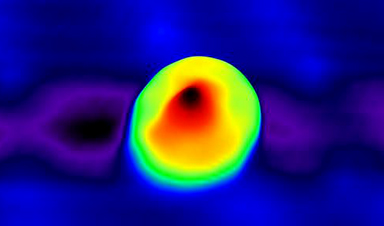
| You can easily rotate a baseball in your hand by twisting your fingers. But you need inventive scientists with access to world-class scientific facilities to rotate an object that is only two billionths of a meter wide. That is a million times smaller than a raindrop. | |
| Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory report they can precisely rotate a single molecule that small on demand (Nature Communications, “Atomically precise control of rotational dynamics in charged rare-earth complexes on a metal surface”). The key ingredient is a single atom of europium, a rare earth element. It rests at the center of a complex of different atoms and gives the molecule many potential applications. |
| “We are able to rotate this europium complex by 60 or 120 degrees to the right or left,” said Saw Wai Hla, physicist at the Center for Nanoscale Materials (CNM), a DOE Office of Science user facility at Argonne, and a physics professor at Ohio University. “The ability to control the motion of a rare earth complex such as this could impact a wide spectrum of technologies.” That includes next generation microelectronics, quantum technologies, catalysis to speed up reactions, conversion of light into electricity and more. | |
| The term “rare earth” is deceptive. The rare earth elements are not exactly rare but are critical materials used in many electronic devices, such as cellular phones, computer hard drives, solar panels and flat screen monitors. The capability to rotate this europium molecule on demand could expand their applications into next generation microelectronics that run with relatively low power, quantum computers and more. | |
| Rare earths readily combine with other elements in the Earth’s crust. It is thus difficult and costly to produce pure rare earths for devices. It is also expensive to harvest them from rare-earth containing waste. The team’s europium complex would reduce the amount of rare earth needed for a particular device and would be much less expensive to manufacture in mass quantities. |
| Key components in the complex are a single europium atom with positive charge and two small molecules with negative charge. The europium atom sits at the center of the complex, while one of the small molecules is on the side and the other at the bottom. | |
| Because opposites attract, these negative and positive charges keep these components together without the need for a chemical bond. And the small molecule at the bottom anchors the complex to a sheet of gold. This sheet acts like a table to hold the whole complex in one place, just as you need a flat solid surface to spin a bottle. | |
| “Normally, if you attach a complex like ours with positive and negative charges to a metal sheet, the charges dissipate,” Hla said. “So, we were thrilled when that did not happen here. Our calculations indicated that the atoms in the complex surrounding the europium atom act as an insulator that prevents the charges from dissipating to the gold sheet.” | |
| The two negatively charged molecules in the complex work together to act as a control unit. To spark the rotation, the team applied electrical energy to a specific point on the complex through the tip of an instrument called a scanning tunneling microscope. This probe not only controls the rotation but also can visualize the complex for study. | |
| At a temperature of 100 Kelvin (minus 208 Fahrenheit), the team’s complex rotates constantly. That rotation stops when they decrease the temperature to an ultracold 5 K. Applying the electric energy starts the desired rotation of 60 or 120 degrees, clockwise or counterclockwise depending on where the electric field is directed. |
| “Developing, fabricating and testing this nanoscale complex would not have been possible without the one-of-a-kind instruments in CNM,” Hla said. | |
| What’s more, a beamline (XTIP) in the Advanced Photon Source, a DOE Office of Science user facility at Argonne, provided the high-brilliance X-ray beam needed to establish that the single europium atom had a positive charge. “XTIP is the world’s first beamline dedicated to the technique of synchrotron X-ray scanning tunneling microscopy,” said Volker Rose, an Argonne physicist with a joint appointment at Ohio University. | |
| “With the XTIP beamline we were able to characterize the elemental and chemical states of the europium-containing molecule,” said assistant physicist Nozomi Shirato. These data established that the single europium atom in the molecule has a positive charge of plus three and does not lose that charge when absorbed on the gold surface. This retention of the charge state is key to the ability to rotate the molecule. | |
| “Our primary mission is to understand at the level of atoms the properties of rare earths, which are critical materials to U.S. industry,” added Hla. “This particular project could beneficially impact many different technologies that exist now or could be developed.” |
News
Scientists Discover DNA “Flips” That Supercharge Evolution
In Lake Malawi, hundreds of species of cichlid fish have evolved with astonishing speed, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study how biodiversity arises. Researchers have identified segments of “flipped” DNA that may allow fish to adapt rapidly [...]
Our books now available worldwide!
Online Sellers other than Amazon, Routledge, and IOPP Indigo Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artifcial Intelligence Global Health Care Equivalency In The Age Of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine And Artificial [...]
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]