Human fingers and toes don't grow outward as you might expect. Instead, our dexterous digits are 'sculpted' within a larger foundational bud.
Now the first human cell atlas of early limb development has at last revealed in exquisite detail exactly how that happens.
Prior to this, our understanding of vertebrate limb development has been largely based on model organisms, such as mice and chicken embryos, and lab-grown stem cells.
Although humans share some similarities with other vertebrates, their biology obviously diverges from ours.
The details of early limb formation have also been rendered a little fuzzy by technological limitations, now surpassed, and restrictions on the use of human embryos for research beyond 14 days, a rule that has been relaxed under strict ethical provisions.
The picture constructed so far had limbs initially emerging as shapeless limb buds protruding from the sides of the embryonic body. Eight weeks later, if all goes to plan, those pouches have transformed into anatomically distinct, recognizable limbs, complete with fingers and toes.
It's a remarkable process in early embryonic development that produces arguably one of our most defining human features: our long, slender, opposable thumbs.
In 2014, scientists described how specific molecules expressed at precise moments in embryonic development moulded the formation of fingers and toes, although those predictions were based on simulations of experimental data.
Now, an international team led by cell biologist Bao Zhang at Sun Yat-sen University in China, has colored in that process in exquisite detail, by analyzing thousands of single cells from donated embryonic tissues that were between 5 and 9 weeks of development.

"We identified 67 distinct cell clusters from 125,955 captured single cells, and spatially mapped them across four first trimester timepoints to shed new light on limb development," the team writes in their published paper.
"In doing so, we uncovered several new cell states," they add.
"What we reveal is a highly complex and precisely regulated process," says Hongbo Zhang, senior author and cell biologist from Sun Yat-sen University in China.
"It is like watching a sculptor at work, chiseling away at a block of marble to reveal a masterpiece. In this case, nature is the sculptor, and the result is the incredible complexity of our fingers and toes."
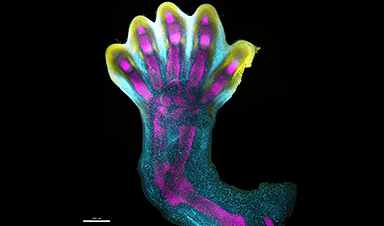
As you can see in the video below, the researchers mapped gene expression patterns to see how those genetic instructions shaped how digits formed.
From hazy beginnings, the expression of IRX1 (represented in aqua in the video below), a gene critical for digit formation, and SOX9 (represented in magenta in the video), a gene essential for skeletal development, overlap in five distinct lengths within the developing limb.
At around 7 weeks of development, programmed cell death instructions are switched on in the undifferentiated cells congregating between these lengths (associated with the expression of MSX1, represented in yellow in the video), and well-defined fingers and toes are revealed.
Like a block of marble being sculpted into a masterpiece by the expression of these genes, our fingers and toes are chiseled out from tip to base as unneeded cells recede.
Small irregularities in this process can lead to limb deformities, which 1 in 500 people are born with – making them some of the most frequently reported syndromes at birth.
The researchers also mapped the expression of genes linked with congenital conditions, such as short fingers (brachydactyly) or webbed digits (syndactyly), to get a better sense of where limb development gets off course.
"For the first time, we have been able to capture the remarkable process of limb development down to single-cell resolution in space and time," says Sarah Teichmann, senior author and computational biologist at the Wellcome Sanger Institute.
She says creating single-cell atlases is "deepening our understanding of how anatomically complex structures form, helping us uncover the genetic and cellular processes behind healthy human development, with many implications for research and healthcare."
Importantly, the researchers also showed that limb formation in humans and mice does follow similar trajectories, with some differences in activated genes and cell types.
The study has been published in Nature.
News
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]