| Researchers at Duke University have developed a unique type of nanoparticle called a “nanorattle” that greatly enhances light emitted from within its outer shell. | |
| Loaded with light scattering dyes called Raman reporters commonly used to detect biomarkers of disease in organic samples, the approach can amplify and detect signals from separate types of nanoprobes without needing an expensive machine or medical professional to read the results. | |
| In a small proof-of-concept study, the nanorattles accurately identified head and neck cancers through an AI-enabled point-of-care device that could revolutionize how these cancers and other diseases are detected in low-resource areas to improve global health. | |
| The results appear in the Journal of Raman Spectroscopy (“Machine Learning Using Convolutional Neural Networks for SERS Analysis of Biomarkers in Medical Diagnostics”). |
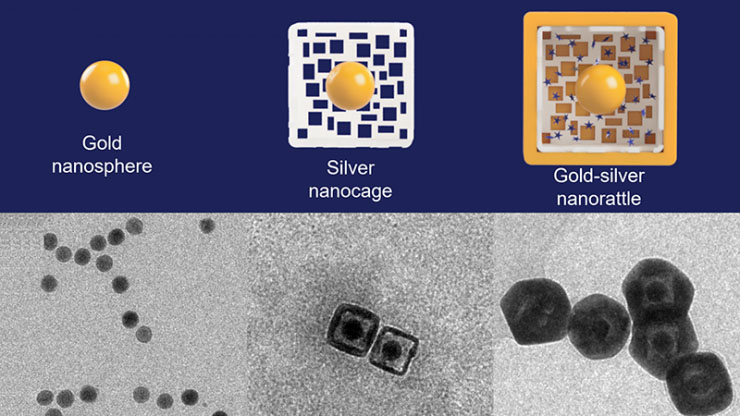
The starting gold nanosphere seeds (left) are surrounded by a hollow, porous silver cage (middle) and become a nanorattle filled with light-scattering dyes inside a gold outer shell (right). The nanorattles can amplify and detect signals from separate types of nanoprobes without needing an expensive machine or medical professional to read the results. (Image: Duke University)
| “The concept of trapping Raman reporters in these so-called nanorattles has been done before, but most platforms had difficulty controlling the interior dimensions,” said Tuan Vo-Dinh, the R. Eugene and Susie E. Goodson Distinguished Professor of Biomedical Engineering at Duke. | |
| “Our group has developed a new type of probe with a precisely tunable gap between the interior core and outer shell, which allows us to load multiple types of Raman reporters and amplify their emission of light called surface-enhanced Raman scattering,” Vo-Dinh said. | |
| To make nanorattles, researchers start with a solid gold sphere about 20 nanometers wide. After growing a layer of silver around the gold core to make a larger sphere (or cube), they use a corrosion process called galvanic replacement that hollows out the silver, creating a cage-like shell around the core. The structure is then soaked in a solution containing positively charged Raman reporters, which are drawn into the outer cage by the negatively charged gold core. The outer hulls are then covered by an extremely thin layer of gold to lock the Raman reporters inside. | |
| The result is a nanosphere (or nanocube) about 60 nanometers wide with an architecture that resembles a rattle—a gold core trapped within a larger outer silver-gold shell. The gap between the two is only about a few nanometers, which is just large enough to fit the Raman reporters. | |
| Those tight tolerances are essential to controlling the Raman signal enhancement the nanorattles produce. | |
| When a laser shines on the nanorattles, it travels through the extremely thin outer shell and hits the Raman reporters within, causing them to emit light of their own. Because of how close the surfaces of the gold core and the outer gold/silver shell are together, the laser also excites groups of electrons on the metallic structures, called plasmons. These groups of electrons create an extremely powerful electromagnetic field due to the plasmons’ interaction of the metallic core-shell architecture, a process called plasmonic coupling, which amplifies the light emitted by the Raman reporters millions of times over. | |
| “Once we had the nanorattles working, we wanted to make biosensing devices to detect infectious diseases or cancers before people even know they’re sick,” Vo-Dinh said. “With how powerful the signal enhancement of the nanorattles is, we thought we could make a simple test that could be easily read by anybody at the point-of-care.” | |
| In the new paper, Vo-Dinh and his collaborators apply the nanorattle technology to a lab-on-a-stick device capable of detecting head and neck cancers, which appear anywhere between the shoulders and the brain, typically in the mouth, nose and throat. Survival rate for these cancers have hovered between 40 and 60 percent for decades. While those statistics have improved in recent years in the United States, they have gotten worse in low-resource settings, where risk factors such as smoking, drinking and betel nut chewing are much more prevalent. | |
| “In low-resource settings, these cancers often present in advanced stages and result in poor outcomes due in part to limited examination equipment, lack of trained healthcare workers and essentially non-existent screening programs,” said Walter Lee, professor of head and neck surgery & communication sciences and radiation oncology at Duke, and a collaborator on the research. | |
| “Having the ability to detect these cancers early should lead to earlier treatment and improvement in outcomes, both in survival and quality of life,” Lee said. “This approach is exciting since it does not depend on a pathologist review and potentially could be used at the point of care.” | |
| The prototype device uses specific genetic sequences that act like Velcro for the biomarkers the researchers are looking for — in this case, a specific mRNA that is overly abundant in people with head and neck cancers. When the mRNA in question is present, it acts like a tether that binds nanorattles to magnetic beads. These beads are then concentrated and held in place by another magnet while everything else gets rinsed away. Researchers can then use a simple, inexpensive handheld device to look for light emitted from the nanorattles to see if any biomarkers were caught. | |
| In the experiments, the test determined whether or not 20 samples came from patients that had head and neck cancer with 100% accuracy. The experiments also showed that the nanorattle platform is capable of handling multiple types of nanoprobes, thanks to a machine learning algorithm that can tease apart the separate signals, meaning they can target multiple biomarkers at once. This is the goal of the group’s current project funded by the National Institutes of Health. | |
| “Many mRNA biomarkers are overly abundant in multiple types of cancers, while other biomarkers can be used to evaluate patient risk and future treatment outcome,” Vo-Dinh said. “Detecting multiple biomarkers at once would help us differentiate between cancers, and also look for other prognostic markers such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV), and both positive and negative controls. Combining mRNA detection with novel nanorattle biosensing will result in a paradigm shift in achieving a diagnostic tool that could revolutionize how these cancers and other diseases are detected in low-resource areas”. |
News
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]





















