy gains have been demonstrated. In other words, it has not been shown that electrons really have increased in speed significantly. A team of laser physicists at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) has now succeeded in demonstrating the first nanophotonic electron accelerator – at the same time as colleagues from Stanford University.
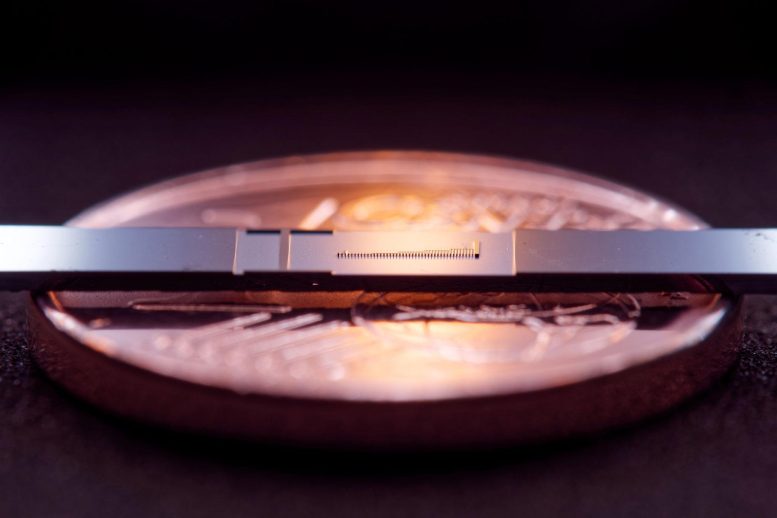
For the first time, FAU researchers have succeeded in measurably accelerating electrons in structures that are only a few nanometers in size. In the picture, you can see the microchip with the structures and, in comparison, a 1 cent coin. Credit: FAU/Julian Litzel
Particle Accelerators and Their Nanophotonic Evolution
When people hear "particle accelerator," most will probably think of CERN's Large Hadron Collider in Geneva, the approximately 27-kilometer-long ring-shaped tunnel that researchers from around the globe used to conduct research into unknown elementary particles. Such huge particle accelerators are the exception, however. We are more likely to encounter them in other places in our day-to-day lives, for example in medical imaging procedures or during radiation to treat tumors. Even then, however, the devices are several meters in size and still rather bulky, with room for improvement in terms of performance.
Particles are accelerated by ultrashort laser pulses illuminating the nanostructures. "The dream application would be to place a particle accelerator on an endoscope in order to be able to administer radiotherapy directly at the affected area within the body," explains Dr. Tomáš Chlouba, one of the four lead authors of the recently published paper.
This dream may still be far beyond the grasp of the FAU team from the Chair of Laser Physics led by Prof. Dr. Peter Hommelhoff and consisting of Dr. Tomáš Chlouba, Dr. Roy Shiloh, Stefanie Kraus, Leon Brückner and Julian Litzel, but they have now succeeded in taking a decisive step in the right direction by demonstrating the nanophotonic electron accelerator. "For the first time, we really can speak about a particle accelerator on a chip," enthuses Dr. Roy Shiloh.
Guiding Electrons + Acceleration = Particle Accelerator
Just over two years ago the team made their first major breakthrough: they succeeded in using the alternating phase focusing (APF) method from the early days of acceleration theory to control the flow of electrons in a vacuum channel over long distances. This was the first major step on the way towards building a particle accelerator. Now, all that was needed to gain major amounts of energy was acceleration.
"Using this technique, we have now succeeded not only in guiding electrons but also in accelerating them in these nano-fabricated structures over a length of half a millimeter," explains Stefanie Kraus. Whilst this might not sound like much of an achievement to many, it is a huge success for the field of accelerator physics. "We gained energy of 12 kiloelectron volts. That is a 43 percent gain in energy," explains Leon Brückner.
In order to accelerate the particles over such large distances (when seen from the nanoscale), the FAU physicists combined the APF method with specially developed pillar-shaped geometrical structures.
This demonstration is just the beginning, however. Now the aim is to increase the gain in energy and electron current to such an extent that the particle accelerator on a chip is sufficient for applications in medicine. For this to be the case, the gain in energy would have to be increased by a factor of approximately 100. "In order to achieve higher electron currents at higher energies at the output of the structure, we will have to expand the structures or place several channels next to each other," Tomáš Chlouba explains the next steps of the FAU laser physicists.
A Global Pursuit for Miniaturization
What the Erlangen laser physicists succeeded in doing was demonstrated almost simultaneously by colleagues at Stanford University in the United States: Their results are currently under review, but can be viewed on a repository. The two teams are working together on the realization of the "Accelerator on a chip" in a project funded by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
"In 2015, the FAU- and Stanford-led ACHIP team had a vision for a revolutionary approach to particle accelerator design," said Dr. Gary Greenburg of the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, "and we are delighted that our support has helped turn this vision into reality."
Reference: "Coherent nanophotonic electron accelerator" by Tomáš Chlouba, Roy Shiloh, Stefanie Kraus, Leon Brückner, Julian Litzel and Peter Hommelhoff, 18 October 2023, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06602-7
![]()
News
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]





















