Research from Weill Cornell Medicine reveals that astrocyte receptors impact cognitive functions differently in males and females, suggesting a need for sex-specific approaches in developing treatments targeting these brain cells.
Scientists at Weill Cornell Medicine have discovered the first evidence that receptors in astrocytes, brain cells that support and regulate neurons, can have contrasting effects on cognitive function in male and female preclinical models. This research highlights the role of astrocytes in contributing to gender-specific brain mechanisms.
While many studies have tested the behavioral effects of astrocytic receptors, none of them have addressed whether biological sex plays a role and most have tested only males. This study, published on May 24 in Cell Reports, challenges the long-standing assumption that astrocytic signaling has similar cognitive effects in both sexes.
"Our study reveals that previously reported cognitive effects in males can't be extrapolated to females," said Dr. Anna G. Orr, the Nan and Stephen Swid Assistant Professor of Frontotemporal Dementia Research and an assistant professor of neuroscience in the Feil Family Brain and Mind Research Institute and the Helen and Robert Appel Alzheimer's Research Institute at Weill Cornell Medicine.
Changes in astrocytic receptors are seen in various neurological conditions with known sex differences, including neurodegenerative disorders, schizophrenia, stroke, and epilepsy. However, the mechanisms promoting sex differences remain poorly understood.
How do Male and Female Brains Differ?
In the study, Dr. Samantha M. Meadows, first author and former graduate student in the Orr lab, focused on mGluR3, a predominant glutamate receptor in astrocytes and a top-altered gene in dementia. The team used gene editing and stimulation of engineered receptors in animal models to selectively manipulate astrocytes and examine the effects of mGluR3 and related receptors on learning, memory, and other cognitive and behavioral outcomes.
The researchers found that increasing astrocytic mGluR3 levels enhanced memory in older females and reducing these levels was sufficient to impair memory in young females, demonstrating that mGluR3 promotes memory recall in females. However, in males, reducing mGluR3 enhanced memory, and increasing the receptor had no effects. "Interestingly, the cognitive impact of these receptors is not conserved among sexes," Dr. Meadows said.
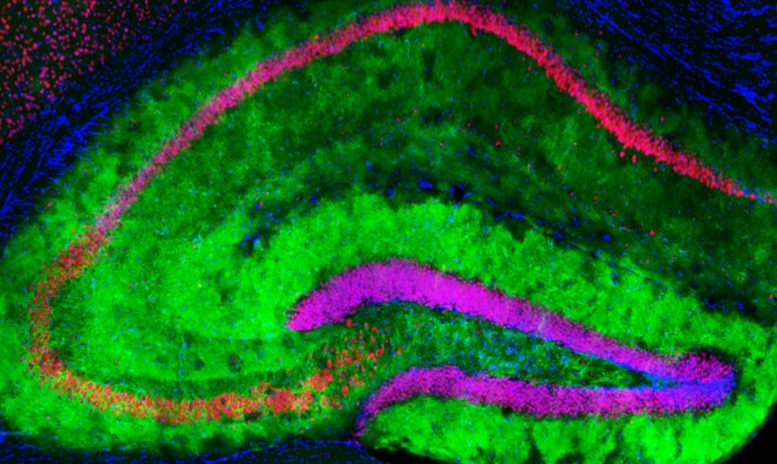
This image of the mouse hippocampus, a part of the brain involved in learning and memory, shows mGluR3 receptors on astrocytes (green), neurons (red), and cell nuclei (blue). Credit: Orr Lab
To understand if these divergent effects were unique to mGluR3 or reflected a broader feature of astrocytic receptor signaling, Dr. Meadows worked with co-author Dr. Adam L. Orr, an assistant professor of research in neuroscience in the Brain and Mind Research Institute and the Appel Alzheimer's Disease Research Institute, to selectively stimulate different astrocytic receptors while mice performed tasks involving learning and memory.
To their surprise, the team found further evidence that receptor activation caused either memory enhancement or impairment, depending on biological sex. "Normal brain function seems to require a sex-specific balance in astrocytic signaling," Dr. Adam Orr said.
This study suggests that mGluR3 modulators being developed for treating disorders such as schizophrenia and anxiety may need further study to assess their impact on different sexes. "Therapeutics influencing astrocytic receptors may cause sex-specific cognitive effects in part due to the divergent roles of astrocytes in males and females," said Dr. Anna Orr.
The lab is investigating what may cause the differential effects and if other brain functions are also changed in a sex-specific way.
Reference: "Hippocampal astrocytes induce sex-dimorphic effects on memory" by Samantha M. Meadows, Fernando Palaguachi, Minwoo Wendy Jang, Avital Licht-Murava, Daniel Barnett, Till S. Zimmer, Constance Zhou, Samantha R. McDonough, Adam L. Orr and Anna G. Orr, 24 May 2024, Cell Reports.
DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114278
News
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]