For decades, a substantial number of proteins, vital for treating various diseases, have remained elusive to oral drug therapy. Traditional small molecules often struggle to bind to proteins with flat surfaces or require specificity for particular protein homologs. Typically, larger biologics that can target these proteins demand injection, limiting patient convenience and accessibility.
“There are many diseases for which the targets were identified but drugs binding and reaching them could not be developed,” says Heinis. “Most of them are types of cancer, and many targets in these cancers are protein-protein interactions that are important for the tumor growth but cannot be inhibited.”
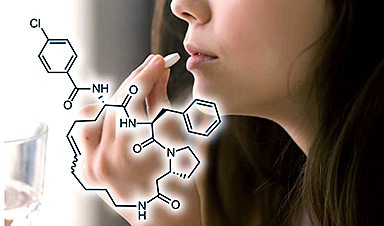
The study focused on cyclic peptides, which are versatile molecules known for their high affinity and specificity in binding challenging disease targets. At the same time, developing cyclic peptides as oral drugs has proven difficult because they are rapidly digested or poorly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract.
“Cyclic peptides are of great interest for drug development as these molecules can bind to difficult targets for which it has been challenging to generate drugs using established methods,” says Heinis. “But the cyclic peptides cannot usually be administered orally—as a pill—which limits their application enormously.”
Cyclizing breakthrough
The research team targeted the enzyme thrombin, which is a critical disease target because of its central role in blood coagulation; regulating thrombin is key to preventing and treating thrombotic disorders like strokes and heart attacks.
To generate cyclic peptides that can target thrombin and are sufficiently stable, the scientists developed a two-step combinatorial synthesis strategy to synthesize a vast library of cyclical peptides with thioether bonds, which enhance their metabolic stability when taken orally.
“We have now succeeded in generating cyclic peptides that bind to a disease target of our choice and can also be administered orally,” says Heinis. “To this end, we have developed a new method in which thousands of small cyclic peptides with random sequences are chemically synthesized on a nanoscale and examined in a high-throughput process.”
Two steps, one pot
The new method process involves two steps, and takes place in the same reactive container, a feature that chemists refer to as “one pot.”
The first step is to synthesize linear peptides, which then undergo a chemical process of forming a ring-like structure—in technical terms, being “cyclized.” This is done with using “bis-electrophilic linkers”—chemical compounds used to connect two molecular groups together—to form stable thioether bonds.
In the second phase, the cyclized peptides undergo acylation, a process that attaches carboxylic acids to them, further diversifying their molecular structure.
The technique eliminates the need for intermediate purification steps, allowing for high-throughput screening directly in the synthesis plates, combining the synthesis and screening of thousands of peptides to identify candidates with high affinity for specific disease targets—in this case, thrombin.
Using the method, the Ph.D. student leading the project, Manuel Merz, was able to generate a comprehensive library of 8,448 cyclic peptides with an average molecular mass of about 650 Daltons (Da), only slightly above the maximum limit of 500 Da recommended for orally-available small molecules.
The cyclic peptides also showed a high affinity for thrombin.
When tested on rats, the peptides showed oral bioavailability up to 18%, which means that when the cyclic peptide drug is taken orally, 18% of it successfully enters the bloodstream, and to have a therapeutic effect. Considering that orally-administered cyclic peptides generally show a bioavailability below 2%, increasing that number to 18% is a substantial advance for drugs in the biologics category—which includes peptides.
Setting targets
By enabling the oral availability of cyclic peptides, the team has opened up possibilities for treating a range of diseases that have been challenging to address with conventional oral drugs. The method’s versatility means it can be adapted to target a wide array of proteins, potentially leading to breakthroughs in areas where medical needs are currently unmet.
“To apply the method to more challenging disease targets, such as protein-protein interactions, larger libraries will likely need to be synthesized and studied,” says Manuel Merz. “By automating further steps of the methods, libraries with more than one million molecules seem to be within reach.”
In the next step of this project, the researchers will target several intracellular protein-protein interaction targets for which it has been difficult to develop inhibitors based on classical small molecules. They are confident that orally applicable cyclic peptides can be developed for at least some of them.
More information: Alexander L. Nielsen, De novo development of small cyclic peptides that are orally bioavailable, Nature Chemical Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41589-023-01496-y
Journal information: Nature Chemical Biology
News
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]