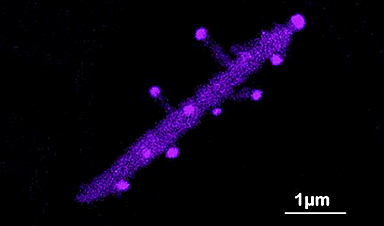
| A research team of Ehime University paved a way to achieve unexplored III-V semiconductor nanostructures. They grew branched GaAs nanowires with a nontoxic Bi element employing characteristic structural modifications correlated with metallic droplets, as well as crystalline defects and orientations. | |
| The finding provides a rational design concept for the creation of semiconductor nanostructures with the concentration of constituents beyond the fundamental limit, making it potentially applicable to novel efficient near-infrared devices and quantum electronics. | |
| Nanowire is a rod-structure with a diameter typically narrower than several hundred nanometers. Due to its size and structure, it exhibits characteristic properties which are not found in larger bulk materials. The study of III-V semiconductor nanowires has attracted much interest in recent decades due to their potential application in nanoscale quantum, photonic, electronic, and energy conversion, and in biological devices, based on their one-dimensional nature and large surface to volume ratio. | |
| The introduction of an epitaxial heterostructure facilitates control of the transport and electronic properties of such devices, showing the potential for realizing integrated systems based on III-V compounds and Si with superior electronic and optical functions. |
| III-V compound semiconductors are one of the highest in mobility and photon-electron conversion efficiency in existence. Among them, GaAs is a representative III-V compound semiconductor, which is utilized for high speed transistors, as well as high-efficiency near-infrared light-emitting diodes, lasers, and solar cells. Optical devices based on III-V GaAs suffer from intrinsic losses related to heat generation. | |
| To circumvent this, the use of dilute bismide GaAsBi alloy with a nontoxic Bi element has recently gained attention because the introduction of Bi suppresses heat generation while increasing electron-light conversion efficiency. Therefore, incorporating dilute bismide GaAsBi alloy into nanowires is a rational approach for developing high-performance optoelectronic nanodevices. | |
| Meanwhile, branched or tree-like nanowires offer an approach to increase structural complexity and enhance the resulting functions which in turn enable the realization of higher dimensionality structures, lateral connectivity, and interconnection between the nanowires. |
Image Credit: Ehime University
News This Week
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]