Fabrication of materials using data-based techniques is being welcomed as a new strategy that will replace human scientists’ hit and miss tests and labor demanding jobs. In an article published to the chemRxiv* preprint server, a Robotic Scientist framework that may provide unparalleled capabilities for logical design, retrosynthesis, and programmable fabrication of nanoparticles is discussed.
The Robotic Scientist framework is taught to fabricate gold nanocrystals by using multidisciplinary domains such as artificial intelligence, automated robotics, and big data.
Data-Driven Fabrication of Materials
Data-guided development of materials is being hailed as a new paradigm for shifting laborious activities and trial-and-error tests away from human researchers and towards robotic scientists or chemical fabrication mechanized systems.
The sophisticated Human-AI-Robot cooperation system is expediting the multidisciplinary breakthrough in the fabrication of materials towards a Robotic Scientist for mechanized creation.
Convergence of chemical research, theoretical modeling, purpose-driven databases, configurable cyber networks, and mechanized physical systems is required in this growing discipline.
One of the potential objectives is digitized material generation, which involves gradually collecting information, efficiently revealing data links, and producing viable solutions over time based on prior iterations.
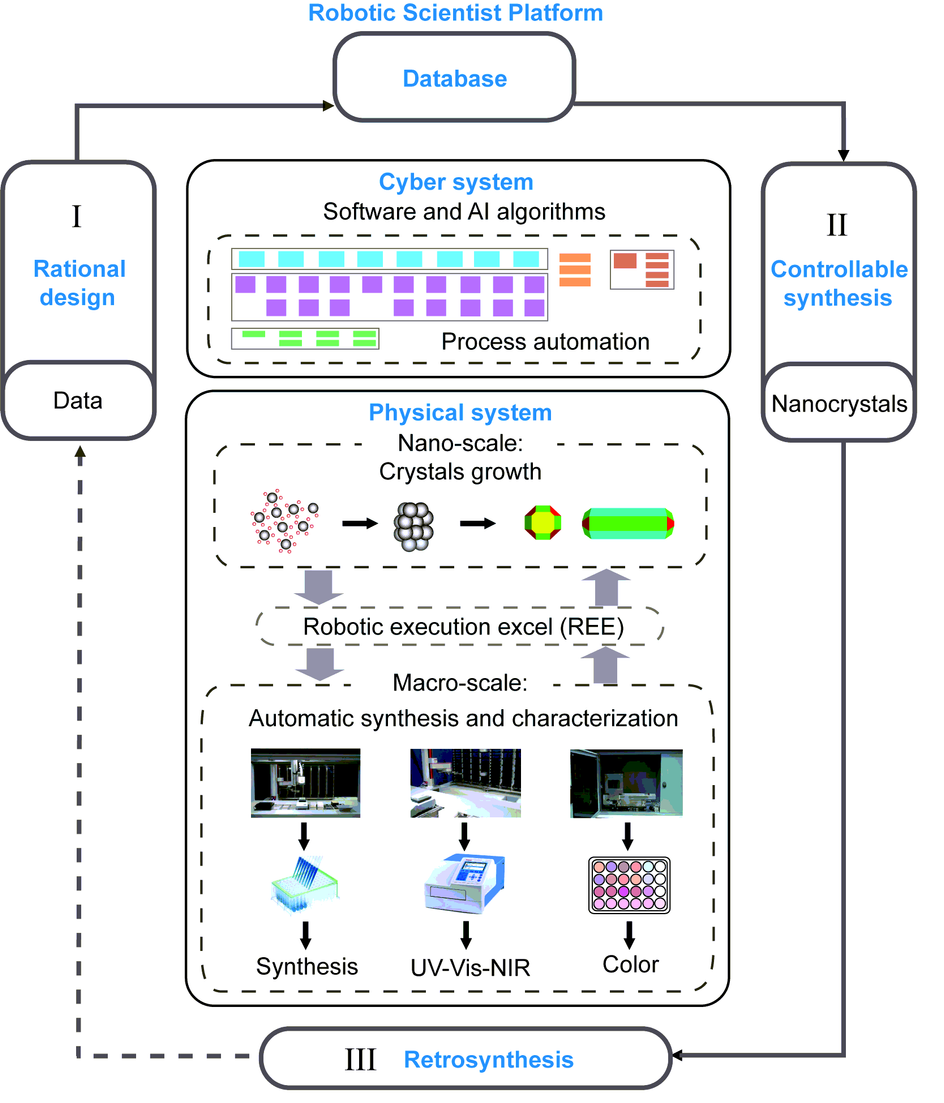
Figure 1. Robotic Scientist platform. Convergence of the database, cyber system, and physical system and process flow: I. Rational design, II. Controllable synthesis, and III. Retrosynthesis for closed-loop synthesis of nanocrystals based on the Robotic Scientist platform. © Zhao, H., Chen, W., et al. (2022)
Existing Work on Automated Fabrication Processes
Significant endeavors have been undertaken in the last decade to achieve digital production of substances.
On the macro-scale, layer-by-layer computerized additive production of 3D substances has been established. Artificial biology is a micro-scale milestone for the computerized fabrication of biomaterials using cells as the hardware on which genes are programmed
Lately, there has been considerable growth in biological programming languages and autonomous systems for chemical synthesis on a small scale. Simultaneously, a computerized chemist has been reported in order to find photocatalysts, opening the door to automated synthetic material research on the micro-scale.
Nonetheless, there are several limits to computerized fabrication, such as material searches lacking conceptual models, blind modification of substances without science-based methodology, and a lack of hardware-software integration to enable material innovations.
As an example, this study illustrates how the Robotic Scientist framework, which allows logical design, controlled fabrication, and retrosynthesis of nanocrystals, may address these challenges.
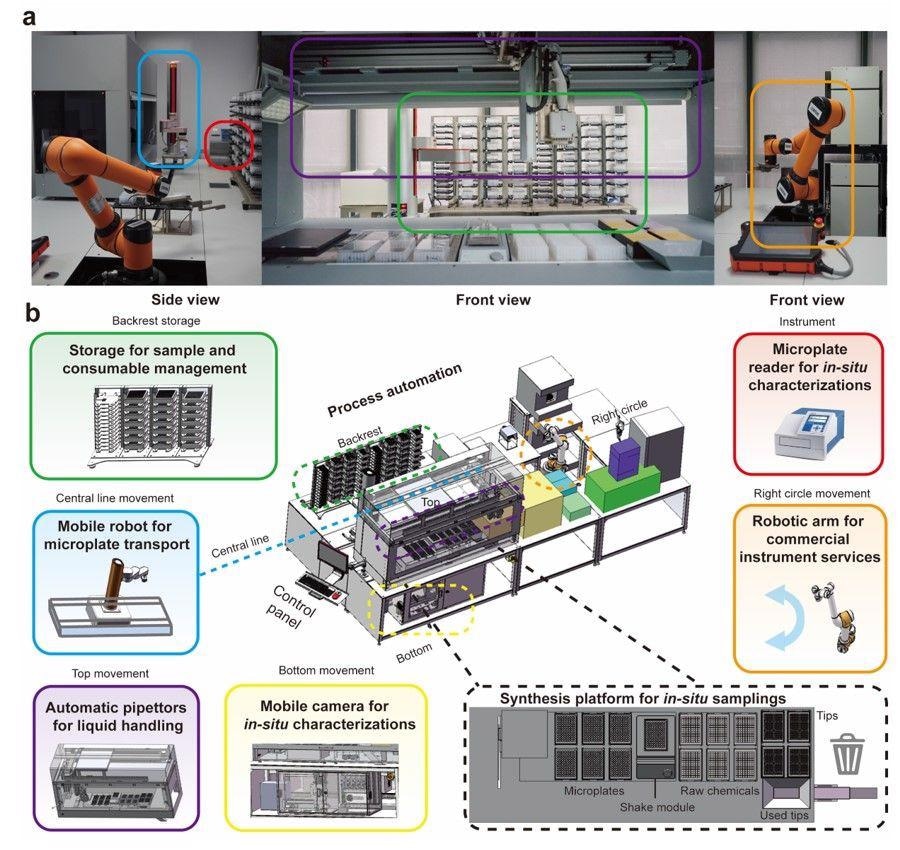
Figure 2. Illustration of the Robotic Scientist platform. a, Photograph. b, Schematic representation. The color frames in the photograph and schematic representation match each other. Backrest: Storage for the sample, microplates and pipette tips; Central line: Mobile robot for microplate transport; Top: Three automatic pipettors for liquid handling; Bottom: Mobile color-ultra-sensitive camera for in situ color characterization; Platform: Synthesis platform for in situ sampling; Instrument: Microplate reader for in situ UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectrophometry; Right circle: Robotic arm for instrument services. © Zhao, H., Chen, W., et al. (2022)
Advantages of the Proposed Robotic Scientist
Educating scientists with the necessary expertise requires significant resources, and alternative biochemical and material synthesizing processes might result in a wide range of results, even for qualified professionals.
Furthermore, the majority of artificial synthesis is trial-and-error and arduous, with inevitable inadvertent errors.
The Robotic Scientist framework reported is a significant development in automation relevant to nanocrystal production and represents an important leap towards data-guided materials development.
The merging of Robotic Scientist-aided production on the macro level and nanocrystal development on the nanoscale results in a complex tight loop comprising logical design, controlled fabrication, and retrosynthesis.
Here, existing chemical information based on data analytics, thermodynamics and kinetic models, and machine learning models were coupled to speed logical design of nanocrystal structure given initial assumptions.
To prevent unguided tuning of materials, orthogonal tests, as well as one, two, and three-factor experimentations, were carried out in cycles, and a database was built for successful training of the machine learning models to allow controlling the fabrication of nanoscale crystals.
The readily available large data set (on-site categorized UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectra and RGB color results) and smaller data set (ex-situ TEM validation) were produced in these procedures to ascertain the Au nanocrystals genome, and genome understanding plays a critical role in assisting the retrosynthesis operation.
The researchers proved that the Robotic Scientist can be taught in the same way as a human scientist can for retrosynthesis and scalable fabrication of the desired gold nanocrystals.
Using the Robotic Scientist platform, this effort centers on developing a closed-loop (design-synthesis-retrosynthesis) of automation in nanoscale crystal fabrication.
Even though a full Robotic Scientist was an idealistic goal, the developed model is a solid stepping stone toward a Robotic Scientist with the key abilities of scientific hypotheses, tests by combining hardware and computer components, and result interpretation.
Future initiatives are expected to narrow the gap, with ultimate automation of all phases of nanocrystal production.
Although the Robotic Scientist was only shown for gold nanocrystals in this study, the findings show that automation has the potential to expedite data-driven materials discovery on the nanoscale.
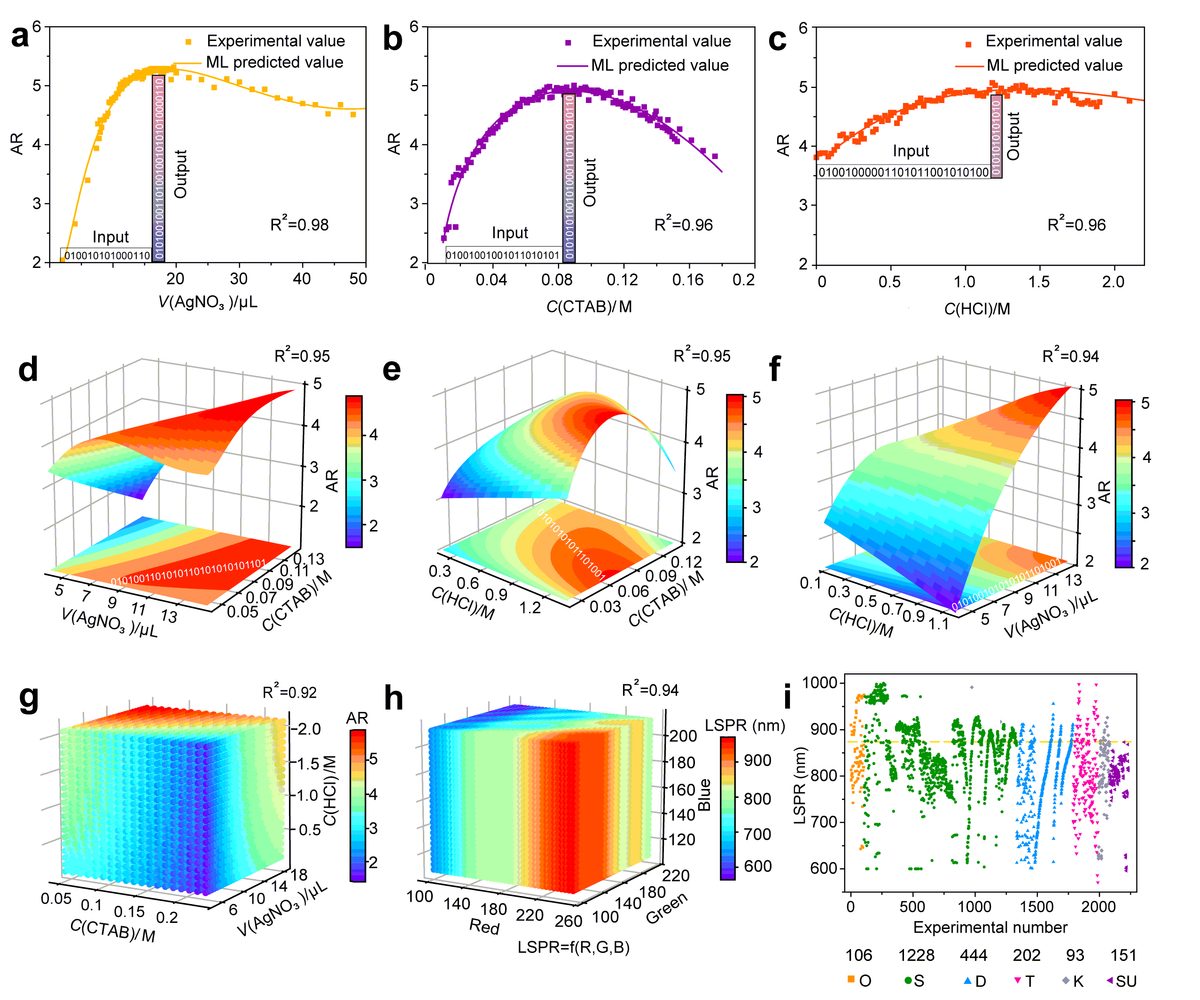
Figure 3. Controllable synthesis, ML prediction, and database construction. a–c, Single-factor ML predicted models. d–f, Double-factor ML predicted models. g, Triple-factor ML predicted models. h, LSPR-color model. i, Overview of the number of experiments: O, S, D, T, K, and SU represent the orthogonal, single-, double-, triple-factor, kinetics, and scale-up experiments, respectively. The relationship between the experimental factors (as inputs) and AR (as outputs) is identified, and ‘01010101’ is the schematic diagram of the controllable range. © Zhao, H., Chen, W., et al. (2022)
*Important Notice
ChemRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive or treated as established information.
News
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]