The University of Warwick and QuantIC researchers at Heriot Watt University and the University of Glasgow performed a study in optical sensing, which could considerably enhance the precision of measuring nanoscopic structures.
QuantIC is part of the UK National Quantum Technologies Program and is the UK Quantum Technology Hub in Quantum Enhanced Imaging.
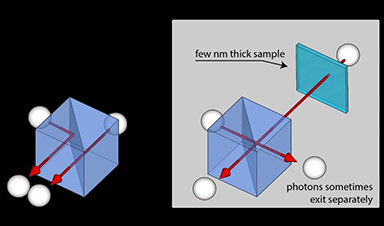
The researchers used pairs of photons, which are essential components of energy that make up light, to develop a method that determines the thickness of objects that are less than a 100,000th of the width of a human hair.
In the latest technique, two near-identical photons are fired onto a component called a beamsplitter and their subsequent behavior is monitored – with some 30,000 photons detected every second, and 500bn in use during an entire experiment.
Identical photons tend to ‘buddy up’ and continue to travel together – the outcome of a mild quantum interference effect. As a result of this, the team’s newly developed setup provides the same stability and precision as current one-photon methods that, owing to the equipment needed, are more expensive.
Providing a host of promising applications, such as research to better understand DNA, cell membranes, and even quality control for nanoscopic 2D materials of one atom’s thickness, for example, graphene, the latest study represents a major improvement on current two-photon techniques with up to 100 times better resolution.
Image Credit: University of Warwick
News This Week
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]













Leave A Comment