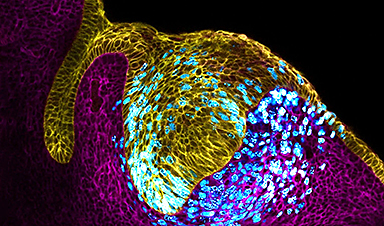
Finding your way through the winding streets of certain cities can be a real challenge without a map. To orient ourselves, we rely on a variety of information, including digital maps on our phones, as well as recognizable shops and landmarks. Cells in our bodies face a similar problem when building our organs during embryogenesis. They need instructions on where to go and how to behave. Luckily, like cell phone towers in a city, embryos feature special cells in specific locations, known as organizers, that send signals to other cells and help them organize to build our complex organs.
Some of these signals are molecules sent from the organizer, a privileged signaling center. Cells around it receive stronger or weaker signals depending on their location, and they take decisions accordingly. Errors in the location of these messaging centers in the tissue lead to embryonic malformations that can be fatal. Scientists have known the relevance of these signaling centers for a long time, but how these appear at specific locations remained elusive.
Discovery Through International Collaboration
It took an international collaboration of physicists and biologists to pinpoint the answer. Several years ago, the laboratories of Prof. Ophir Klein at Cedars-Sinai Guerin Children’s and the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and Prof. Otger Campàs at the Physics of Life Excellence Cluster of TU Dresden and the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB), had a hint of how it may work and joined forces. Together, they figured out that it is the mechanical pressure inside the growing tissue that dictates where the signaling center will emerge.
“Our work shows that both mechanical pressure and molecular signaling play a role in organ development,” said Ophir Klein, MD, PhD, Executive Director of Cedars-Sinai Guerin Children’s, where he is also the David and Meredith Kaplan Distinguished Chair in Children’s Health, and co-corresponding author of the study.
Mechanical Pressure in Organizing Cells
The study, published in Nature Cell Biology, shows that as cells grow in the embryonic incisor tooth, they feel the growing pressure and use this information to organize themselves. “It’s like those toys that absorb water and grow in size,” said Neha Pincha Shroff, PhD, a postdoctoral scholar in the School of Dentistry at UCSF, and co-first author of the study. “Just imagine that happening in a confined space. What happens in the incisor knot is that the cells multiply in number in a fixed space and this causes a pressure to build up at the center, which then becomes a cluster of specialized cells.” Like people in a crowded bar, cells in the tissue start feeling the squeeze from their peers. The researchers found that the cells feeling the stronger pressure stop growing and start sending signals to organize the other surrounding cells in the tooth. They were literally pressed into becoming the tooth organizer.
“We were able to use microdroplet techniques that our lab previously developed to figure out how the buildup of mechanical pressure affects organ formation,” said co-corresponding author of the study Otger Campàs, Ph.D., who is currently Managing Director, Professor and Chair of Tissue Dynamics at the Physics of Life Excellence Cluster of TU Dresden, and former Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at UCSB. “It is really exciting that tissue pressure has a role in establishing signaling centers. It will be interesting to see if or how mechanical pressure affects other important developmental processes.”
Embryos use several of these signaling centers to guide cells as they form tissues and organs. Like building skyscrapers or bridges, sculpting our organs involves tight planning, a lot of coordination, and the right structural mechanics. Failure in any of these processes can be catastrophic when it comes to building a bridge, and it can also be damaging for us when growing in the womb.
“By understanding how an embryo forms organs, we can start to ask questions about what goes wrong in children born with congenital malformations,” said Ophir Klein. “This work may lead to additional research into how birth defects are formed and can be prevented.”
Reference: “Proliferation-driven mechanical compression induces signalling centre formation during mammalian organ development” by Neha Pincha Shroff, Pengfei Xu, Sangwoo Kim, Elijah R. Shelton, Ben J. Gross, Yucen Liu, Carlos O. Gomez, Qianlin Ye, Tingsheng Yu Drennon, Jimmy K. Hu, Jeremy B. A. Green, Otger Campàs and Ophir D. Klein, 3 April 2024, Nature Cell Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s41556-024-01380-4
The study was funded by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (OK and OC) in the USA, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft under Germany’s Excellence Strategy, and the Cluster of Excellence Physics of Life of TU Dresden (OC).
News
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]