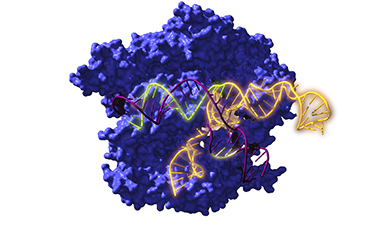
An international research group has for the first time reconstructed ancestors dating back 2.6 billion years of the well-known CRISPR-Cas system, and studied their evolution over time. The results suggest that the revitalized systems not only work, but are more versatile than current versions and could have revolutionary applications. Nature Microbiology has published the results of this research, which, in the opinion of the research team, “opens up new avenues for gene editing.”
The acronym CRISPR refers to the repeated sequences present in the DNA of bacteria and archaea (prokaryotic organisms). Among the repeats, these microorganisms harbor fragments of genetic material from viruses that infected their ancestors; that enables them to recognize a repeat infection and defend themselves by cutting the invaders’ DNA using Cas proteins associated with these repeats. It is a mechanism (CRISPR-Cas system) of antiviral defense. This ability to recognize DNA sequences is the basis of their usefulness, and they act as if they were molecular scissors. Nowadays CRISPR-Cas technology enables pieces of genetic material to be cut and pasted into any cell, so that it can be used to edit DNA.
Current research efforts focus on finding new versions of CRISPR-Cas systems with distinct properties in the farthest reaches of the globe. To do this, systems of different species living in extreme environments are explored, or molecular design techniques are applied to modify them. A radically different way of finding new systems is to look for them in the past, which is in fact the basis of this research.
The Nanobiotechnology group at nanoGUNE, led by Raúl Pérez-Jiménez, has spent years studying the evolution of proteins from the origin of life right up to the present day. Ancestral reconstructions of proteins and genes from extinct organisms are carried out to see what qualities they have and whether they can be used in biotechnological applications. It is a journey back in time conducted by means of biocomputing techniques. In this work, which has just been published in the journal Nature Microbiology, the evolutionary history of CRISPR-Cas systems, from ancestors dating back 2.6 billion years to the present day, has been reconstructed for the first time.
The research team carried out the computational reconstruction of the ancestral CRISPR sequences, synthesized them, and studied and confirmed their functionality. “What is surprising is that we can revitalize Cas proteins that must have existed billions of years ago and find that they already had the capacity then to operate as gene editing tools; we have now confirmed that by successfully editing genes in human cells,” explained Lluís Montoliu, researcher at the National Biotechnology Center of the CSIC (CNB-CSIC) and CIBERER, and head of the team that has functionally validated these ancestral Cas proteins in human cells in culture.
Another interesting finding in the study is that the CRISPR-Cas system has gradually become more complex over time, which is a sign of the adaptive nature of the system; it has been gradually adapting to new virus threats that have been hanging over bacteria throughout evolution.
“This research signifies an extraordinary advance in knowledge about the origin and evolution of CRISPR-Cas systems. About how the selective pressure of viruses has over billions of years been fine-tuning rudimentary, initially not very selective machinery; this had been taking place until a sophisticated defense mechanism was produced; it is a mechanism capable of distinguishing with great precision between its own DNA, which it must preserve, and the genetic material of unwanted invaders, which it must destroy,” said University of Alicante researcher Francis Mojica, who discovered the CRISPR-Cas technique. On the applied side, “the work represents an original approach to the development of CRISPR tools to generate new tools and improve those derived from existing ones in current organisms,” added Mojica.
“Current systems are highly complex and are adapted to function within a bacterium. When the system is used outside this environment, for example in human cells, it is rejected by the immune system and there are also certain molecular restrictions that limit its use. Oddly enough, in ancestral systems some of these restrictions disappear, which gives these systems greater versatility for new applications,” said Pérez-Jiménez.
Miguel Angel Moreno, head of the Genetics Service at HRYC-IRYCIS-CIBERER, said, “The ingenuity that an ancestral nuclease could have, insofar as it does not so specifically recognize some regions of the genome, turns them into more versatile tools for correcting mutations that until now could not be edited or were not corrected very efficiently.” His team has developed the Mosaic Finder tool, which, by means of massive sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, has enabled the effect of genome editing carried out by these ancestral Cas in human cells in culture to be characterized.
Ylenia Jabalera, researcher in the project at nanoGUNE, says, “This scientific achievement can make available gene editing tools with properties different from the current ones, and which are much more flexible; that opens up new avenues in DNA manipulation and treatment of diseases such as ALS, cancer and diabetes, or even in diagnostic tools for diseases.”
News
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]