A new approach for cancer treatment involves the use of microalgal-derived nanoparticles. A recent review in Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology examines their potential as a sustainable and biocompatible solution.
Promise and Limitations
Nanoparticles (NPs), defined as particles of between one and 100 nanometers, possess unique physical, chemical, and biological properties that are not observed in bulk materials. Their enhanced surface area, quantum effects, and increased reactivity make them particularly valuable in drug delivery, imaging, and cancer therapeutics.
However, traditional synthesis methods often involve hazardous chemicals or energy-intensive processes, raising toxicity and environmental concerns that hinder their wider clinical adoption. To address this, researchers are increasingly turning to green synthesis, using biological systems to produce nanoparticles under milder, more environmentally friendly conditions.
Microalgae are a particularly attractive source. Rich in enzymes, bioactive compounds, and metabolites, microalgae can reduce metal ions into nanoparticles without toxic reagents or high temperatures. The resulting biogenic nanoparticles offer high biocompatibility and can be tailored to induce cytotoxicity in cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues.
Harnessing Microalgae for Nanoparticle Synthesis
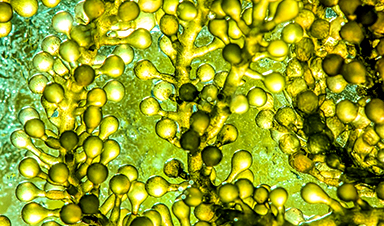
The review assessed numerous studies that showcase how various microalgal species, including Chlorella, Spirulina, and Scenedesmus, have been used to synthesize metallic nanoparticles such as silver (AgNPs).
Typically, microalgal biomass is suspended in aqueous solutions of metal salts, commonly silver nitrate, and bioreduction is initiated through metabolic extracts or secreted compounds. A visible color change, often from clear to yellow or brown, signals successful nanoparticle formation.
To characterize these particles, researchers use techniques like transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to assess morphology, UV-visible spectroscopy for optical properties, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) for elemental analysis, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to evaluate surface chemistry and functional groups.
Microalgae like Dunaliella salina have also been employed to produce gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with similarly impressive biomedical potential.
Such nanoparticles can form either intracellularly, via metal ion uptake and reduction inside the cells, or extracellularly, where secreted metabolites mediate reduction on cell surfaces or in the surrounding medium. This multi-pathway mechanism includes key stages: activation (reduction and nucleation), growth (particle aggregation), and termination (stabilization or biomineralization).
Tailoring Nanoparticle Properties for Cancer Therapy
The review focuses on how synthesis parameters, like temperature, reactant concentration, and the specific microalgal strain, can affect the size, shape, and surface charge of the synthesized nanoparticles.
Studies have shown that these characteristics directly influence biological activity and therapeutic efficacy. Those cited in the review demonstrate that microalgal nanoparticles can be fine-tuned for targeted cytotoxic effects against various cancer cell lines while exhibiting low toxicity in healthy cells.
The mechanism behind this is believed to involve several pathways, including the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), disruption of cancer cell membrane integrity, and the induction of apoptosis.
Due to their small size, nanoparticles can also take advantage of the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, enabling them to accumulate selectively in tumor tissues. Functionalizing the nanoparticle surface with targeting ligands or anticancer drugs further enhances specificity and improves therapeutic outcomes.
Opportunities and Ongoing Challenges
The review highlights several advantages of microalgal-based nanoparticle synthesis. These include sustainability, low production costs, scalability, and the ability to control physicochemical properties through natural capping agents, which help stabilize the nanoparticles and support their compatibility for biomedical applications.
The authors also highlight the opportunities for integrating synthetic biology and genetic engineering to enhance microalgal strains. By fine-tuning metabolic pathways, it may be possible to increase both the yield and quality of nanoparticles.
However, more research is still required to achieve consistent nanoparticle size and morphology, understand long-term biocompatibility, and establish standardized, reproducible production protocols. While in vitro studies have shown promising results, translating these findings into clinically viable therapies will require extensive in vivo testing and regulatory validation.
Journal Reference
Garlapati V.K., et al. (2025). Sustainable production of microalgal nanoparticles through green synthesis towards cancer treatment. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 13, 1621876. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1621876, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/bioengineering-and-biotechnology/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2025.1621876/full
News
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]