The University of Warwick and QuantIC researchers at Heriot Watt University and the University of Glasgow performed a study in optical sensing, which could considerably enhance the precision of measuring nanoscopic structures.
QuantIC is part of the UK National Quantum Technologies Program and is the UK Quantum Technology Hub in Quantum Enhanced Imaging.
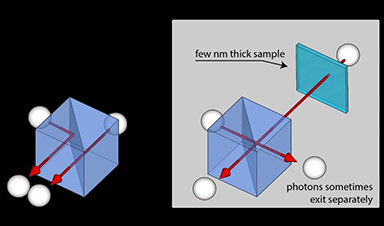
The researchers used pairs of photons, which are essential components of energy that make up light, to develop a method that determines the thickness of objects that are less than a 100,000th of the width of a human hair.
In the latest technique, two near-identical photons are fired onto a component called a beamsplitter and their subsequent behavior is monitored – with some 30,000 photons detected every second, and 500bn in use during an entire experiment.
Identical photons tend to ‘buddy up’ and continue to travel together – the outcome of a mild quantum interference effect. As a result of this, the team’s newly developed setup provides the same stability and precision as current one-photon methods that, owing to the equipment needed, are more expensive.
Providing a host of promising applications, such as research to better understand DNA, cell membranes, and even quality control for nanoscopic 2D materials of one atom’s thickness, for example, graphene, the latest study represents a major improvement on current two-photon techniques with up to 100 times better resolution.
Image Credit: University of Warwick
News This Week
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]













Leave A Comment