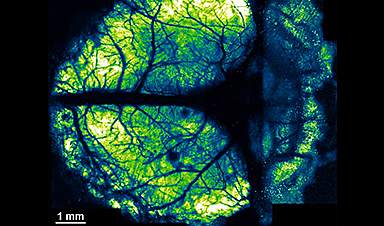
The human brain has billions of neurons. Working together, they enable higher-order brain functions such as cognition and complex behaviors. To study these higher-order brain functions, it is important to understand how neural activity is coordinated across various brain regions.
Although techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) are able to provide insights into brain activity, they can show only so much information for a given time and area. Two-photon microscopy involving the use of cranial windows is a powerful tool for producing high-resolution images, but conventional cranial windows are small, making it difficult to study distant brain regions at the same time.
Now, a team of researchers led by the Exploratory Research Center on Life and Living Systems (ExCELLS) and the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) have introduced a new method for in vivo brain imaging, enabling large-scale and long-term observation of neuronal structures and activities in awake mice.
This method is called the “nanosheet incorporated into light-curable resin” (NIRE) method, and it uses fluoropolymer nanosheets covered with light-curable resin to create larger cranial windows.
“The NIRE method is superior to previous methods because it produces larger cranial windows than previously possible, extending from the parietal cortex to the cerebellum, utilizing the biocompatible nanosheet and the transparent light-curable resin that changes in form from liquid to solid,” says lead author Taiga Takahashi of the Tokyo University of Science and ExCELLS.
In the NIRE method, light-curable resin is used to fix polyethylene-oxide–coated CYTOP (PEO-CYTOP), a bioinert and transparent nanosheet, onto the brain surface. This creates a “window” that fits tightly onto the brain surface, even the highly curved surface of the cerebellum, and maintains its transparency for a long time with little mechanical stress, allowing researchers to observe multiple brain regions of living mice.
“Additionally, we showed that the combination of PEO-CYTOP nanosheets and light-curable resin enabled the creation of stronger cranial windows with greater transparency for longer periods of time compared with our previous method. As a result, there were few motion artifacts, that is, distortions in the images caused by the movements of awake mice,” says Takahashi.
The cranial windows allowed for high-resolution imaging with sub-micrometer resolution, making them suitable for observing the morphology and activity of fine neural structures.
“Importantly, the NIRE method enables imaging to be performed for a longer period of more than 6 months with minimal impact on transparency. This should make it possible to conduct longer-term research on neuroplasticity at various levels—from the network level to the cellular level—as well as during maturation, learning, and neurodegeneration,” explains corresponding author Tomomi Nemoto at ExCELLS and NIPS.
This study is a significant achievement in the field of neuroimaging because this novel method provides a powerful tool for researchers to investigate neural processes that were previously difficult or impossible to observe. Specifically, the NIRE method’s ability to create large cranial windows with prolonged transparency and fewer motion artifacts should allow for large-scale, long-term, and multi-scale in vivo brain imaging.
“The method holds promise for unraveling the mysteries of neural processes associated with growth and development, learning, and neurological disorders. Potential applications include investigations into neural population coding, neural circuit remodeling, and higher-order brain functions that depend on coordinated activity across widely distributed regions,” says Nemoto.
In sum, the NIRE method provides a platform for investigating neuroplastic changes at various levels over extended periods in animals that are awake and engaged in various behaviors, which presents new opportunities to enhance our understanding of the brain’s complexity and function.
More information: Taiga Takahashi et al, Large-scale cranial window for in vivo mouse brain imaging utilizing fluoropolymer nanosheet and light-curable resin, Communications Biology (2024).
Journal information: Communications Biology
News
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]