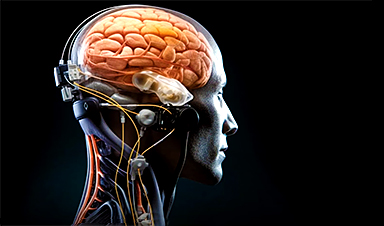
Summary: In a pioneering study, researchers designed a wireless brain-spine interface enabling a paralyzed man to walk naturally again. The ‘digital bridge’ comprises two electronic implants — one on the brain and another on the spinal cord — that decode brain signals and stimulate the spinal cord to activate leg muscles.
Remarkably, the patient experienced significant recovery in sensory perceptions and motor skills, even when the interface was off. The team hopes to extend the technology’s applications to include restoring arm and hand functions, and assisting stroke patients.
Key Facts:
- The brain-spine interface is composed of two electronic implants that work together to decode brain signals and stimulate the spinal cord, resulting in the activation of leg muscles and enabling natural movement.
- The patient experienced significant improvement in sensory perceptions and motor skills, indicating potential development of new nerve connections even when the interface was not active.
- The team plans to explore applications of the technology to restore other functions and assist stroke patients, and there are ongoing efforts to commercialize the technology globally through ONWARD Medical, in partnership with CEA and EPFL.
Source: EPFL
Neuroscientists and neurosurgeons from EPFL/CHUV/UNIL and CEA/CHUGA/UGA report in the journal Nature that they have re-established the communication between the brain and spinal cord with a wireless digital bridge, allowing a paralyzed person to walk again naturally.
“We have created a wireless interface between the brain and the spinal cord using brain-computer interface (BCI) technology that transforms thought into action.”, summarizes Grégoire Courtine, Professor of Neuroscience at EPFL, CHUV and UNIL. Published in the journal Nature,
“Walking naturally after spinal cord injury using a brain-spine interface” presents the situation of Gert-Jan, 40 years old, who suffered a spinal cord injury following a bicycle accident that left him paralyzed.“The digital bridge enabled him to regain natural control over the movement of his paralyzed legs, allowing him to stand, walk, and even climb stairs. Gert-Jan explains that he has recovered the pleasure of being able to share a beer standing at a bar with friends : “This simple pleasure represents a significant change in my life”.
A digital bridge involving two electronic implants: one on the brain, the other on the spinal cord
To establish this digital bridge, two types of electronic implants are needed. Neurosurgeon Jocelyne Bloch, who is a professor at CHUV, UNIL and EPFL, explains: “We have implanted WIMAGINE® devices above the region of the brain that is responsible for controlling leg movements.
“These devices developed by the CEA allows to decode the electrical signals generated by the brain when we think about walking. We also positioned a neurostimulator connected to an electrode array over the region of the spinal cord that controls leg movement.
Guillaume Charvet, head of the BCI program at CEA, adds: “Thanks to algorithms based on adaptive artificial intelligence methods, movement intentions are decoded in real time from brain recordings.”
These intentions are then converted into sequences of electrical stimulation of the spinal cord, which in turn activate leg muscles to achieve the desired movement. This digital bridge operates wirelessly, allowing the patient to move around independently.
Recovery of neurological functions
Rehabilitation supported by the digital bridge enabled Gert-Jan to recover neurological functions that he had lost since his accident.
Researchers were able to quantify remarkable improvements in his sensory perceptions and motor skills, even when the digital bridge was switched off. This digital repair of the spinal cord suggests that new nerve connections have developed.
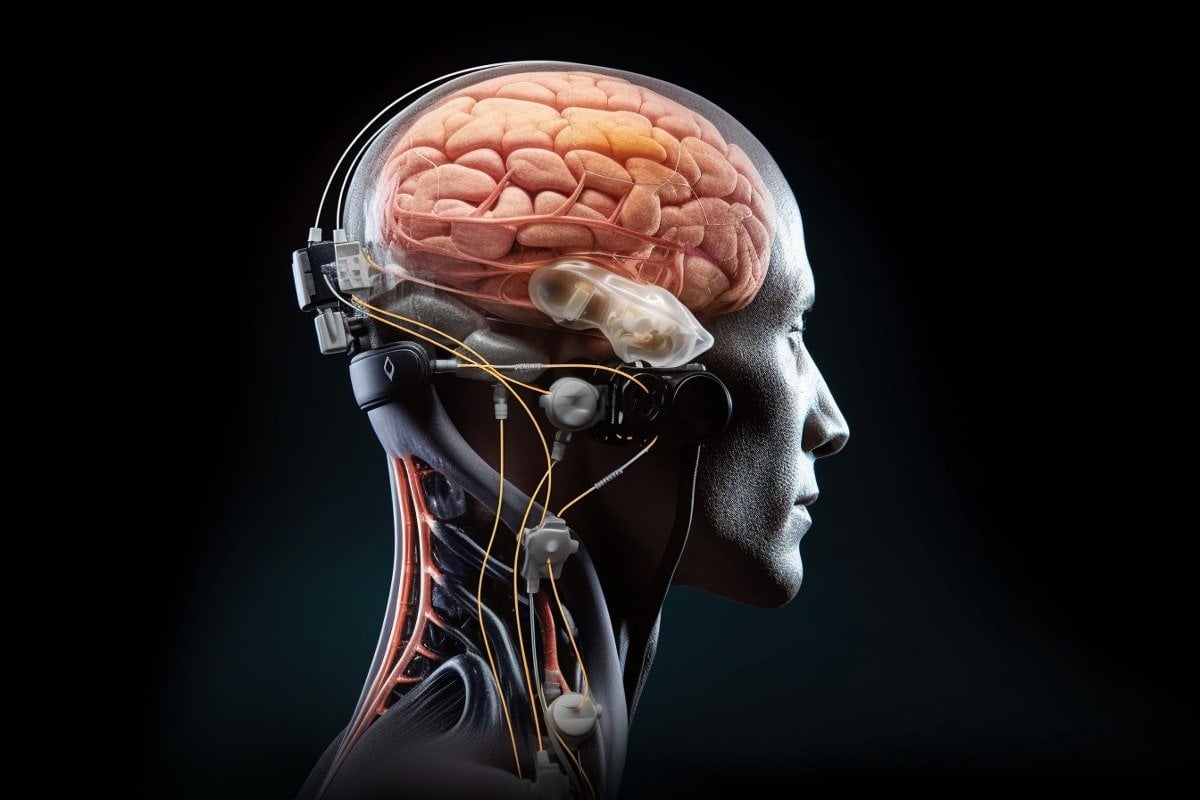
At this stage, the digital bridge has only been tested in one person. Jocelyne Bloch and Grégoire Courtine explain that, in the future, a comparable strategy could be used to restore arm and hand functions.
They add that the digital bridge could also be applied to other clinical indications, such as paralysis due to stroke.
The company ONWARD Medical, along with CEA and EPFL has received support from the European Commission trough its European Innovation Council (EIC) to develop a commercial version of the digital bridge, with the goal of making the technology available worldwide.
News
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]