Melissa, a 30-year-old educator, came to the emergency department with a sudden onset of double vision. She had not been in an accident or suffered any trauma and had never experienced this symptom before. However, she noted that a few months earlier, the vision in one of her eyes had become blurred and then returned to normal shortly after. She told herself it was a sign of fatigue after a period of intense work on a screen.
After some basic optometric tests, then more advanced tests of visual perception, the visual episodes were thought to be related to multiple sclerosis. Melissa was then referred to a neuro-ophthalmology specialist who confirmed the diagnosis, and she was quickly treated.
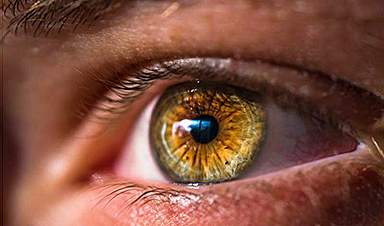
Is Melissa’s case unique? Over my 30 years working as an optometrist, I’ve seen many patients with different vision and eye health problems, the cause of which turned out to be an illness they didn’t know they had.
As a professor at the School of Optometry at the Université de Montréal, I teach students that certain ocular symptoms can be linked to general health problems. Optometrists are trained to identify the various diseases that can manifest themselves through the eyes and to work with other health professionals to manage them.
Diabetes
Because diabetes will affect almost 8% of the population by 2030, screening is a crucial issue. However, it is estimated that diabetes is not generally diagnosed until six to 13 years after its onset. An eye health examination can shorten this delay since it is often possible to identify characteristic lesions of the disease at the back of the eye before other symptoms of diabetes appear.
Early diagnosis is crucial since within five years of diagnosis (i.e., 11 to 15 years after the onset of diabetes), 25% of patients with Type 1 (juvenile diabetes) and 40% of those with Type 2 (adult diabetes) who are treated with insulin will develop eye lesions that can have a major effect on their vision. Early identification and rigorous monitoring of eye health significantly reduces the risk of blindness, which can happen when the disease is not treated.
Unmasking the silent killer
If diabetes affects a significant number of patients without them knowing it, what can be said about high blood pressure and high cholesterol? These two conditions significantly increase the risk of coronary heart disease or stroke in our societies.
The eye is the only place in the human body where blood vessels can be seen without having to make an incision or use invasive techniques.
- High blood pressure (known as the silent killer) can be seen by crushing of vessels and very specific signs on the retina.
- Hypercholesterolemia creates cholesterol deposits inside the vessels.
- Atherosclerosis is associated with Hollenhorst plaques, also visible inside the vessels.
- Cholesterol can also be seen in the cornea (lipid arc) or in the adnexa (xanthelasma).
In all these cases, very often the symptoms experienced by the patient are so few, or progress so slowly, that he or she considers them almost normal.
Normotensive or open-angle glaucoma
The absence of symptoms is also the norm for glaucoma. This pathology of the optic nerve is usually associated with excessive production of aqueous humor in the eye or a deficit in its evacuation.
The pressure inside the eye then increases and through different mechanisms leads to the loss of nerve fibers in the nerve. The visual field narrows very slowly (and therefore can go unnoticed), so the person ends up with tunnel vision after several years.
By the time this loss of vision affects them, it is often late, so the damage to the optic nerve can be very extensive. This damage is mainly ocular, although it can also be induced by the effect of certain drugs (such as cortisone).
Normotensive glaucoma is of a completely different nature. In this case, the pressure inside the eye remains normal but the nerve is still damaged. The mechanisms at play are different from those in chronic open-angle glaucoma.
Normotensive glaucoma is often associated with low blood pressure or conditions such as sleep apnea. If it is present, the patient must be referred to a family doctor for a thorough investigation.
The disease of the century
Because cancer is becoming so widespread and is expressed in so many ways, we call it the disease of the century. Cancers that affect the eye (retinoblastoma) can also cause metastases to the lungs and liver.
Here again, the disease often develops without symptoms until it is too late. So early detection is crucial, because the patient’s very survival is at stake.
Other types of asymptomatic retinal pigment (shaped like a bear’s paw) may be associated with cancer of the colon, which has a very negative prognosis if management is delayed.
A simple visual field measurement may reveal abnormalities that some patients are unaware of, or that they consider so benign they don’t bother to report them. However, many visual field abnormalities hide brain tumors, such as pituitary adenoma, or nerve fibers compressed by blood vessels.
Abnormal eye movements, asymmetric pupillary responses, sudden reading problems or the appearance of diplopia are all yellow flags that require further ocular and neurological investigation.
Rather than the mirror of the soul, the eyes become an open window on our overall health. That makes regular consultations with an optometrist more important than ever, even when there are no symptoms. Many disorders can be detected and treated to either minimize illnesses or prevent them altogether.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
News
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]